Navigating the Seismic Landscape: Understanding the USGS Earthquake Hazards Map
Related Articles: Navigating the Seismic Landscape: Understanding the USGS Earthquake Hazards Map
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Seismic Landscape: Understanding the USGS Earthquake Hazards Map. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Seismic Landscape: Understanding the USGS Earthquake Hazards Map

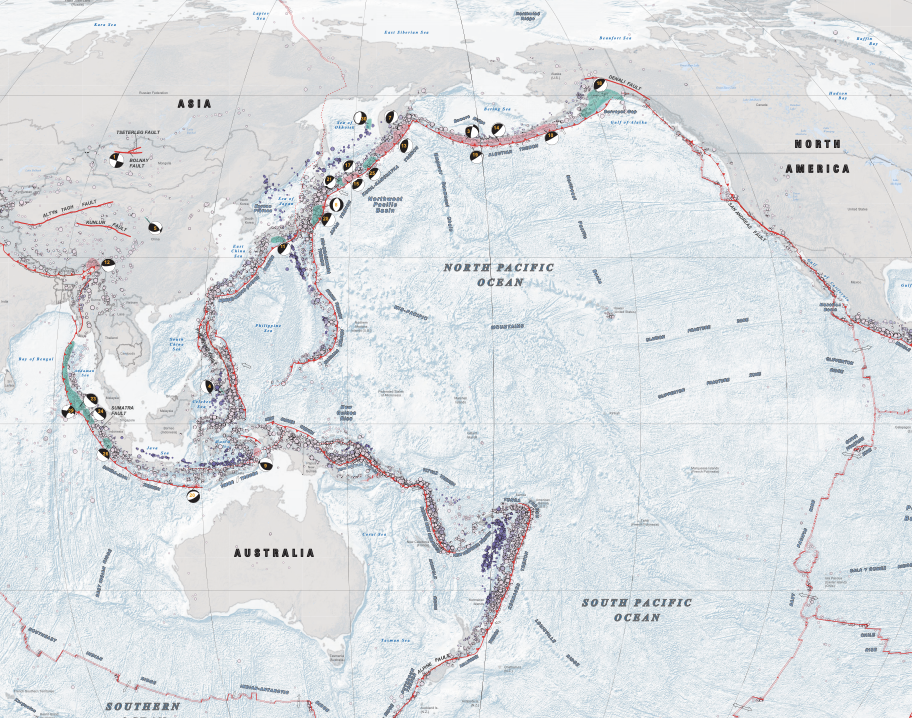
The Earth’s crust is a dynamic tapestry, constantly shifting and rearranging itself. These movements, often imperceptible, can manifest in dramatic ways, particularly through earthquakes. The United States Geological Survey (USGS) has developed a comprehensive and invaluable tool for understanding and mitigating earthquake risks – the USGS Earthquake Hazards Map. This map, a product of extensive scientific research and data analysis, provides a vital resource for individuals, communities, and policymakers alike.
Unveiling the Seismic Landscape:
The USGS Earthquake Hazards Map is not merely a static representation of earthquake occurrences. It is a dynamic and multifaceted tool that integrates a wealth of scientific data to present a nuanced picture of earthquake hazards across the United States. The map incorporates:
- Earthquake History: Past earthquakes, their locations, magnitudes, and associated damage are meticulously documented, providing a historical perspective on seismic activity.
- Fault Lines: The map highlights major fault lines, the geological fractures in the Earth’s crust where tectonic plates interact, creating zones of heightened seismic vulnerability.
- Seismic Hazard Levels: Using sophisticated models, the map assigns seismic hazard levels to different regions, reflecting the likelihood and intensity of future earthquakes. These levels are crucial for informing building codes, infrastructure design, and emergency preparedness.
- Ground Shaking Intensity: The map provides estimates of ground shaking intensity, a crucial factor in determining the potential impact of earthquakes on buildings, infrastructure, and the environment.
- Liquefaction Potential: The map identifies areas susceptible to liquefaction, a phenomenon where saturated soil loses its strength during earthquakes, potentially leading to ground failure and structural damage.
