Navigating the Earth’s Magnetic Field: Understanding Magnetic Variation Maps
Related Articles: Navigating the Earth’s Magnetic Field: Understanding Magnetic Variation Maps
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Earth’s Magnetic Field: Understanding Magnetic Variation Maps. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Navigating the Earth’s Magnetic Field: Understanding Magnetic Variation Maps
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Navigating the Earth’s Magnetic Field: Understanding Magnetic Variation Maps
- 3.1 Unveiling the Mystery of Magnetic Variation
- 3.2 Navigating with Accuracy: The Importance of Magnetic Variation Maps
- 3.3 Navigating the Map: Understanding the Key Elements
- 3.4 Using Magnetic Variation Maps: A Practical Guide
- 3.5 FAQs on Magnetic Variation Maps
- 3.6 Tips for Effective Use of Magnetic Variation Maps
- 3.7 Conclusion: Navigating the Future with Magnetic Variation Maps
- 4 Closure
Navigating the Earth’s Magnetic Field: Understanding Magnetic Variation Maps
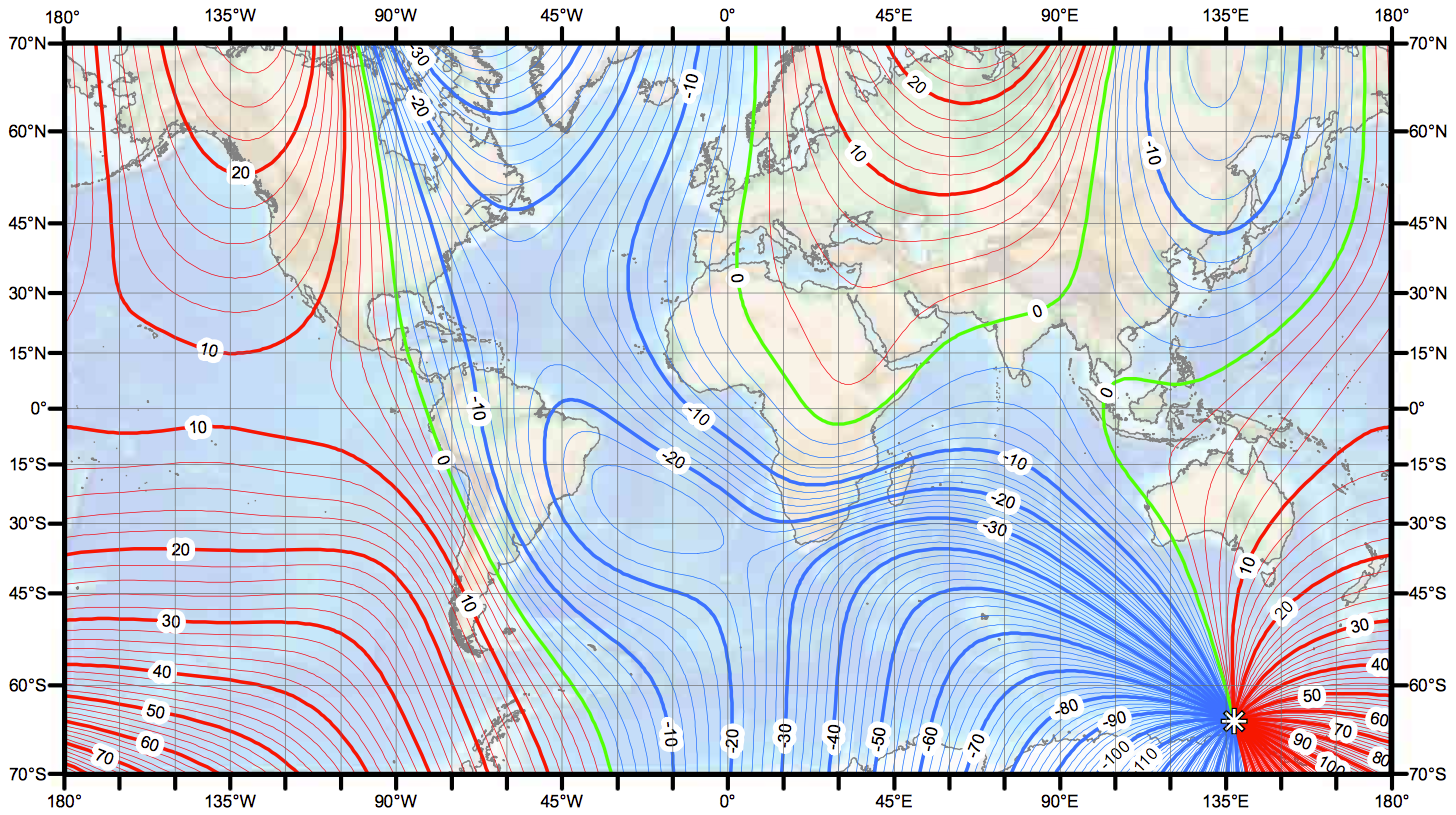
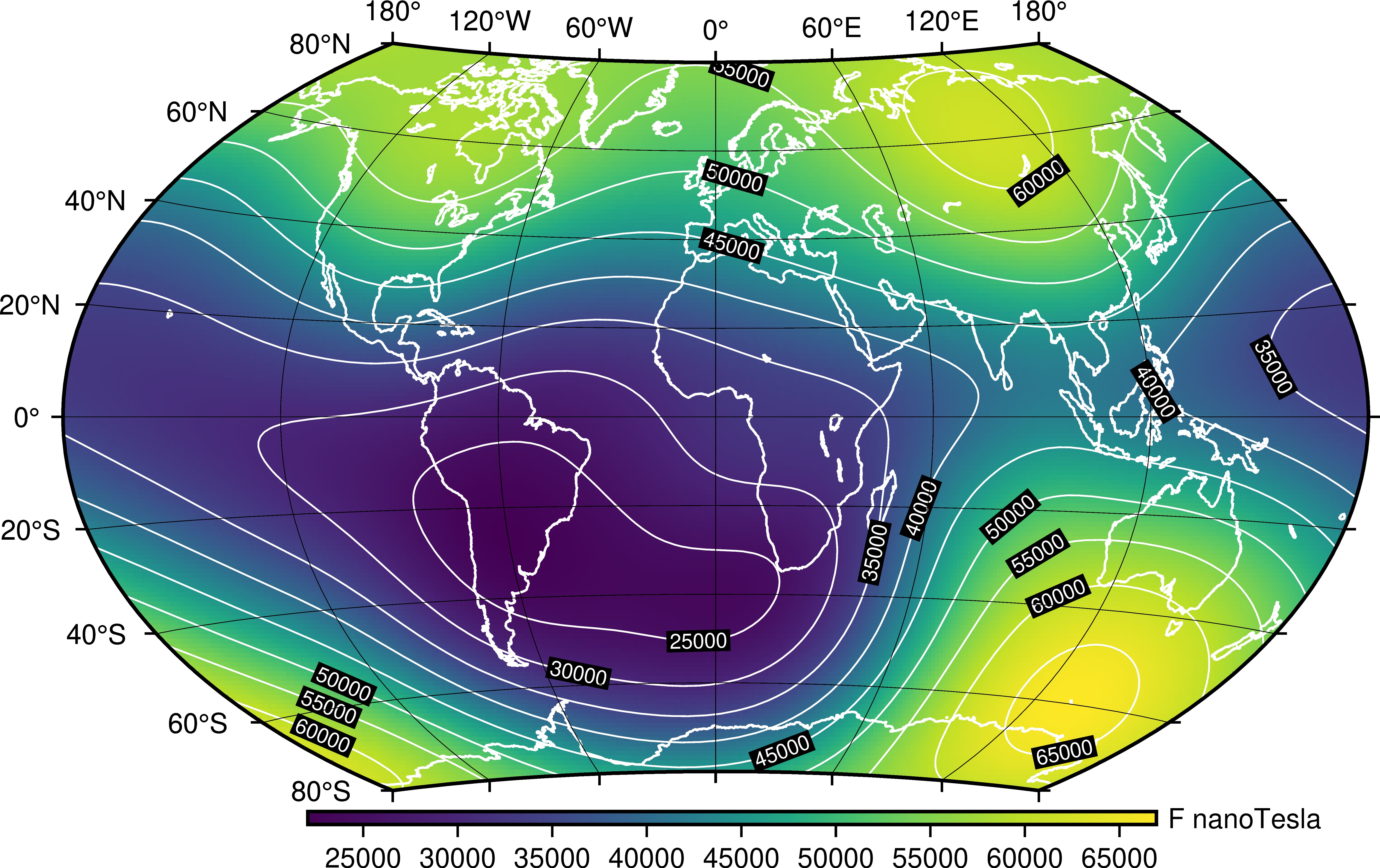
The Earth’s magnetic field is a dynamic force, constantly shifting and evolving. This invisible shield protects us from harmful solar radiation, but it also presents challenges for navigation. One of these challenges is magnetic variation, the difference between true north (geographic north) and magnetic north (the direction a compass needle points). Magnetic variation maps are essential tools for understanding and accounting for this variation, ensuring accurate navigation across the globe.
