The Saskatchewan River: A Lifeline Across the Canadian Prairies
Related Articles: The Saskatchewan River: A Lifeline Across the Canadian Prairies
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to The Saskatchewan River: A Lifeline Across the Canadian Prairies. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Saskatchewan River: A Lifeline Across the Canadian Prairies
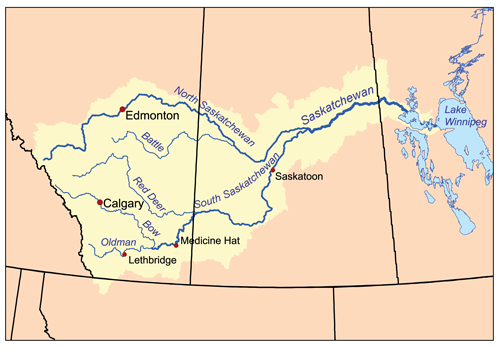
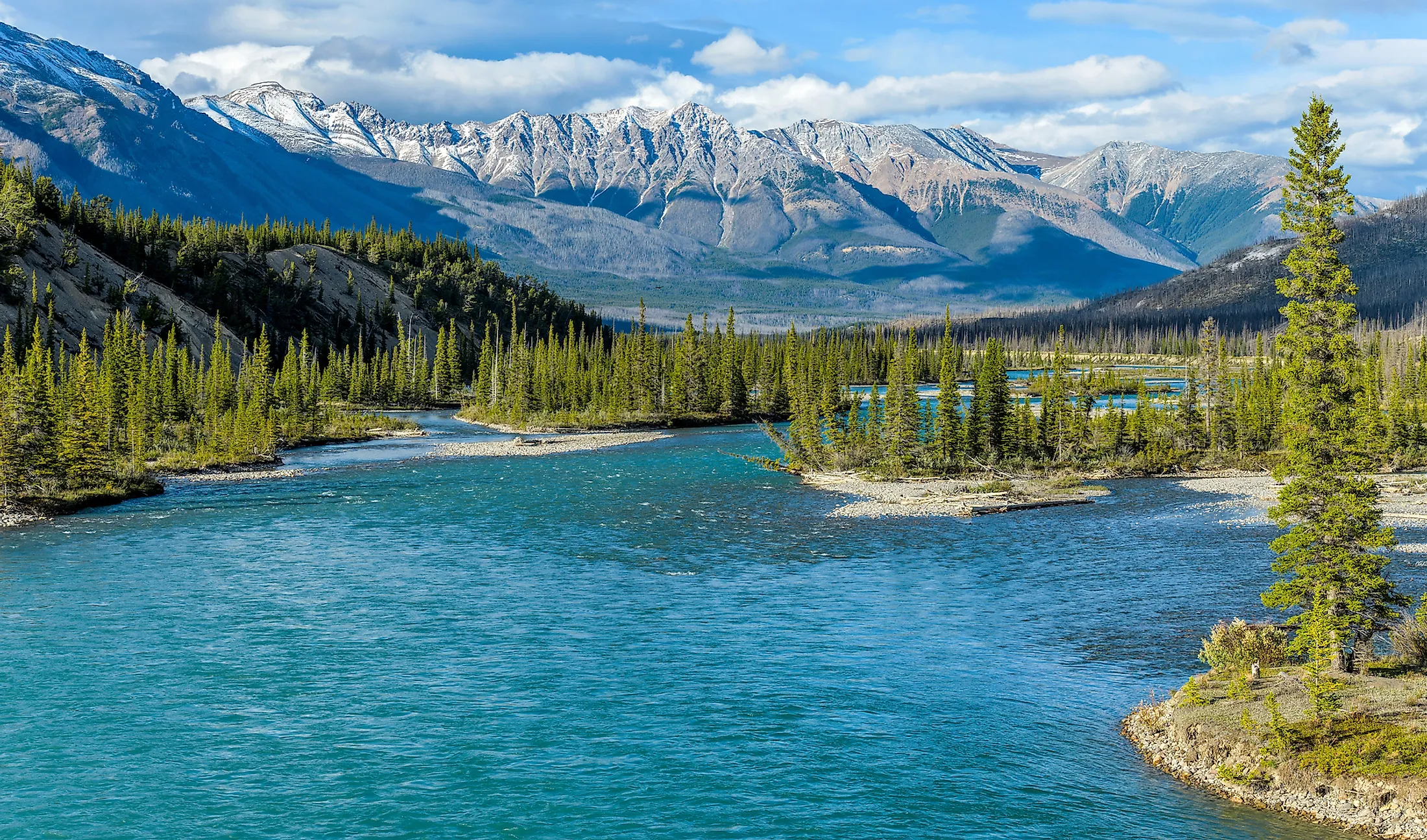
The Saskatchewan River, a majestic waterway snaking through the heart of Canada’s prairies, plays a vital role in the region’s history, ecology, and economy. This article delves into the river’s geography, its significance to the surrounding environment and human communities, and its historical and contemporary importance.
