Navigating the Landscape of PFAS Contamination: Understanding the EPA’s PFAS Map
Related Articles: Navigating the Landscape of PFAS Contamination: Understanding the EPA’s PFAS Map
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Landscape of PFAS Contamination: Understanding the EPA’s PFAS Map. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Landscape of PFAS Contamination: Understanding the EPA’s PFAS Map

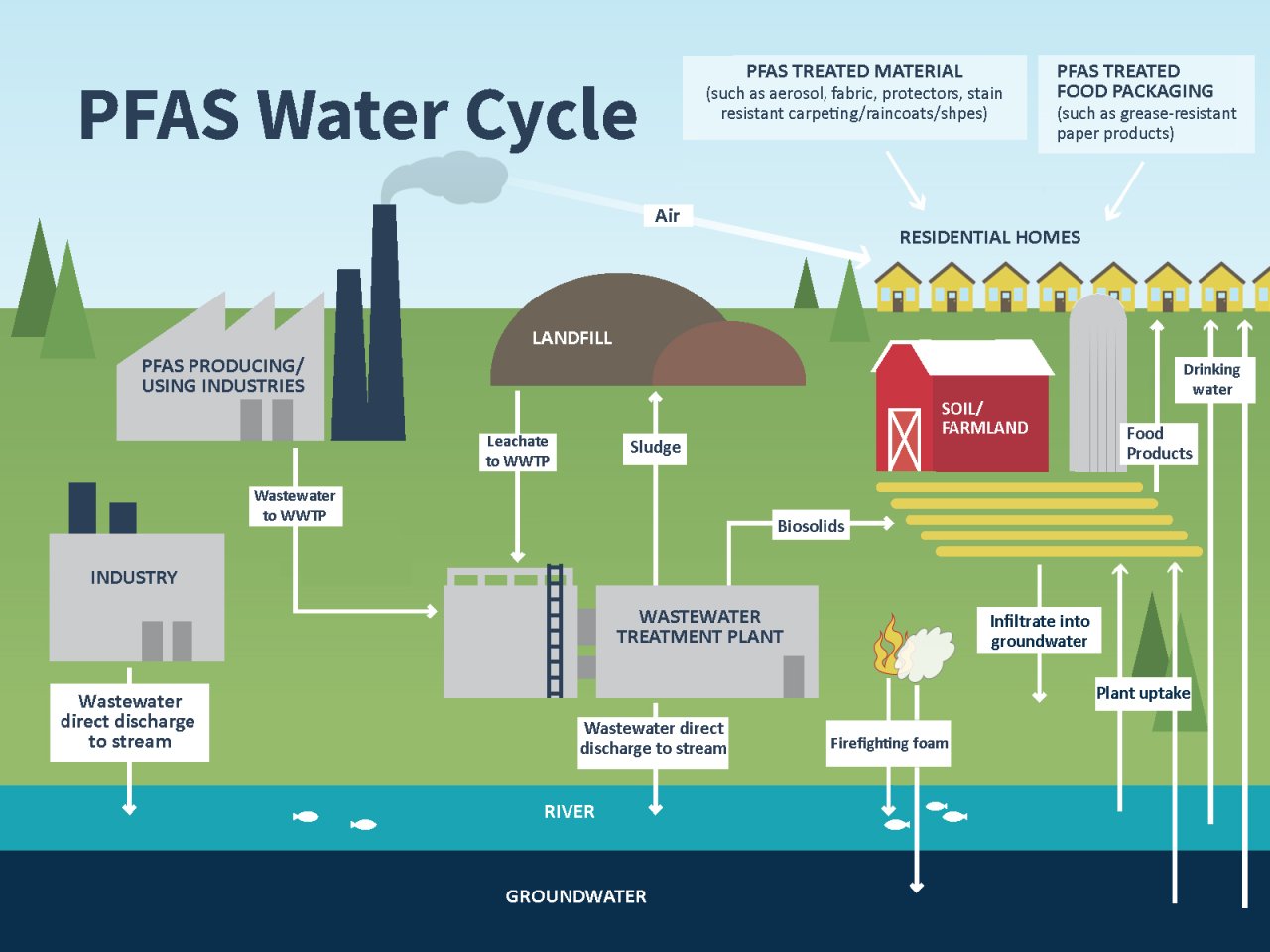
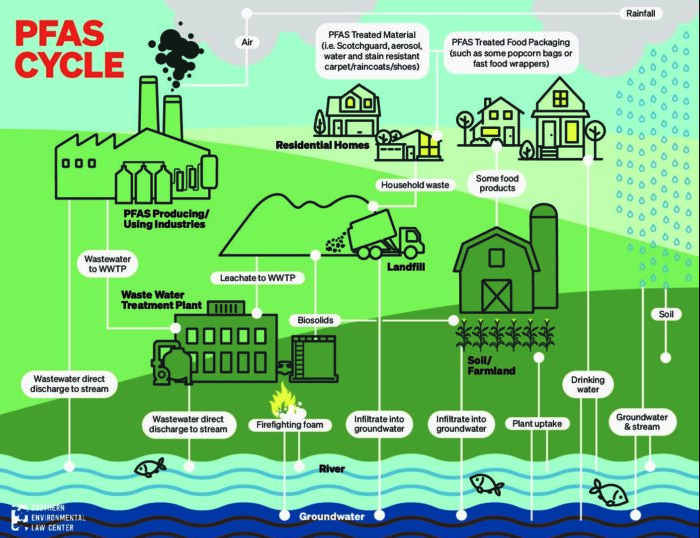
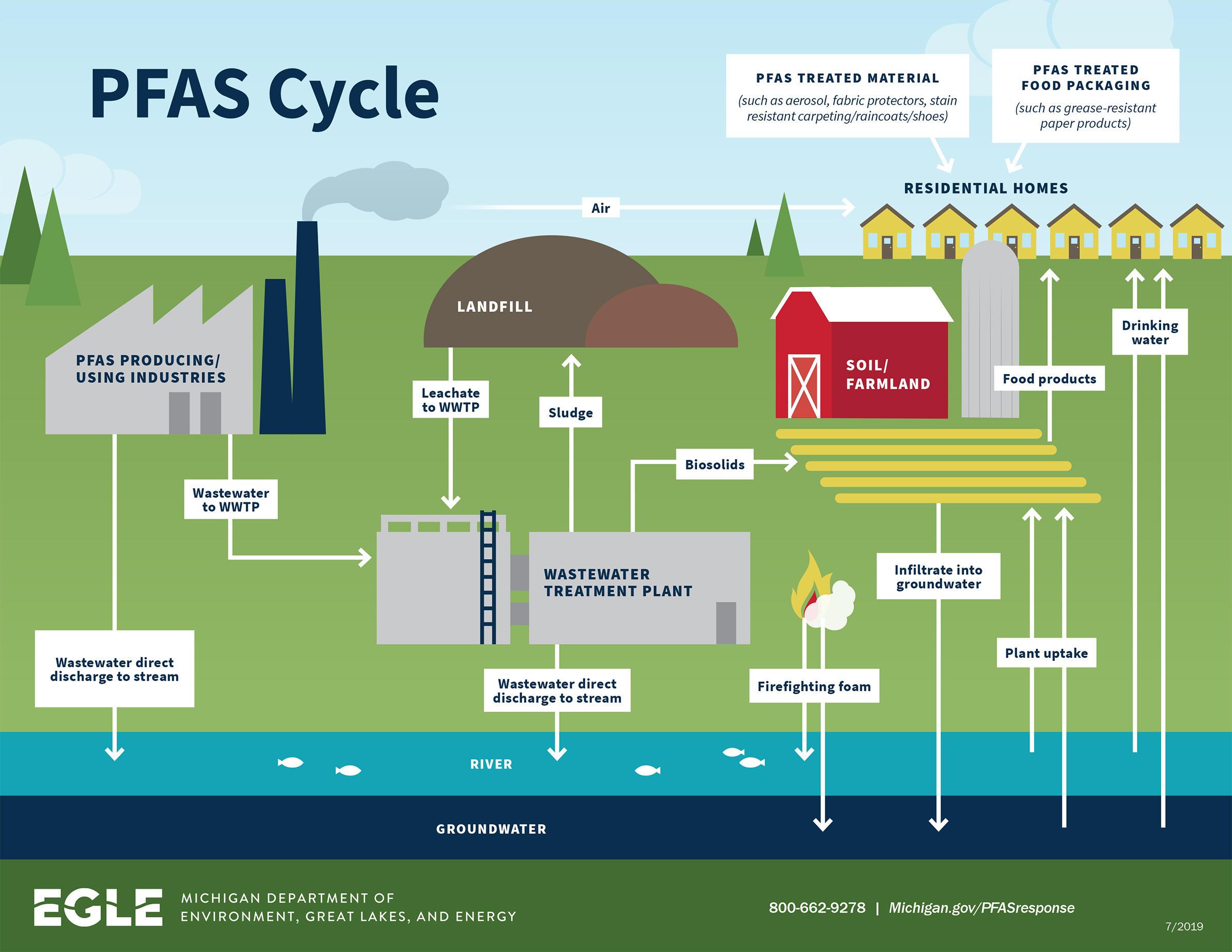
Per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) are a group of man-made chemicals with unique properties that make them valuable for various applications, including non-stick cookware, firefighting foam, and food packaging. However, these same properties also contribute to their persistence in the environment and potential for harm to human health. Recognizing the growing concern about PFAS contamination, the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) has developed a comprehensive resource to inform the public and stakeholders about the extent and potential risks associated with these chemicals.
The EPA’s PFAS Map: A Visual Guide to Contamination
The EPA’s PFAS Map is an interactive online tool that provides a clear and accessible visual representation of PFAS contamination across the United States. It is a valuable resource for understanding the distribution of PFAS in various environmental media, including drinking water, soil, and air. The map serves multiple purposes:
- Visualizing the Extent of Contamination: The map clearly shows the locations where PFAS have been detected in various environmental samples. This allows for a better understanding of the geographic scope of contamination and potential areas of concern.
