Navigating the Complex Landscape: A Comprehensive Look at the Gaza Strip and West Bank Map
Related Articles: Navigating the Complex Landscape: A Comprehensive Look at the Gaza Strip and West Bank Map
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Complex Landscape: A Comprehensive Look at the Gaza Strip and West Bank Map. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Complex Landscape: A Comprehensive Look at the Gaza Strip and West Bank Map
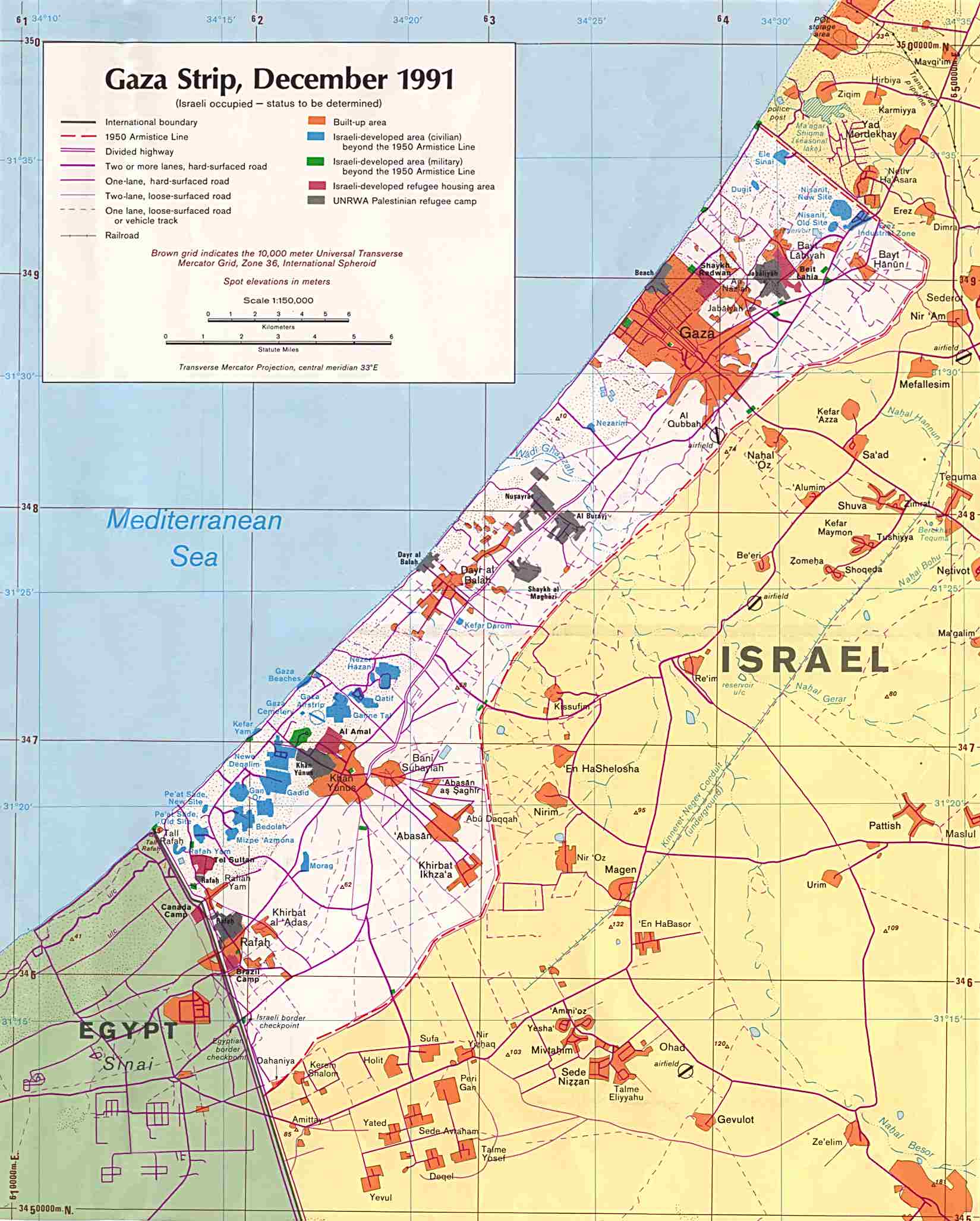
The Gaza Strip and the West Bank, two Palestinian territories, are geographically distinct yet intricately linked by their shared history, political realities, and ongoing struggle for self-determination. Understanding the complexities of these territories necessitates a thorough examination of their geographical features, political boundaries, and the historical context that has shaped their present state.
