The Importance of Scale in Maps: A Comprehensive Guide to Drawing a Scale
Related Articles: The Importance of Scale in Maps: A Comprehensive Guide to Drawing a Scale
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to The Importance of Scale in Maps: A Comprehensive Guide to Drawing a Scale. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: The Importance of Scale in Maps: A Comprehensive Guide to Drawing a Scale
- 2 Introduction
- 3 The Importance of Scale in Maps: A Comprehensive Guide to Drawing a Scale
- 3.1 Understanding Map Scale: The Foundation of Accurate Representation
- 3.2 Drawing a Scale on a Map: A Step-by-Step Guide
- 4 Closure
The Importance of Scale in Maps: A Comprehensive Guide to Drawing a Scale

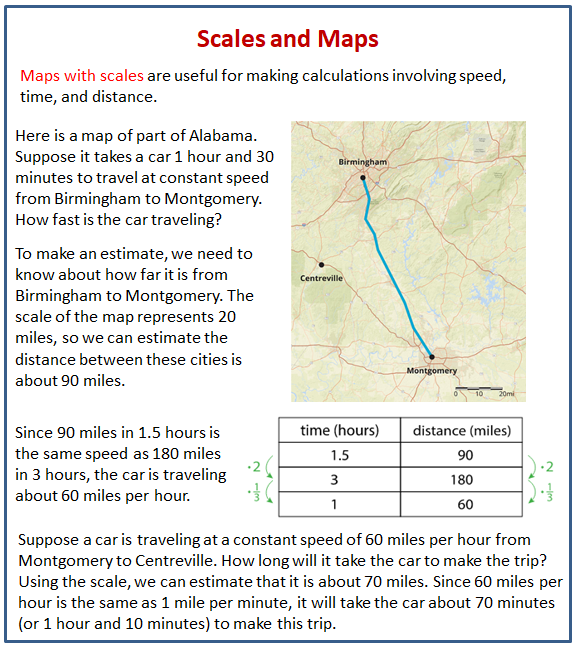
Maps are visual representations of the world, but their effectiveness hinges on one crucial element: scale. Scale defines the relationship between distances on the map and the corresponding distances on the ground. Without an accurate scale, a map becomes misleading, rendering it useless for navigation, planning, or analysis.
This guide delves into the intricacies of drawing a scale on a map, outlining its significance and providing practical steps for its accurate representation.
Understanding Map Scale: The Foundation of Accurate Representation
Map scale is expressed in various ways, each serving a specific purpose:
1. Verbal Scale: This straightforward method states the relationship between map distance and ground distance in words. For example, "1 centimeter on the map represents 10 kilometers on the ground."
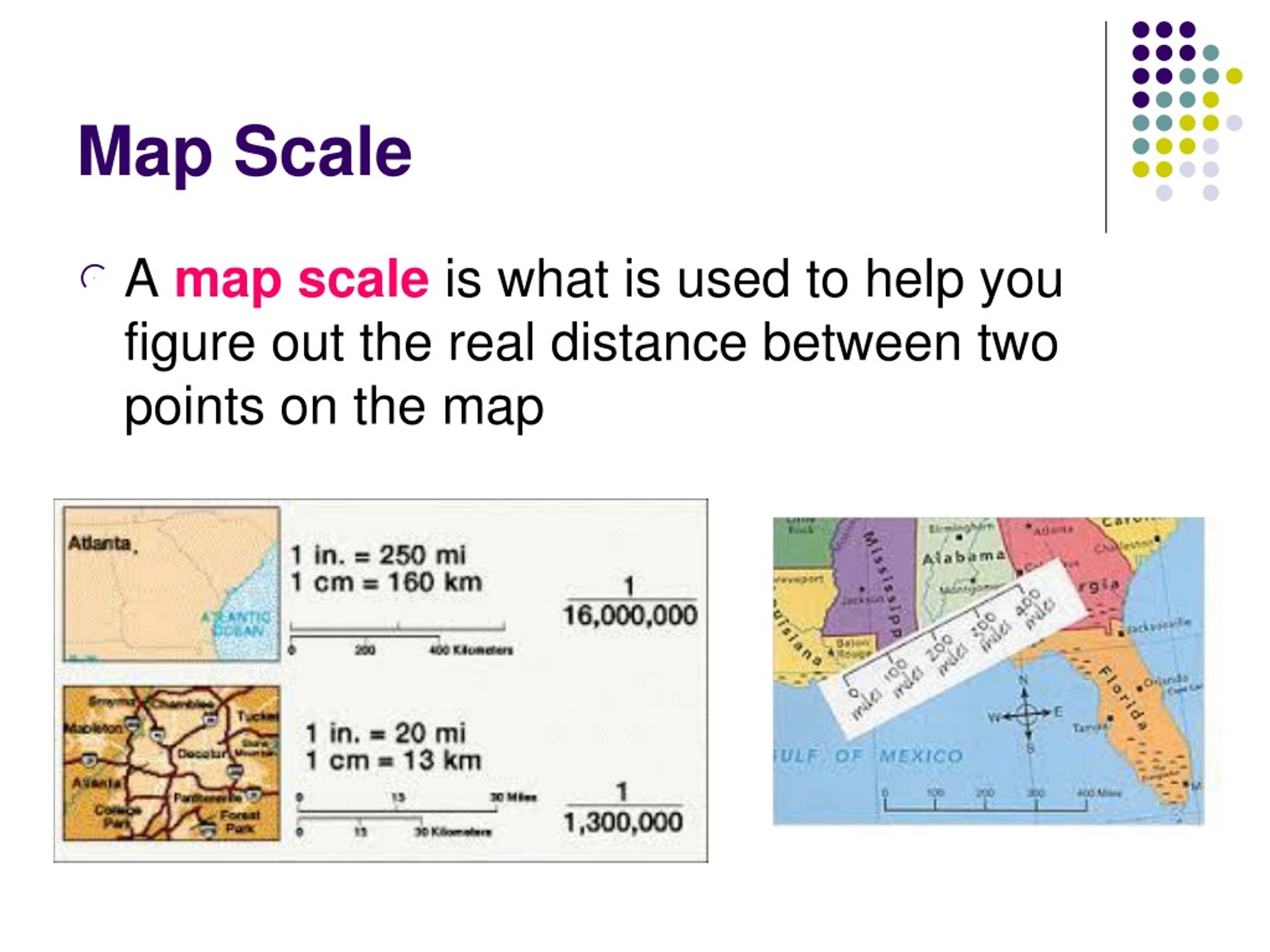
2. Representative Fraction (RF): RF expresses scale as a ratio, typically written as 1:100,000. This means one unit on the map represents 100,000 units on the ground. The units are usually the same (e.g., centimeters or inches).
