Delving into the Depths: Understanding Florida’s Swamp Ecosystems
Related Articles: Delving into the Depths: Understanding Florida’s Swamp Ecosystems
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Delving into the Depths: Understanding Florida’s Swamp Ecosystems. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Delving into the Depths: Understanding Florida’s Swamp Ecosystems
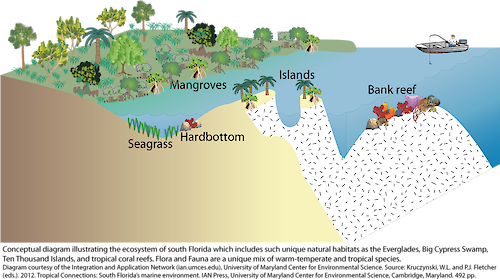
Florida, renowned for its sunshine and beaches, harbors another, less celebrated landscape: its vast and intricate network of swamps. These wetlands, often misconstrued as desolate wastelands, are vital ecosystems teeming with life and playing a critical role in the state’s ecological balance. This exploration delves into the complexities of Florida’s swamps, examining their unique characteristics, ecological significance, and the challenges they face.
A Tapestry of Wetlands: Exploring the Diverse Swamps of Florida
Florida’s swamps, collectively known as the Everglades, are not a singular entity but a mosaic of distinct wetland types, each with its own unique characteristics and inhabitants.
-
Cypress Swamps: Dominated by towering cypress trees, these swamps are characterized by their dark, acidic waters and dense canopies that filter sunlight. They serve as havens for diverse wildlife, including alligators, wading birds, and numerous fish species.
-
Mangrove Swamps: Found along the coast, these swamps are defined by their salt-tolerant mangrove trees. Their intricate root systems provide crucial habitat for numerous marine species and serve as natural barriers against storm surges.
-
Prairie Swamps: These open wetlands are characterized by grasses and herbaceous plants, often interspersed with scattered trees. They are vital for water storage and filtration, supporting a unique array of wildlife, including wading birds, amphibians, and reptiles.
-
Pocosins: These acidic, nutrient-poor swamps are dominated by evergreen shrubs and trees. They are home to a distinct flora and fauna, including carnivorous plants and rare bird species.
The Ecological Symphony: Unraveling the Importance of Florida’s Swamps
Beyond their captivating beauty, Florida’s swamps play a vital role in the state’s ecological health and human well-being:
-
Water Filtration and Storage: Swamps act as natural filters, removing pollutants and excess nutrients from water. They also act as vast reservoirs, storing water during periods of heavy rainfall and releasing it gradually, mitigating flooding and drought.
-
Habitat for Diverse Species: Swamps provide critical habitat for a wide array of flora and fauna, including endangered and threatened species. They support a complex food web, sustaining populations of fish, amphibians, reptiles, birds, and mammals.
-
Coastal Protection: Mangrove swamps, in particular, act as natural barriers against storm surges and erosion, protecting coastal communities from the impacts of hurricanes and sea-level rise.
-
Economic Benefits: Swamps contribute to the state’s economy through tourism, fishing, and other recreational activities. They also provide valuable resources, such as timber and medicinal plants.
Challenges and Conservation Efforts: Protecting Florida’s Wetlands
Despite their ecological significance, Florida’s swamps face numerous challenges:
-
Habitat Loss and Fragmentation: Urbanization, agriculture, and infrastructure development have led to significant loss and fragmentation of swamp habitats, disrupting ecological processes and isolating wildlife populations.
-
Pollution: Runoff from agricultural and urban areas introduces pollutants into swamps, harming water quality and threatening wildlife.
-
Climate Change: Rising sea levels, increased temperatures, and altered precipitation patterns threaten swamp ecosystems and the species they support.
Conservation efforts are crucial to protect Florida’s swamps. These efforts include:
-
Land Acquisition and Preservation: Establishing protected areas and acquiring land for conservation ensures the long-term survival of these vital ecosystems.
-
Restoration and Management: Restoring degraded swamps and implementing sustainable management practices help mitigate the impacts of human activities and promote ecological recovery.
-
Public Education and Outreach: Raising awareness about the importance of swamps and engaging the public in conservation efforts is essential for ensuring their protection.
Navigating the Swamp: A Guide to Understanding Florida’s Wetlands
Understanding Florida’s swamps requires a multi-faceted approach, encompassing both scientific research and public engagement.
-
Scientific Research: Continued research is vital to understand the complexities of swamp ecosystems, identify threats, and develop effective conservation strategies.
-
Citizen Science: Engaging the public in scientific research through citizen science programs can help gather valuable data and promote public awareness.
-
Education and Outreach: Educational programs and public outreach initiatives are crucial for fostering appreciation and understanding of swamps and their importance.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: What are the main threats to Florida’s swamps?
A: The main threats to Florida’s swamps include habitat loss and fragmentation due to development, pollution from agricultural and urban runoff, and the impacts of climate change.
Q: What are the benefits of preserving Florida’s swamps?
A: Preserving Florida’s swamps provides numerous benefits, including water filtration and storage, habitat for diverse wildlife, coastal protection, and economic opportunities.
Q: How can I help protect Florida’s swamps?
A: You can help protect Florida’s swamps by supporting conservation organizations, reducing your environmental footprint, and advocating for responsible land use policies.
Tips for Exploring Florida’s Swamps
- Visit a State Park: Many state parks offer opportunities to explore swamps and learn about their ecology.
- Take a Guided Tour: Guided tours led by experienced naturalists provide insights into the unique features and inhabitants of swamps.
- Respect the Environment: Stay on designated trails, avoid disturbing wildlife, and dispose of waste responsibly.
Conclusion
Florida’s swamps are a testament to the intricate beauty and vital role of wetlands. Their unique characteristics, ecological significance, and the challenges they face underscore the importance of conservation efforts. By understanding and appreciating these remarkable ecosystems, we can ensure their continued existence for generations to come.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Delving into the Depths: Understanding Florida’s Swamp Ecosystems. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!