A Glimpse into the Geography
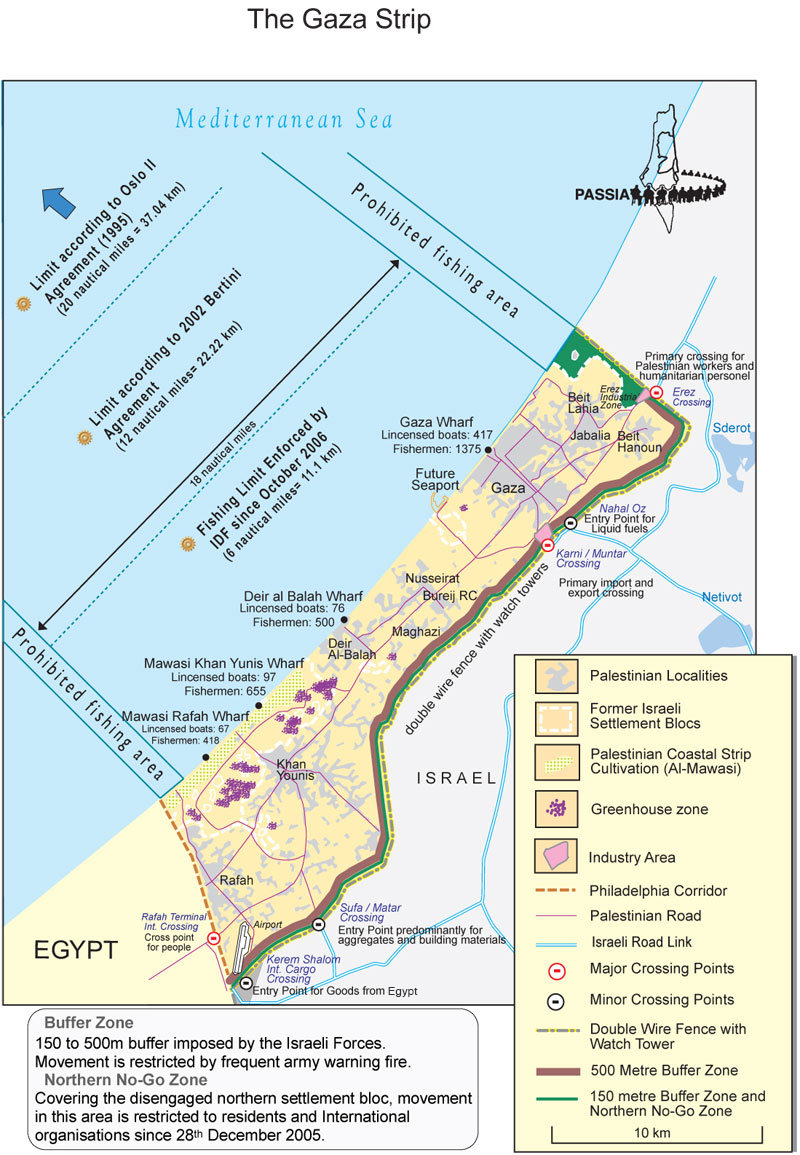
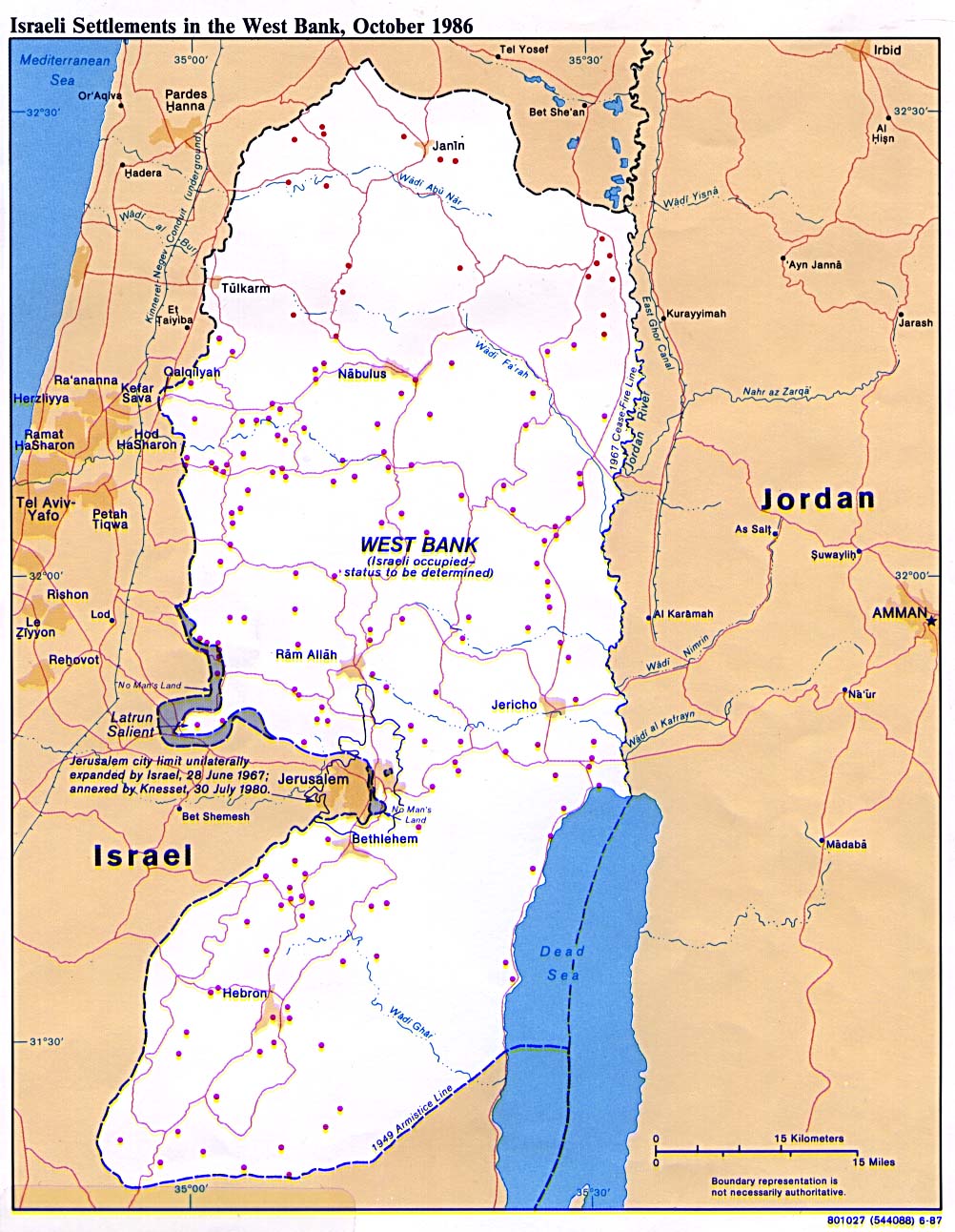
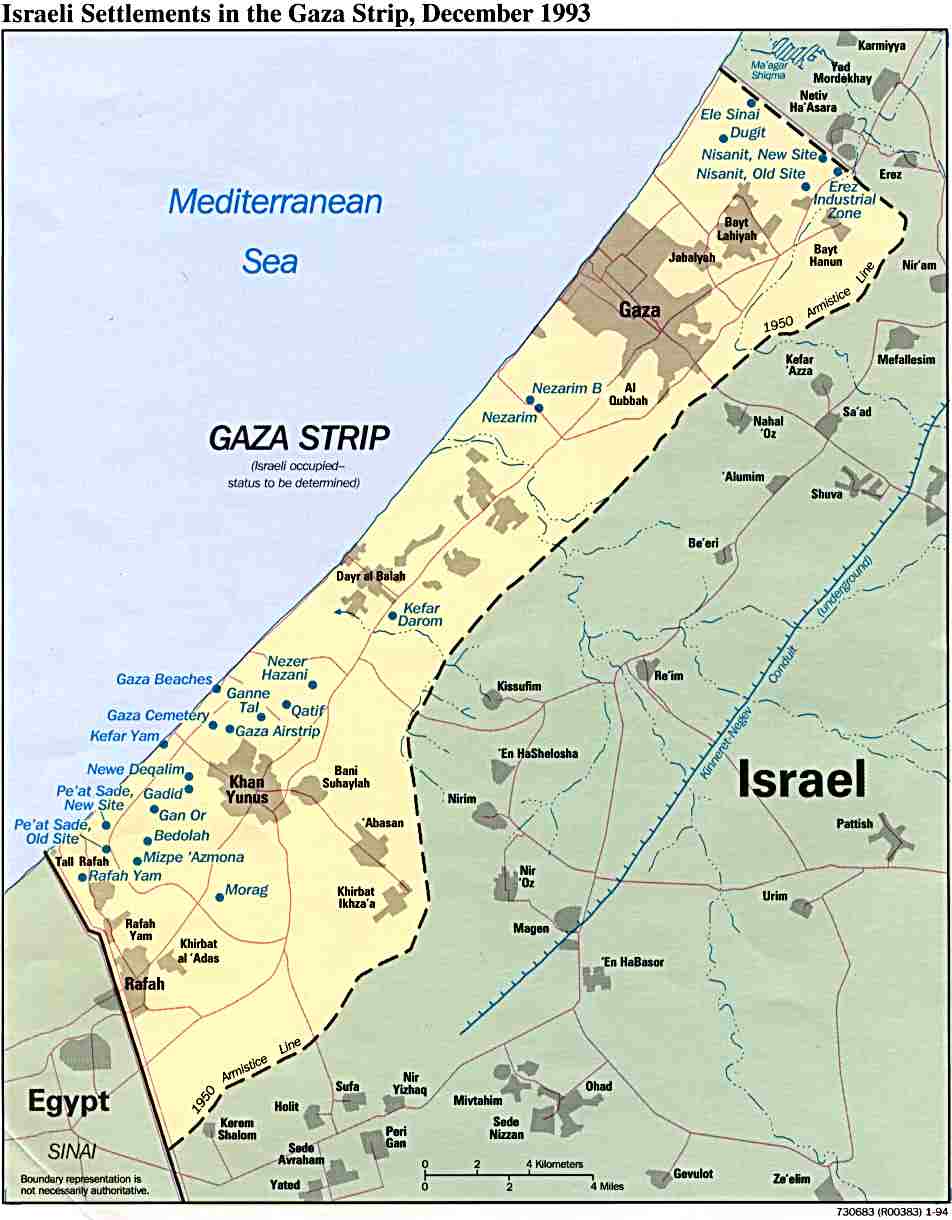
The Gaza Strip, a narrow coastal region bordering Egypt to the south and Israel to the north and east, is characterized by its densely populated urban centers, limited agricultural land, and the absence of natural resources. The West Bank, located on the western side of the Jordan River, boasts a diverse landscape, encompassing hills, valleys, and the Jordan Valley. It is home to a significant number of Palestinian settlements, as well as a diverse range of economic activities.
Political Boundaries: A Contested Landscape
The political map of the Gaza Strip and West Bank is marked by its complexity and ambiguity. The Oslo Accords of the 1990s aimed to establish a two-state solution, with the creation of a Palestinian state alongside Israel. However, the implementation of these agreements has been fraught with challenges, leading to a fragmented and contested landscape.