Unveiling the Mystery of Magnetic Variation
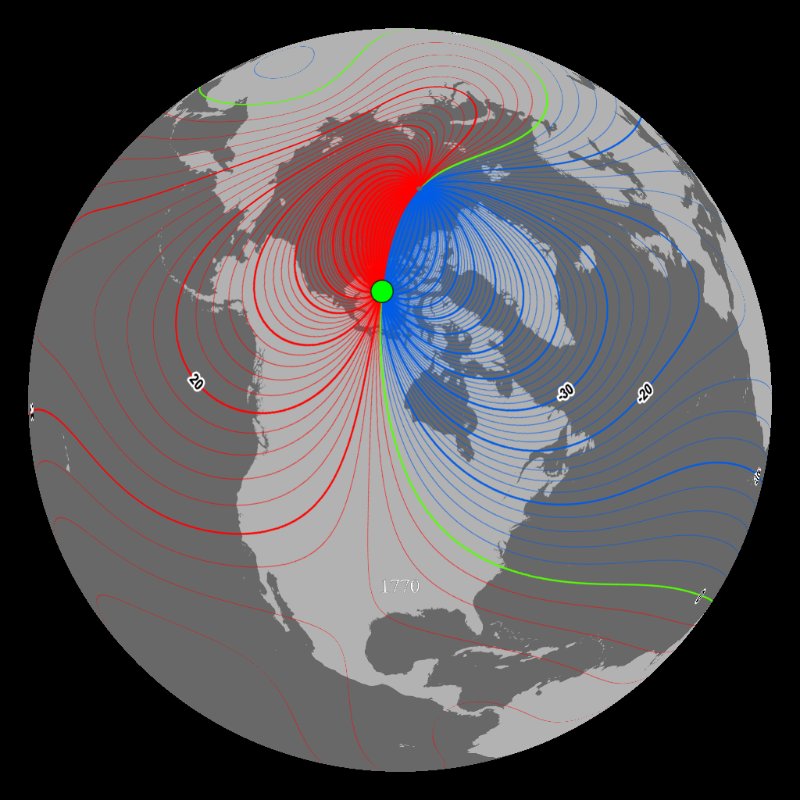
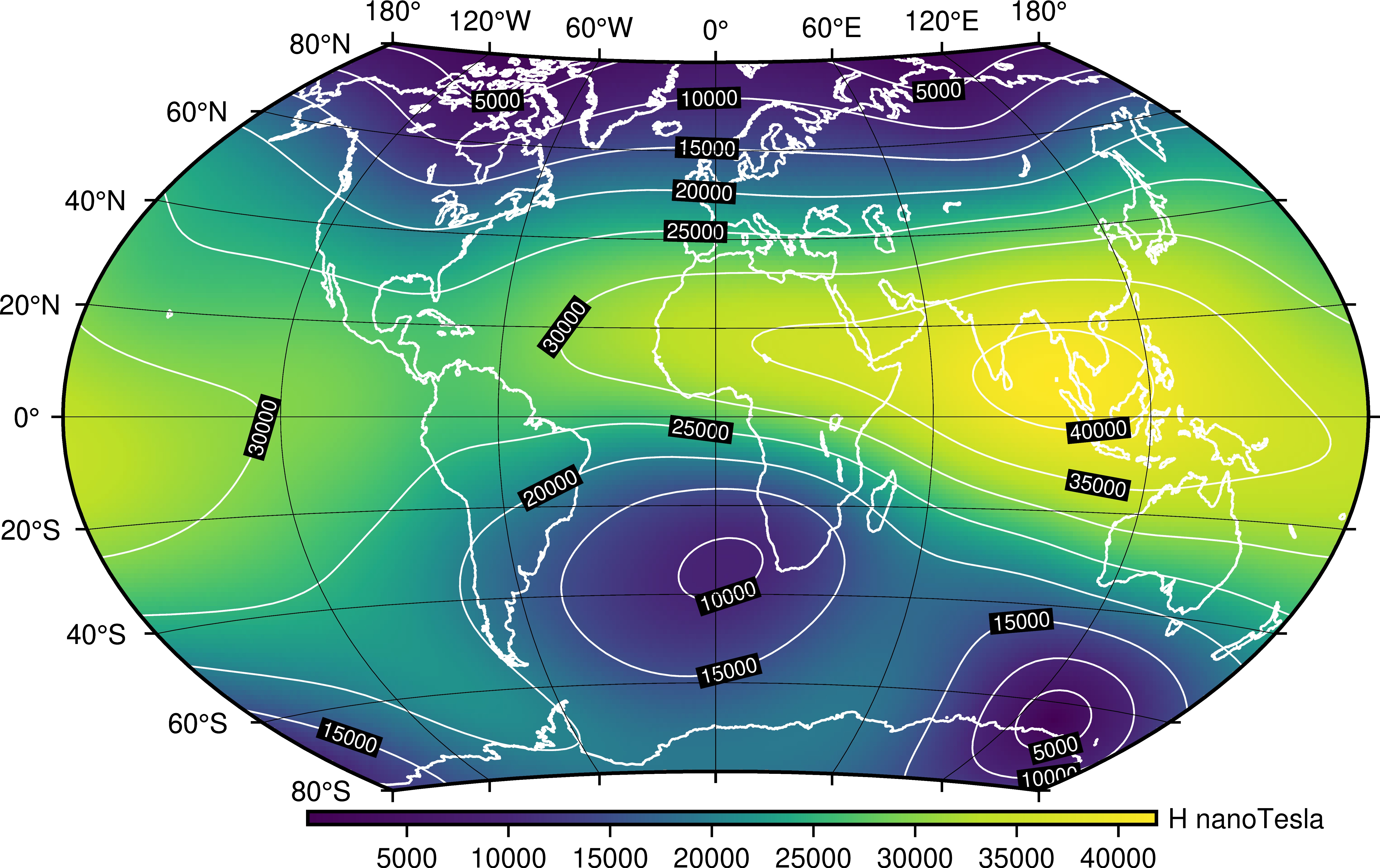
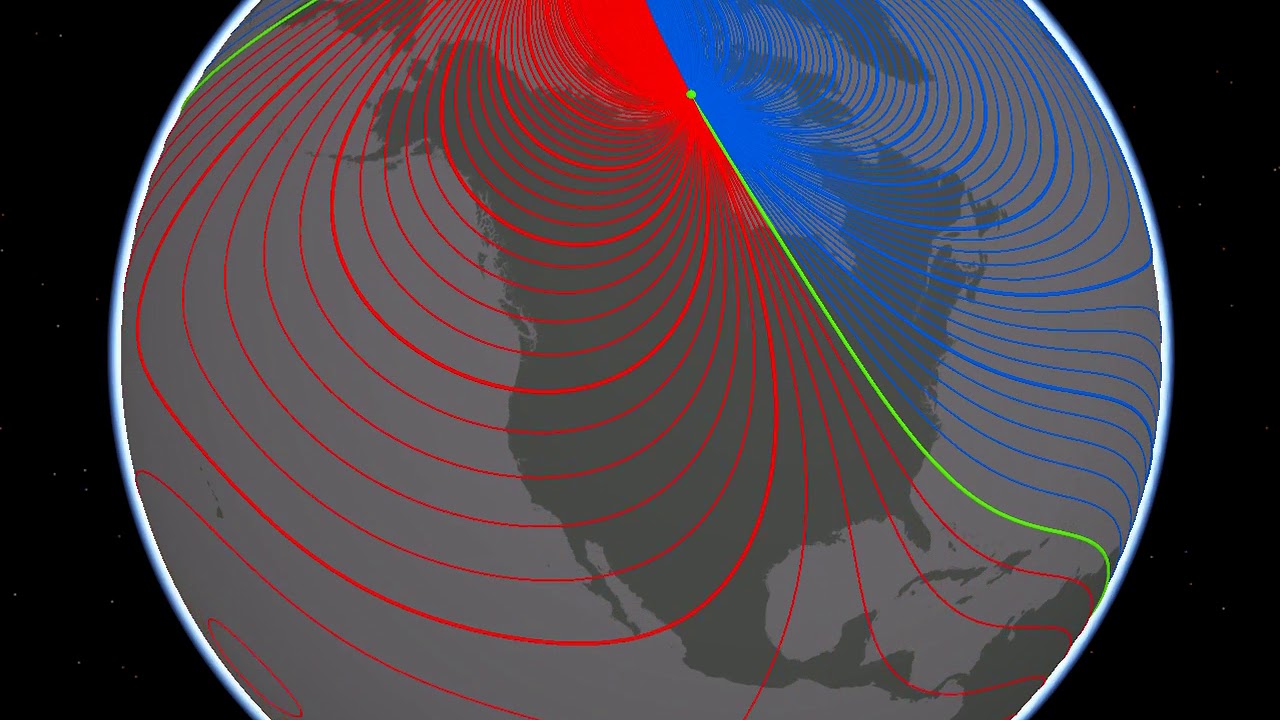
Magnetic variation arises because the Earth’s magnetic field is not perfectly aligned with the planet’s rotational axis. The magnetic poles, where the field lines converge, are not fixed in place but wander over time, influenced by complex geological processes within the Earth’s core. This constant movement creates a dynamic magnetic field, with varying angles between true north and magnetic north at different locations.