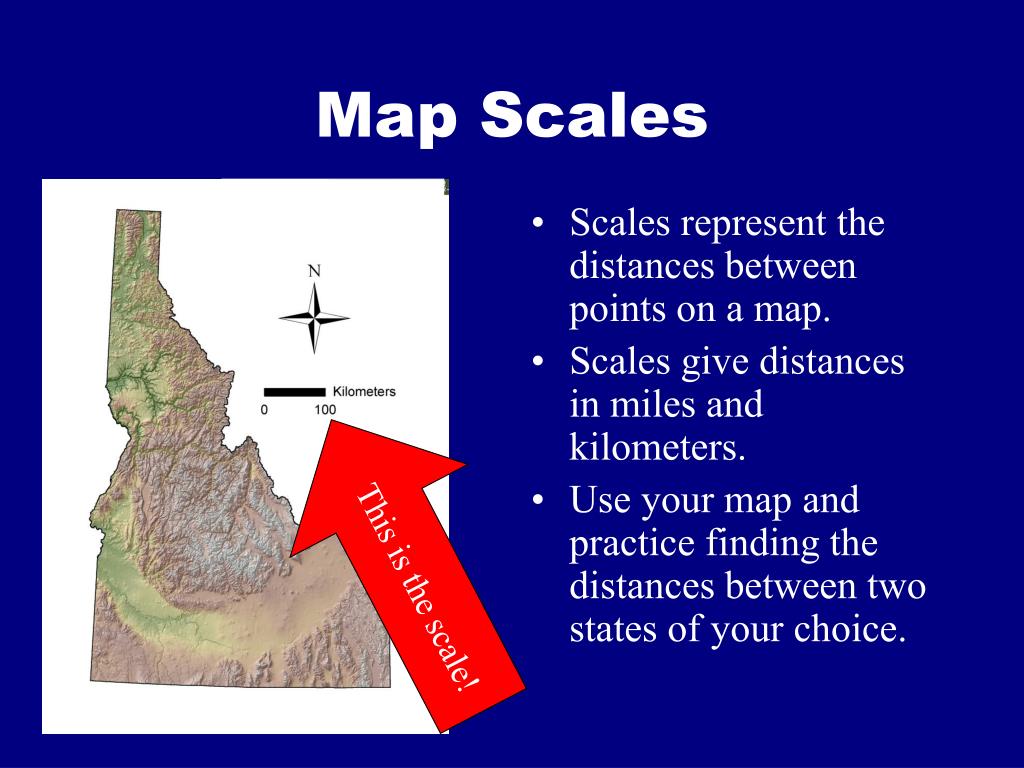
3. Graphic Scale: A graphic scale, often referred to as a bar scale, provides a visual representation of the map’s scale. It consists of a line divided into segments, each representing a specific distance on the ground.
Choosing the Right Scale:
The choice of scale depends on the map’s purpose. For detailed maps depicting small areas like city plans, a large scale (e.g., 1:10,000) is appropriate. Conversely, maps showcasing vast regions like countries require a smaller scale (e.g., 1:10,000,000) to accommodate the larger area.
Drawing a Scale on a Map: A Step-by-Step Guide
Drawing a scale on a map is a crucial step in ensuring its accuracy and usability. Here’s a detailed guide:
1. Determine the Map’s Purpose and Scope:
Before drawing a scale, consider the map’s intended use. This will determine the appropriate scale and the level of detail required. For example, a map for hiking needs a larger scale than a map for planning a road trip.
2. Choose a Scale:
Select a suitable scale based on the map’s purpose and scope. Refer to existing maps or consult with cartographers for guidance.
3. Calculate the Scale Bar Length:
Once the scale is chosen, determine the length of the scale bar. This involves converting the chosen scale to the map’s units. For example, if the chosen scale is 1:100,000 and the map uses centimeters, the scale bar length for 1 kilometer (100,000 centimeters) would be 1 centimeter.
4. Draw the Scale Bar:
Using a ruler or other measuring tool, draw a straight line representing the scale bar. Divide the line into segments corresponding to the desired distance units (e.g., kilometers, miles).
5. Label the Scale Bar:
Clearly label the scale bar segments with the corresponding distances on the ground. For example, "1 km," "2 km," etc.
**6. Add a





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Importance of Scale in Maps: A Comprehensive Guide to Drawing a Scale. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!