- Tsunami Risk: Coastal areas are assessed for their vulnerability to tsunamis, giant waves triggered by underwater earthquakes or landslides.
Beyond the Visual:
The USGS Earthquake Hazards Map is not merely a visual representation; it is a powerful tool for decision-making and risk assessment. It provides:
- Data for Building Codes: The map’s data is essential for developing and enforcing building codes that ensure structures can withstand seismic forces. By understanding the potential ground shaking intensity and liquefaction risk in a particular area, engineers can design buildings that are resilient to earthquakes.
- Guidance for Infrastructure Design: Critical infrastructure, such as bridges, dams, and power grids, are particularly vulnerable to earthquake damage. The map helps engineers design these structures to withstand seismic forces, ensuring their functionality during and after earthquakes.
- Informed Emergency Planning: The map provides crucial data for developing effective emergency plans and response strategies. By understanding the potential impacts of earthquakes, communities can prepare for evacuations, disaster relief, and post-earthquake recovery.
- Public Awareness: The map serves as an educational tool, raising public awareness about earthquake hazards and the importance of preparedness. By visualizing the potential risks, individuals can make informed decisions about their safety and resilience.
FAQs about the USGS Earthquake Hazards Map:
1. How often is the USGS Earthquake Hazards Map updated?
The USGS Earthquake Hazards Map is constantly updated with new data and scientific advancements. The map is revised periodically, typically every few years, to incorporate new information and improve its accuracy.
2. What are the limitations of the USGS Earthquake Hazards Map?
While the USGS Earthquake Hazards Map is a valuable tool, it is important to note that it is based on scientific models and estimations. The actual occurrence and impact of earthquakes can vary, and the map should be used as a guide rather than a definitive prediction.
3. Can the USGS Earthquake Hazards Map predict earthquakes?
While the map provides information about the likelihood and intensity of future earthquakes, it cannot predict the precise timing or location of earthquakes. Earthquakes are complex natural phenomena, and current scientific understanding does not allow for accurate prediction.
4. How can I use the USGS Earthquake Hazards Map for personal preparedness?
The USGS Earthquake Hazards Map can help you understand the potential earthquake risks in your area. By identifying your location on the map, you can assess the likelihood and intensity of ground shaking, liquefaction, and tsunami risk. This information can inform your preparedness plans, such as securing your home, creating an emergency kit, and establishing communication plans.
5. What are some resources available for learning more about earthquakes?
The USGS website provides a wealth of information on earthquakes, including their causes, effects, and preparedness strategies. You can also consult with local emergency management agencies and organizations like the American Red Cross for additional resources and guidance.
Tips for Utilizing the USGS Earthquake Hazards Map:
- Explore the map features: Familiarize yourself with the different layers and data available on the map, including earthquake history, fault lines, seismic hazard levels, and ground shaking intensity.
- Identify your location: Locate your home or workplace on the map to understand the potential risks in your area.
- Review the hazard levels: Pay attention to the seismic hazard levels assigned to your location and understand the associated risks.
- Consider liquefaction potential: If you live in an area with high liquefaction potential, take steps to mitigate the risks, such as reinforcing your foundation or ensuring adequate drainage.
- Prepare for tsunamis: If you live in a coastal area, learn about tsunami warning systems and evacuation routes.
- Share the information: Share your knowledge of the USGS Earthquake Hazards Map with your family, friends, and community members to promote earthquake preparedness.
Conclusion:
The USGS Earthquake Hazards Map serves as a vital tool for understanding and mitigating earthquake risks in the United States. By integrating a vast array of scientific data, the map provides valuable insights into seismic hazards, enabling informed decision-making for individuals, communities, and policymakers. Its application in building codes, infrastructure design, emergency planning, and public awareness is crucial for enhancing resilience and minimizing the impacts of earthquakes. While the map cannot predict earthquakes, it offers a powerful resource for navigating the seismic landscape and promoting safety in a dynamic and ever-changing Earth.







Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Seismic Landscape: Understanding the USGS Earthquake Hazards Map. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!