Navigating with Accuracy: The Importance of Magnetic Variation Maps
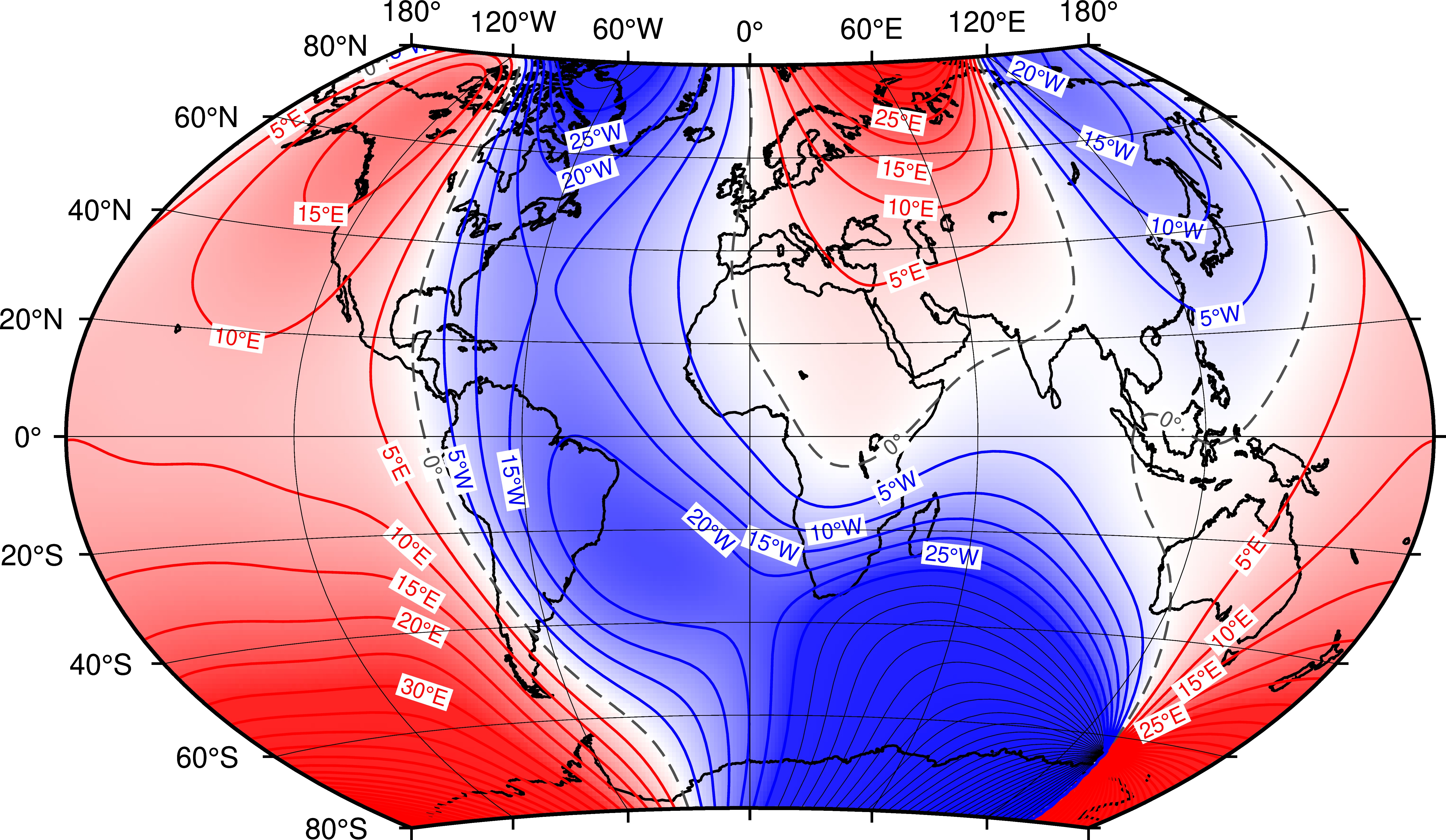
Magnetic variation maps are essential for accurate navigation, especially for activities reliant on compass readings. These maps depict the angular difference between true north and magnetic north at various locations across the globe. They are typically presented as lines of equal variation, known as isogonic lines, which connect points with the same magnetic declination.