A River’s Journey: From Source to Mouth
The Saskatchewan River, the longest river in Canada entirely within its borders, is formed by the confluence of the North Saskatchewan and South Saskatchewan rivers near Prince Albert, Saskatchewan. These two branches, themselves substantial waterways, rise in the Canadian Rockies and traverse the prairies, carving their paths through diverse landscapes.
The North Saskatchewan River: Originating in the Columbia Icefield in Alberta, the North Saskatchewan River flows eastward for over 1,287 kilometers, winding through the Rocky Mountains, foothills, and prairies. Along its course, it receives contributions from numerous tributaries, including the Bow River and the Red Deer River, both significant waterways in their own right.
The South Saskatchewan River: The South Saskatchewan River originates in the Cypress Hills of southwestern Saskatchewan, a region known for its unique geological formations and rich biodiversity. It flows eastward for over 1,392 kilometers, traversing through the prairies and receiving water from tributaries such as the Oldman River and the Bow River.
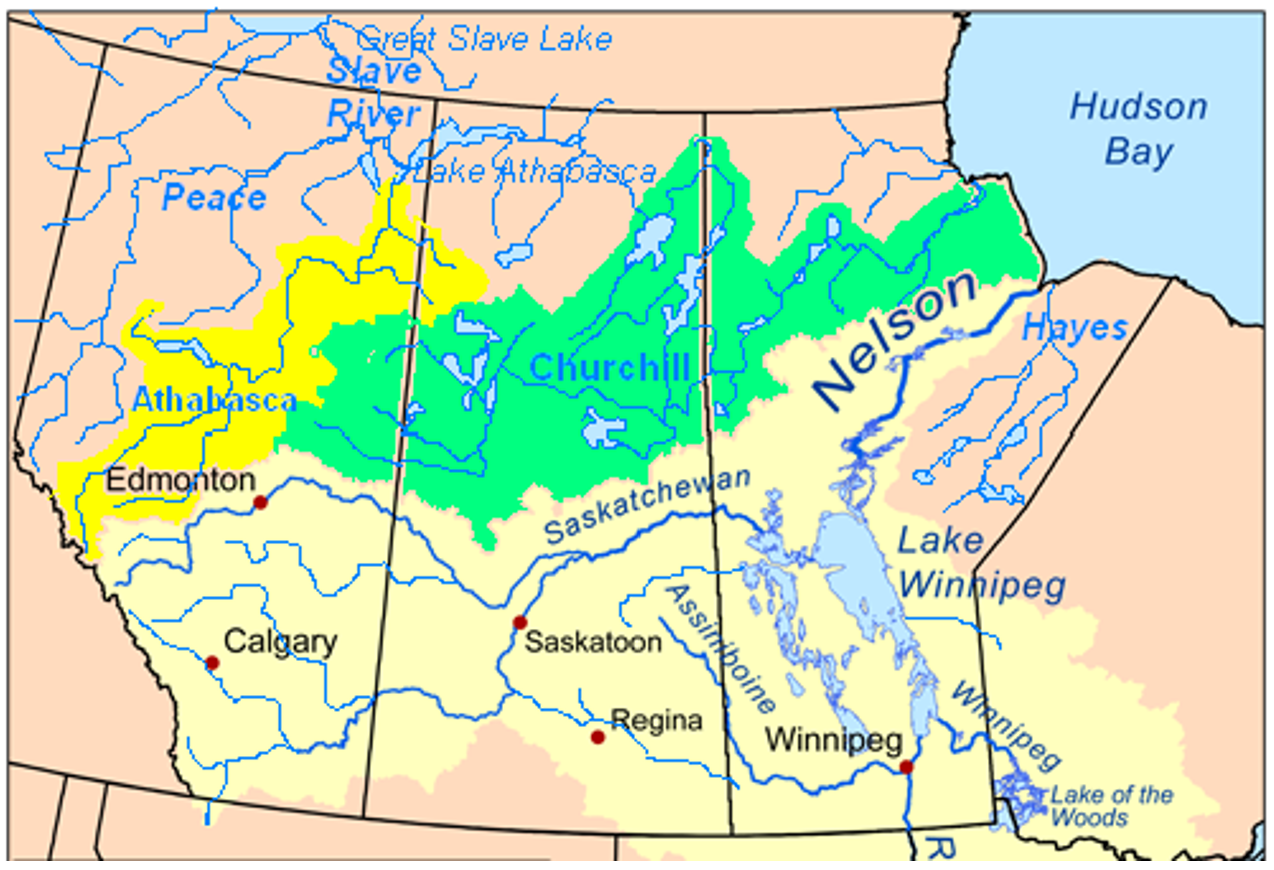
The Saskatchewan River Proper: After their confluence, the Saskatchewan River flows northward for over 1,500 kilometers, eventually emptying into Lake Winnipeg in Manitoba. The river’s journey through the prairies is marked by significant changes in its character. In its upper reaches, the river is often narrow and swift, flowing through rugged canyons and rolling hills. As it progresses eastward, it widens, becoming a more meandering waterway, traversing through vast grasslands and agricultural fields.