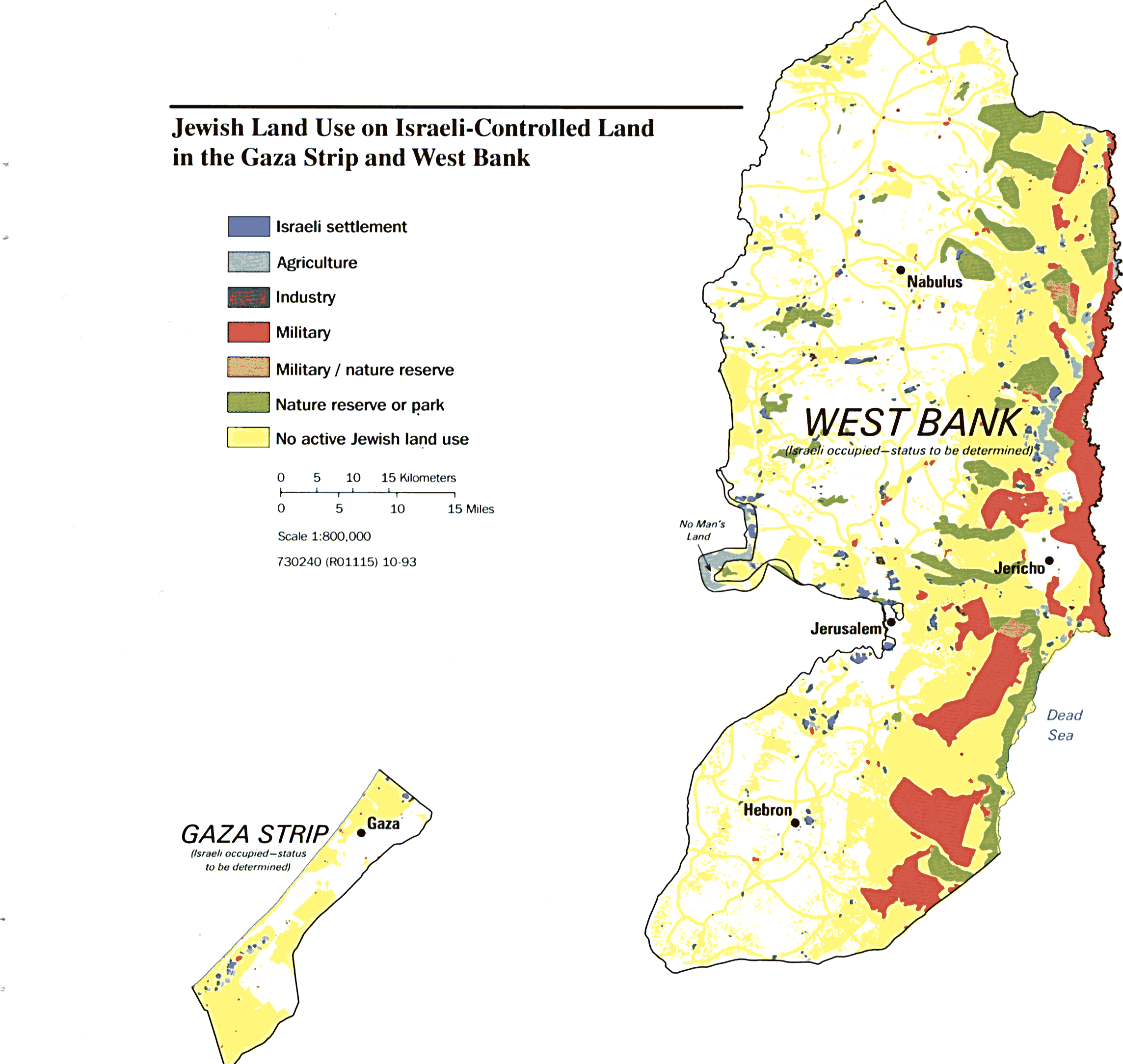
The Gaza Strip has been under the control of Hamas since 2007, while the West Bank remains under the control of the Palestinian Authority (PA), although Israel retains significant control over its borders and security. The Israeli settlements scattered across the West Bank further complicate the political map, raising significant concerns about the viability of a two-state solution.