Benefits of Using Magnetic Variation Maps:
- Accurate Navigation: By understanding the magnetic variation at a specific location, navigators can adjust their compass readings to obtain accurate bearings and directions.
- Precise Course Setting: Magnetic variation maps allow for precise course setting, ensuring vessels and aircraft stay on their intended path.
- Safety and Efficiency: Accurate navigation based on magnetic variation maps enhances safety by minimizing the risk of getting lost or deviating from the planned route. This efficiency improves navigation time and reduces fuel consumption.
- Land Surveying and Mapping: Magnetic variation maps are crucial for land surveying and mapping, ensuring accurate representation of geographical features and boundaries.
- Geophysical Research: Studying magnetic variation provides insights into the Earth’s magnetic field dynamics, aiding in understanding the complex processes within the planet’s core.
Navigating the Map: Understanding the Key Elements
Magnetic variation maps are typically presented with the following key elements:
- Isogonic Lines: These lines connect points with the same magnetic declination, representing the angular difference between true north and magnetic north.
- Magnetic North Pole: The point where the Earth’s magnetic field lines converge.
- True North: The geographic north pole, defined as the intersection of the Earth’s rotational axis with the Earth’s surface.
- Annual Change: The rate at which magnetic declination changes each year at a specific location.
- Grid North: A reference direction used in some mapping systems, often aligned with a specific grid system.
Using Magnetic Variation Maps: A Practical Guide
To utilize a magnetic variation map effectively, follow these steps:
- Identify the Location: Determine the specific location where navigation is required.
- Locate the Isogonic Line: Find the isogonic line corresponding to the location on the map.
- Read the Magnetic Declination: Note the magnetic declination value associated with the isogonic line.
- Apply the Correction: Adjust the compass reading by adding or subtracting the magnetic declination value, depending on whether the declination is east or west.
- Account for Annual Change: Consider the annual change in magnetic declination at the location to further refine the compass reading.
FAQs on Magnetic Variation Maps
1. What is the difference between true north and magnetic north?
True north refers to the geographic north pole, while magnetic north is the direction a compass needle points, influenced by the Earth’s magnetic field.
2. Why does magnetic variation change over time?
Magnetic variation changes due to the dynamic nature of the Earth’s magnetic field, influenced by geological processes within the Earth’s core. The magnetic poles are not fixed in place but wander over time.
3. How often should magnetic variation be checked?
It is recommended to check magnetic variation regularly, ideally every few years, as it changes over time. The frequency of checks depends on the specific location and the level of accuracy required for navigation.
4. Are magnetic variation maps available online?
Yes, several online resources provide magnetic variation maps, including the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) website.
5. What is the significance of the annual change value on a magnetic variation map?
The annual change value indicates the rate at which magnetic declination changes each year at a specific location. This information is crucial for adjusting compass readings over time.
6. Can I use a magnetic variation map for all locations?
Magnetic variation maps are specific to certain regions. It is essential to use a map that covers the area where navigation is required.
Tips for Effective Use of Magnetic Variation Maps
- Use a Reliable Map: Ensure the magnetic variation map is updated and accurate for the relevant time period.
- Consider Annual Change: Account for the annual change in magnetic declination when making adjustments to compass readings.
- Consult Multiple Sources: Verify the magnetic variation values from different sources to ensure consistency.
- Familiarize Yourself with the Map: Understand the key elements and symbols on the map before using it for navigation.
- Practice and Apply: Regularly practice using magnetic variation maps to improve familiarity and accuracy in applying the corrections.
Conclusion: Navigating the Future with Magnetic Variation Maps
Magnetic variation maps play a crucial role in accurate navigation, ensuring the safety and efficiency of various activities. Understanding and applying the information provided by these maps is essential for navigators, surveyors, and researchers alike. As the Earth’s magnetic field continues to evolve, utilizing updated and reliable magnetic variation maps will remain vital for navigating the world with precision and confidence.
![]()


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Earth’s Magnetic Field: Understanding Magnetic Variation Maps. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!
