Navigating the Landscape: Understanding the Significance of Marking Maps
Related Articles: Navigating the Landscape: Understanding the Significance of Marking Maps
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Landscape: Understanding the Significance of Marking Maps. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Navigating the Landscape: Understanding the Significance of Marking Maps
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Navigating the Landscape: Understanding the Significance of Marking Maps
- 3.1 The Historical Roots of Marking Maps: From Ancient Times to Modern Exploration
- 3.2 The Modern Era: From Paper to Pixels, the Enduring Power of Marking Maps
- 3.3 The Importance of Marking Maps: A Multifaceted Perspective
- 3.4 The Future of Marking Maps: Embracing Technology and Innovation
- 3.5 Frequently Asked Questions about Marking Maps
- 3.6 Conclusion: Marking Maps – A Vital Tool for Understanding and Interacting with the World
- 4 Closure
Navigating the Landscape: Understanding the Significance of Marking Maps

In the realm of cartography and navigation, the act of marking a map holds profound significance. It transcends the simple act of placing a symbol on a piece of paper or digital interface; it represents a crucial step in understanding, analyzing, and interacting with the world around us. This article delves into the multifaceted nature of marking maps, exploring its historical roots, practical applications, and the profound impact it has on our understanding of space and place.
The Historical Roots of Marking Maps: From Ancient Times to Modern Exploration
Marking maps is an ancient practice, dating back to the earliest civilizations. Cave paintings, ancient Babylonian clay tablets, and Egyptian papyrus scrolls all depict rudimentary forms of mapmaking, often incorporating markings to denote important features, settlements, and trade routes. These early markings served as vital tools for navigation, communication, and resource management.
The development of more sophisticated mapmaking techniques in the Classical era saw the introduction of standardized symbols and conventions for marking maps. The Greeks, for instance, employed a system of symbols to represent cities, mountains, rivers, and seas. These conventions facilitated the creation of more detailed and accurate maps, paving the way for further exploration and scientific advancement.
The Renaissance period witnessed a surge in cartographic innovation, with the invention of the printing press and the exploration of new lands. This era saw the emergence of detailed nautical charts, marked with intricate details of coastlines, currents, and navigational aids. The ability to mark these charts with precision enabled explorers to chart new territories, navigate uncharted waters, and expand the boundaries of human knowledge.
The Modern Era: From Paper to Pixels, the Enduring Power of Marking Maps
In the modern era, the practice of marking maps has evolved alongside technological advancements. The transition from paper to digital maps has brought about a paradigm shift in the way we interact with spatial information. While the fundamental principles of marking maps remain the same, the tools and methods employed have become increasingly sophisticated.
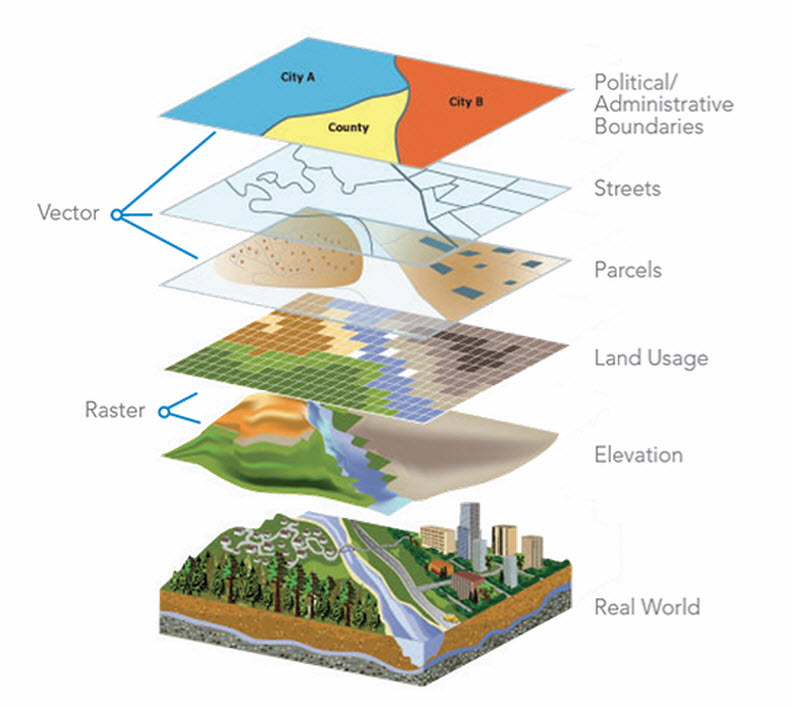
Geographic Information Systems (GIS) software, for instance, allows users to create, analyze, and manipulate digital maps with unparalleled precision. These systems enable the marking of maps with a vast array of data layers, ranging from demographic information to environmental data to infrastructure networks. This ability to overlay different types of data on maps provides a comprehensive understanding of complex relationships and patterns within the environment.