Historical Context: Understanding the Roots of Conflict
The current political situation in the Gaza Strip and West Bank can only be fully understood by examining the historical context that has shaped their present realities. The Arab-Israeli conflict, which began in the early 20th century, has resulted in multiple wars and a protracted struggle over land and resources.
The 1967 Six-Day War saw Israel capture the West Bank, East Jerusalem, and the Gaza Strip, leading to the displacement of hundreds of thousands of Palestinians and the establishment of Israeli settlements in the occupied territories.
The Significance of the Map: A Vital Tool for Understanding and Advocacy
The map of the Gaza Strip and West Bank is not merely a geographical representation; it serves as a critical tool for understanding the complexities of the conflict and advocating for a just and peaceful resolution.
- Visualizing the Conflict: The map provides a visual representation of the political boundaries, settlements, and other key features that contribute to the ongoing conflict. This visual understanding is crucial for building empathy and fostering a deeper understanding of the issues at stake.
- Highlighting the Human Impact: The map can be used to illustrate the impact of the conflict on the Palestinian population, including the displacement of individuals, the restriction of movement, and the limitations on economic development.
- Advocating for Change: The map can serve as a powerful tool for advocating for a just and peaceful solution to the conflict, highlighting the need for international pressure on Israel to end its occupation and for the creation of a viable Palestinian state.
Frequently Asked Questions:
1. What is the difference between the Gaza Strip and the West Bank?
The Gaza Strip is a narrow coastal territory, while the West Bank is a larger region located on the western side of the Jordan River. The Gaza Strip is densely populated and largely urban, while the West Bank has a more diverse landscape and a higher percentage of rural areas.
2. Why is the Gaza Strip under Hamas control?
Hamas won the Palestinian legislative elections in 2006, but its control over the Gaza Strip was solidified in 2007 after a violent conflict with Fatah. This conflict resulted in the division of the Palestinian territories, with Hamas controlling the Gaza Strip and the PA controlling the West Bank.
3. What are Israeli settlements, and why are they controversial?
Israeli settlements are communities established by Israeli citizens in the West Bank and East Jerusalem. They are considered illegal under international law and are a major obstacle to the creation of a viable Palestinian state. Settlements expand Israeli control over Palestinian land and resources, limiting Palestinian self-determination and perpetuating the conflict.
4. What is the two-state solution, and why is it difficult to achieve?
The two-state solution is a framework for peace that envisions the creation of an independent Palestinian state alongside Israel. However, this solution has been difficult to achieve due to a number of factors, including the ongoing conflict, the expansion of Israeli settlements, and the lack of trust between the parties involved.
5. What is the role of the international community in resolving the conflict?
The international community plays a vital role in promoting a peaceful resolution to the conflict. This includes supporting peace negotiations, providing humanitarian aid, and holding both sides accountable for their actions. However, the international community has faced challenges in effectively pressuring both Israel and the Palestinians to make concessions for peace.
Tips for Understanding the Gaza Strip and West Bank Map:
- Focus on key features: Pay attention to the political boundaries, the location of settlements, and the areas under Israeli control.
- Consider the historical context: Understanding the history of the conflict is essential for interpreting the present situation.
- Explore different perspectives: Engage with diverse sources of information to gain a comprehensive understanding of the complex realities on the ground.
- Use the map as a tool for advocacy: Utilize the map to raise awareness about the conflict and to advocate for a just and peaceful solution.
Conclusion:
The Gaza Strip and West Bank map is a powerful tool for understanding the complexities of the Israeli-Palestinian conflict. It provides a visual representation of the contested landscape, highlighting the historical context, the political boundaries, and the human impact of the conflict. By engaging with the map and understanding its significance, individuals can contribute to a more informed and compassionate approach to advocating for a peaceful and just resolution to the conflict.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Complex Landscape: A Comprehensive Look at the Gaza Strip and West Bank Map. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!