A Vital Ecosystem: The River’s Role in the Environment
The Saskatchewan River is more than just a waterway; it is a vital ecosystem supporting a diverse range of flora and fauna. Its banks provide habitat for numerous species of birds, mammals, fish, and reptiles, while its waters nourish a rich network of wetlands, grasslands, and forests.
Biodiversity and Conservation: The river’s ecosystem supports a wide variety of life, including migratory birds like geese, ducks, and sandpipers; mammals like beaver, muskrat, and deer; and fish like walleye, pike, and trout. Its waters are also home to a diverse array of aquatic insects and plants, contributing to the overall health of the surrounding environment.
Water Quality and Management: The Saskatchewan River faces challenges related to water quality, particularly from agricultural runoff, industrial pollution, and urban development. Efforts to manage and protect the river’s ecosystem include water quality monitoring, conservation programs, and public awareness campaigns.
A Lifeline for Communities: The River’s Economic and Cultural Significance
The Saskatchewan River has played a crucial role in the development of the Canadian prairies. It served as a transportation route for Indigenous peoples, who relied on its resources for sustenance and trade. European settlers also recognized the river’s value, using it for transportation, agriculture, and industry.
Historical Significance: The Saskatchewan River played a crucial role in the fur trade, as early explorers and traders used it to access the interior of the continent. It was also a significant route for European settlement, with communities springing up along its banks.
Economic Importance: The river continues to be a vital resource for the region, providing water for irrigation, hydropower generation, and municipal use. It also supports a thriving fishing and tourism industry, attracting visitors from across Canada and beyond.
Cultural Significance: The Saskatchewan River holds deep cultural significance for Indigenous peoples, who have lived along its banks for centuries. It is a source of stories, traditions, and spiritual connection, playing a vital role in their cultural identity.
Challenges and Opportunities: The River’s Future
The Saskatchewan River faces various challenges, including water scarcity, pollution, and climate change. However, it also presents opportunities for sustainable development, conservation, and community engagement.
Water Management: The river’s water resources are increasingly being stressed by growing populations, industrial development, and the effects of climate change. Effective water management strategies are crucial to ensure the river’s sustainability.
Pollution Control: Agricultural runoff, industrial discharge, and urban development contribute to water pollution, affecting the river’s ecosystem and human health. Continued efforts to reduce pollution and improve water quality are essential.
Climate Change: Climate change is impacting the river’s flow, temperature, and water quality. Adaptation strategies are needed to mitigate these effects and ensure the river’s long-term health.
Community Engagement: Public awareness and community engagement are crucial for the river’s protection and sustainable management. By working together, communities can ensure the river’s health for generations to come.
FAQs about the Saskatchewan River
Q: What is the length of the Saskatchewan River?
A: The Saskatchewan River is approximately 1,900 kilometers long, making it the longest river in Canada entirely within its borders.
Q: What are the major tributaries of the Saskatchewan River?
A: The major tributaries of the Saskatchewan River include the North Saskatchewan River, the South Saskatchewan River, the Bow River, the Red Deer River, and the Oldman River.
Q: What are the main cities located on the Saskatchewan River?