- Identifying Potential Health Risks: By linking PFAS detections with known health effects, the map helps identify areas where populations may be exposed to higher levels of these chemicals and potentially face increased health risks.
- Supporting Decision-Making: The data presented on the map empowers communities, policymakers, and environmental agencies to make informed decisions regarding PFAS management, remediation, and prevention.
Understanding the Data Presented on the Map
The EPA’s PFAS Map draws data from various sources, including:
- EPA’s own monitoring programs: The EPA conducts extensive monitoring of PFAS in various environmental media, including drinking water, wastewater, and surface water.
- State and local monitoring programs: Many states and local agencies have their own monitoring programs for PFAS, providing valuable data on contamination levels at the regional and local levels.
- Publicly available data: The EPA incorporates data from other public sources, such as research studies and reports, to further enhance the comprehensiveness of the map.
The map displays data in several ways, including:
- PFAS Detection Locations: Pinpoints on the map indicate locations where PFAS have been detected in environmental samples.
- PFAS Concentration Levels: The map uses color gradients to represent different concentration levels of PFAS in various media.
- Type of PFAS Detected: The map identifies the specific PFAS compounds detected at each location, allowing for a more detailed analysis of the contamination profile.
- Data Source: The map clearly indicates the source of each data point, ensuring transparency and allowing users to understand the origins of the information.
Benefits of the EPA’s PFAS Map
The EPA’s PFAS Map offers numerous benefits to stakeholders:
- Increased Public Awareness: The map provides a readily accessible and easily understandable platform for raising awareness about PFAS contamination and its potential health implications.
- Empowering Communities: The map equips communities with information to engage in discussions about PFAS management, advocate for clean water, and hold responsible parties accountable.
- Supporting Policy Decisions: The map provides valuable data to support policy decisions related to PFAS regulation, remediation, and prevention.
- Facilitating Research and Development: The map serves as a valuable resource for researchers studying PFAS contamination, allowing them to identify areas of focus and prioritize research efforts.
- Promoting Collaboration: The map encourages collaboration between different stakeholders, including government agencies, researchers, and community groups, to address PFAS contamination effectively.
FAQs about the EPA’s PFAS Map
1. What PFAS compounds are included in the map?
The map currently includes data for a variety of PFAS compounds, but the specific compounds may vary depending on the data source. The EPA is continuously expanding the map to include data for a wider range of PFAS.
2. How accurate is the data presented on the map?
The EPA strives to ensure the accuracy and reliability of the data presented on the map. However, the map is a dynamic resource that is continuously updated as new data becomes available. It is important to note that the map reflects the available data at a given point in time and may not represent a complete picture of PFAS contamination.
3. How can I contribute to the map?
The EPA welcomes contributions from individuals and organizations with relevant data on PFAS contamination. If you have data that could be incorporated into the map, you can contact the EPA for guidance on data submission.
4. What actions can I take based on the information presented on the map?
The map provides valuable information that can inform individual actions, such as choosing water filters or avoiding certain products that may contain PFAS. It also empowers communities to advocate for clean water and hold responsible parties accountable.
5. How does the EPA plan to address PFAS contamination?
The EPA is actively working to address PFAS contamination through a multi-pronged approach, including:
- Setting health advisories: The EPA has set health advisories for PFAS in drinking water to guide states and communities in protecting public health.
- Developing regulations: The EPA is developing regulations to limit PFAS discharges from industrial sources and establish maximum contaminant levels for PFAS in drinking water.
- Investing in research: The EPA is investing in research to better understand the health effects of PFAS and develop effective remediation technologies.
- Promoting collaboration: The EPA is working with states, local communities, and other stakeholders to address PFAS contamination collaboratively.
Tips for Using the EPA’s PFAS Map Effectively
- Explore the map features: Familiarize yourself with the various map features, including zoom controls, data filters, and information panels.
- Focus on your area of interest: Use the search function to locate specific locations or areas of concern.
- Compare data across different sources: The map displays data from multiple sources, allowing for a more comprehensive understanding of PFAS contamination.
- Consider data limitations: Remember that the map reflects the available data at a given point in time and may not represent a complete picture of PFAS contamination.
- Use the map to inform decision-making: The map can be a valuable tool for making informed decisions about PFAS management, remediation, and prevention.
Conclusion
The EPA’s PFAS Map is a powerful resource for understanding the extent and potential risks of PFAS contamination. By providing a clear and accessible visual representation of data, the map empowers communities, policymakers, and environmental agencies to make informed decisions regarding PFAS management. It serves as a critical tool for raising awareness, promoting collaboration, and driving action to address this emerging environmental challenge. The EPA’s commitment to updating and expanding the map ensures that it remains a valuable resource for navigating the complex landscape of PFAS contamination and protecting public health.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Landscape of PFAS Contamination: Understanding the EPA’s PFAS Map. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!