The Importance of Marking Maps: A Multifaceted Perspective
Marking maps is not merely a technical exercise; it serves a crucial role in various fields, from scientific research and urban planning to disaster management and environmental conservation. Here are some key areas where marking maps holds significant value:
1. Navigation and Wayfinding: Marking maps has been essential for navigation since the dawn of human civilization. From ancient mariners using celestial bodies to modern drivers relying on GPS systems, the ability to mark a map and identify one’s location is fundamental to traversing the world.
2. Geographic Analysis: Marking maps allows for the visualization and analysis of spatial data. By overlaying different layers of information on a map, researchers can identify trends, patterns, and relationships within a geographical area. This approach is crucial in fields like urban planning, epidemiology, and environmental science.
3. Resource Management: Marking maps plays a critical role in managing natural resources. By mapping out areas of forest cover, water bodies, and mineral deposits, governments and organizations can develop effective strategies for sustainable resource use and conservation.
4. Disaster Management: In the event of natural disasters, marking maps is vital for coordinating rescue efforts, assessing damage, and providing aid to affected populations. Maps can be used to identify evacuation routes, shelter locations, and areas of critical infrastructure.
5. Environmental Conservation: Marking maps is a powerful tool for environmental conservation. By identifying areas of biodiversity, habitat loss, and pollution, conservationists can prioritize efforts to protect vulnerable ecosystems and ensure the sustainability of natural resources.
6. Education and Public Awareness: Marking maps is crucial for educating people about the world around them. By visualizing geographical information, maps can foster an understanding of cultural diversity, historical events, and environmental challenges.
The Future of Marking Maps: Embracing Technology and Innovation
As technology continues to advance, the practice of marking maps is poised for further evolution. The emergence of augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR) technologies offers exciting possibilities for interactive and immersive map experiences.
AR applications, for instance, can overlay digital information on real-world environments, providing users with real-time context and insights. This capability has the potential to revolutionize navigation, urban planning, and environmental monitoring.
VR technologies can create virtual representations of geographical spaces, allowing users to explore and interact with environments in a highly immersive manner. This technology has the potential to enhance education, training, and research in various fields, from architecture to archaeology.
Frequently Asked Questions about Marking Maps
Q: What are the most common types of map markings?
A: The types of map markings vary depending on the purpose of the map. Common markings include:
- Points of Interest: Cities, towns, landmarks, and other notable locations.
- Lines: Roads, rivers, borders, and other linear features.
- Areas: Forests, lakes, deserts, and other defined regions.
- Symbols: Icons representing specific features like hospitals, schools, or airports.