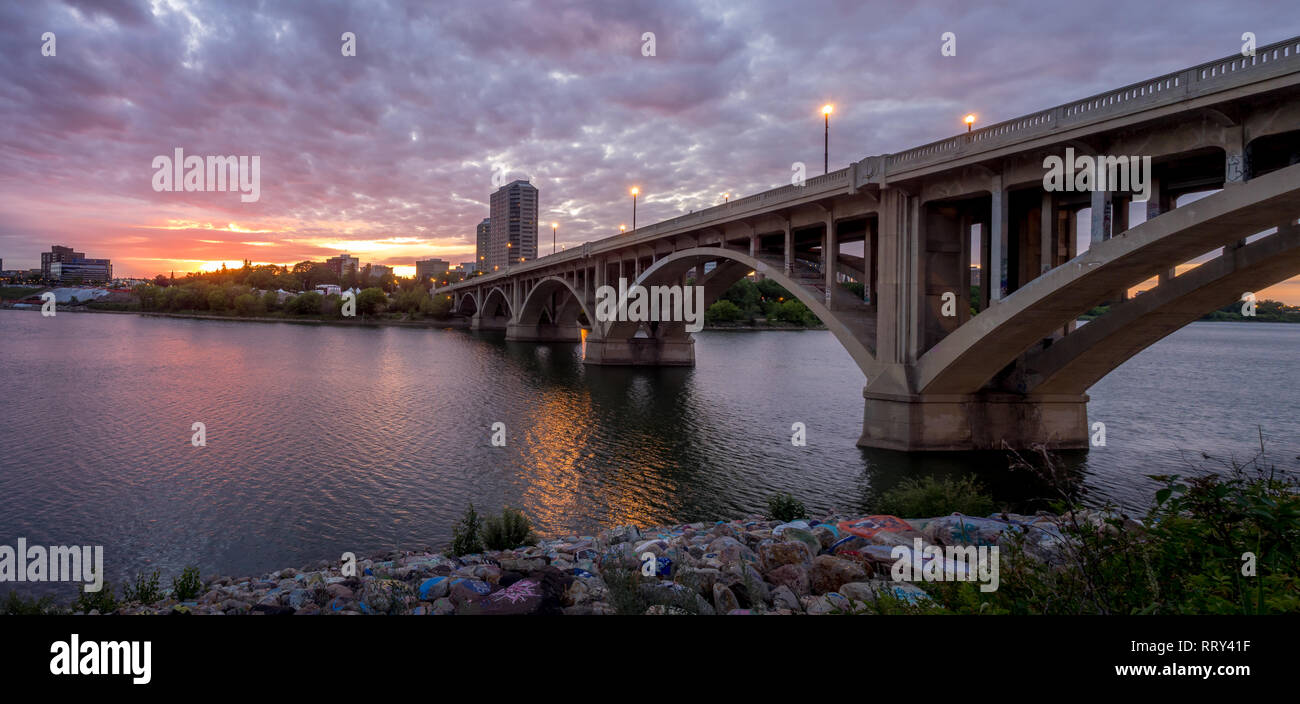
A: Major cities located on the Saskatchewan River include Prince Albert, Saskatoon, and North Battleford in Saskatchewan, and Winnipeg in Manitoba.
Q: What are the main economic activities associated with the Saskatchewan River?
A: The main economic activities associated with the Saskatchewan River include agriculture, hydropower generation, fishing, tourism, and transportation.
Q: What are some of the environmental challenges facing the Saskatchewan River?
A: The Saskatchewan River faces challenges related to water quality, including agricultural runoff, industrial pollution, and urban development. Climate change is also impacting the river’s flow, temperature, and water quality.
Tips for Exploring the Saskatchewan River
1. Visit Prince Albert National Park: This park offers stunning views of the Saskatchewan River, as well as opportunities for hiking, camping, fishing, and wildlife viewing.
2. Explore Saskatoon: The city of Saskatoon is located on the banks of the Saskatchewan River and offers a variety of attractions, including museums, art galleries, and parks.
3. Go Fishing: The Saskatchewan River is known for its excellent fishing, with species like walleye, pike, and trout.
4. Take a River Cruise: Several companies offer river cruises on the Saskatchewan River, providing a unique perspective on the surrounding landscape.
5. Learn about the River’s History: Visit historical sites along the river, such as Fort Carlton and Batoche, to learn about the region’s rich history.
Conclusion
The Saskatchewan River is a vital lifeline for the Canadian prairies, providing water, supporting ecosystems, and enriching the lives of countless people. Its history is interwoven with the stories of Indigenous peoples, European settlers, and modern communities. The river’s future is inextricably linked to the challenges and opportunities facing the region. By understanding the river’s significance, we can work together to ensure its health and sustainability for generations to come.







Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Saskatchewan River: A Lifeline Across the Canadian Prairies. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!