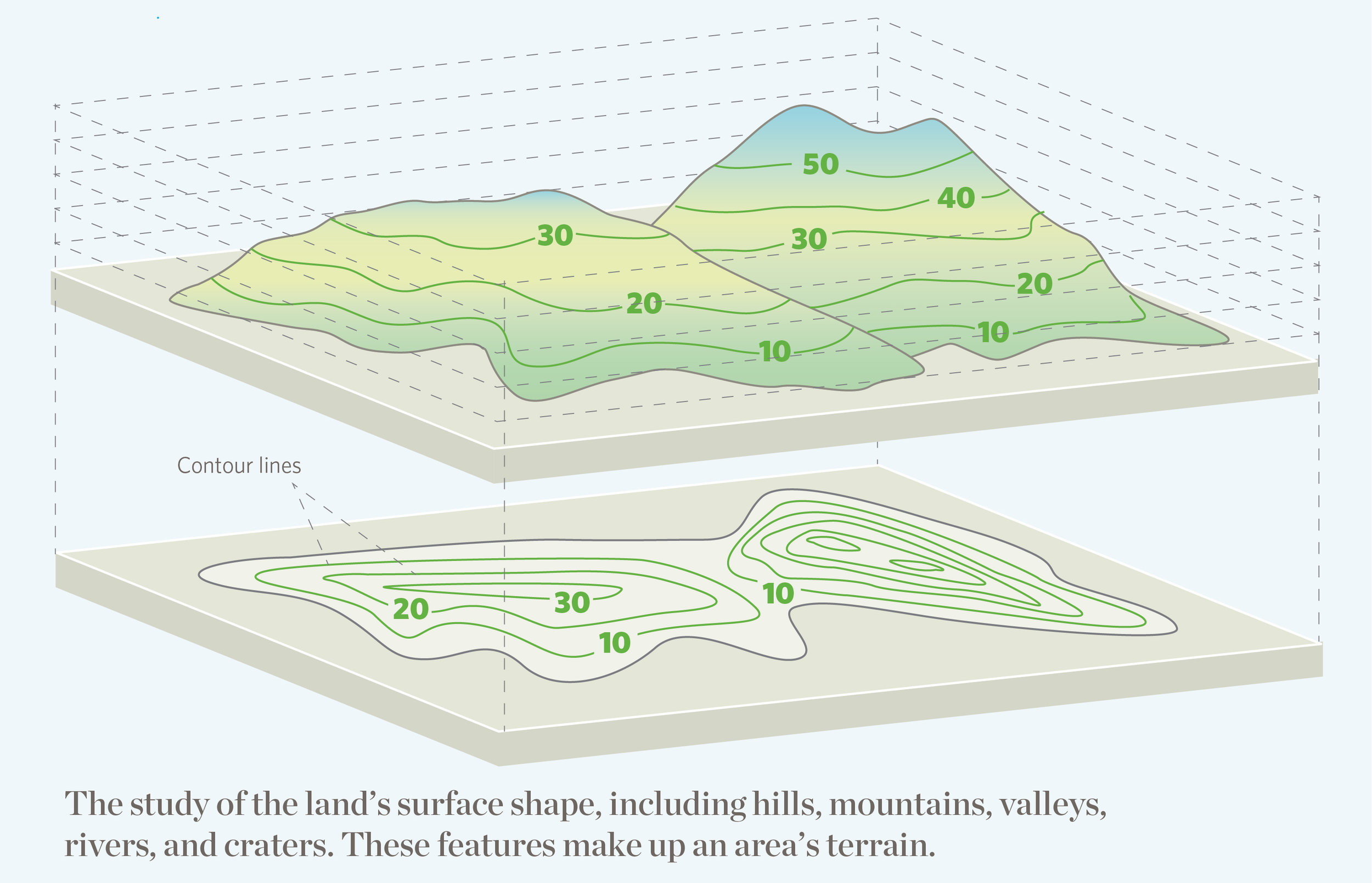
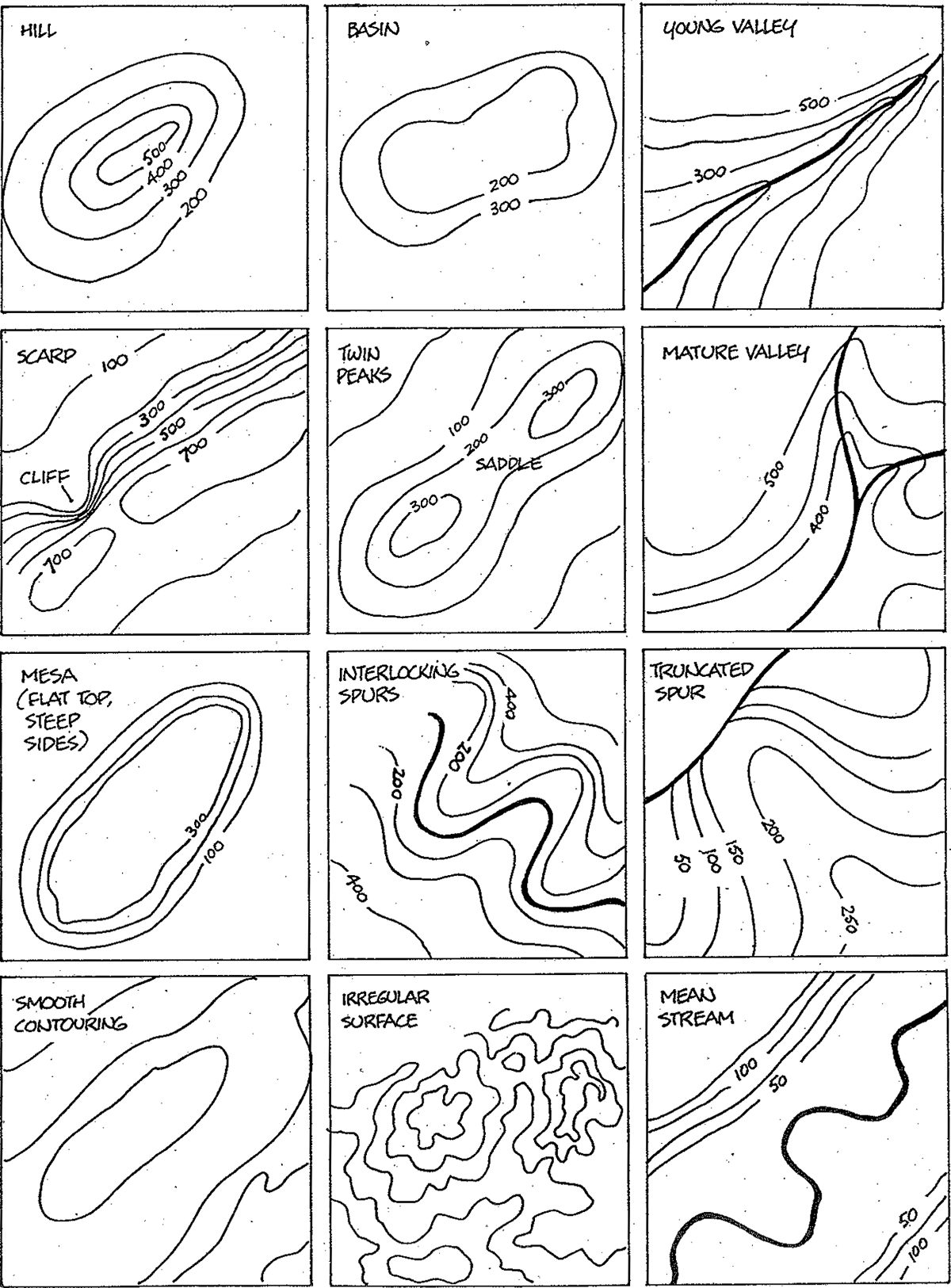
- Data Layers: Geographic information overlays, such as population density, elevation, or rainfall patterns.
Q: What are the benefits of using digital maps over paper maps?
A: Digital maps offer several advantages over traditional paper maps:
- Interactivity: Users can zoom in and out, pan across the map, and access detailed information with a few clicks.
- Real-time updates: Digital maps can be updated in real-time to reflect changes in traffic, weather, or other dynamic conditions.
- Data integration: Digital maps can incorporate various layers of information, providing a comprehensive understanding of a geographical area.
- Accessibility: Digital maps are readily available on smartphones, computers, and other devices, making them easily accessible to a wider audience.
Q: What are some tips for creating effective map markings?
A: Here are some tips for creating effective map markings:
- Clarity and simplicity: Use clear and concise symbols and labels that are easy to understand.
- Consistency: Maintain a consistent style and color scheme throughout the map to ensure visual coherence.
- Relevance: Include only the information that is relevant to the purpose of the map.
- Scale and detail: Choose an appropriate scale and level of detail for the intended audience and purpose.
- Accessibility: Consider the needs of users with disabilities by using clear fonts, contrasting colors, and alternative formats.
Conclusion: Marking Maps – A Vital Tool for Understanding and Interacting with the World
The practice of marking maps has evolved over centuries, from rudimentary cave paintings to sophisticated digital systems. This act of placing symbols and data on a map remains a fundamental tool for understanding, analyzing, and interacting with the world around us.
Marking maps provides a visual representation of geographical information, enabling us to navigate, analyze, manage resources, and address critical issues like disaster management and environmental conservation. As technology continues to advance, the practice of marking maps will undoubtedly continue to evolve, offering even more powerful tools for exploring, understanding, and shaping our world.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Landscape: Understanding the Significance of Marking Maps. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!
