The Virginia-Maryland Border: A Historical and Geographical Tapestry
Related Articles: The Virginia-Maryland Border: A Historical and Geographical Tapestry
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to The Virginia-Maryland Border: A Historical and Geographical Tapestry. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Virginia-Maryland Border: A Historical and Geographical Tapestry
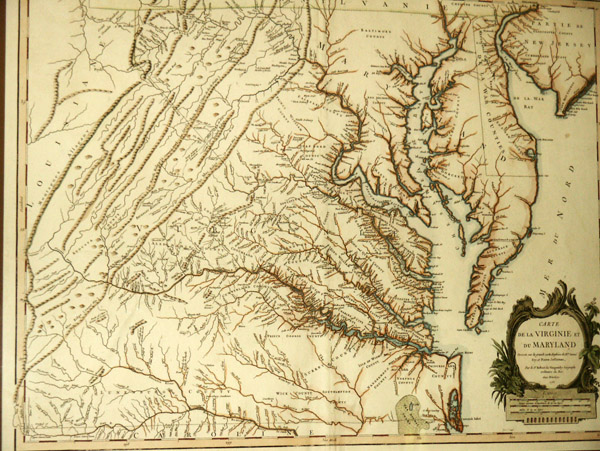
The border between Virginia and Maryland, a seemingly simple line on a map, is a complex and fascinating entity. It is a historical artifact, a geographical boundary, and a dynamic space that has witnessed centuries of change and interaction. This article delves into the intricate details of the Virginia-Maryland border, exploring its origins, evolution, and present-day significance.
Historical Origins: A Story of Compromise and Conflict
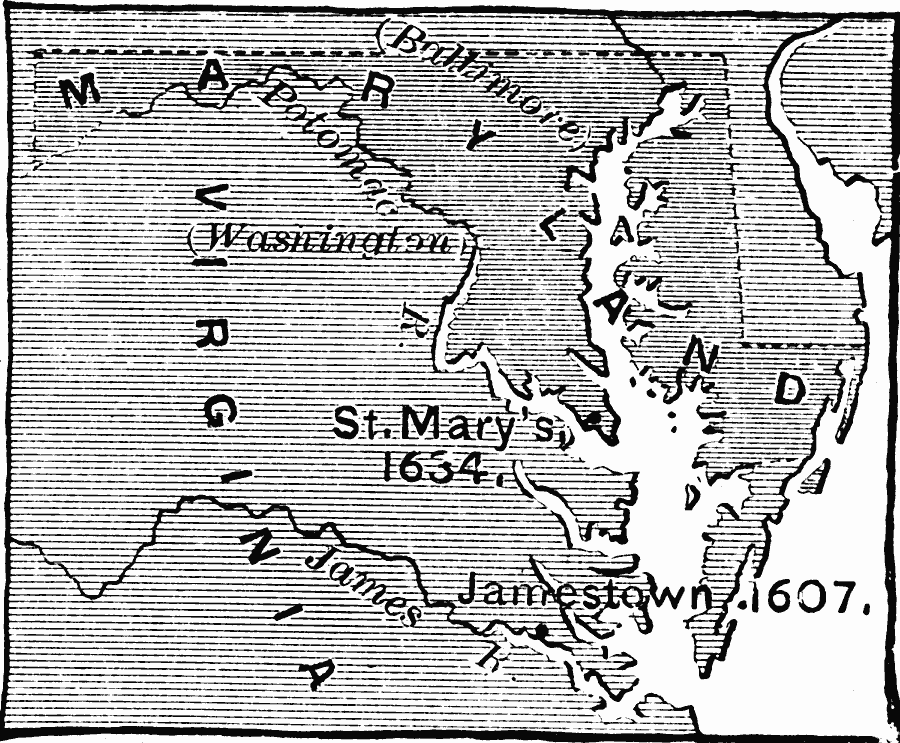
The Virginia-Maryland border is a product of colonial history, shaped by competing claims, negotiated boundaries, and evolving political realities. Its origins can be traced back to the early 17th century, when English colonists began establishing settlements in the Chesapeake Bay region.
-
Early Grants and Disputes: The Virginia Company of London received a charter in 1606, granting it vast territory in North America. This territory encompassed land that would later become both Virginia and Maryland. However, the charter lacked precise boundaries, leading to disputes over land ownership.
-
The Maryland Charter: In 1632, King Charles I granted a charter to Lord Baltimore, establishing the Province of Maryland. This charter also lacked precise boundaries, but it explicitly stated that the northern boundary of Maryland would be a line drawn "from the furthest head of the Bay of Chesapeake, and to the furthest head of the Bay of Delaware." This vague description set the stage for future conflicts.
-
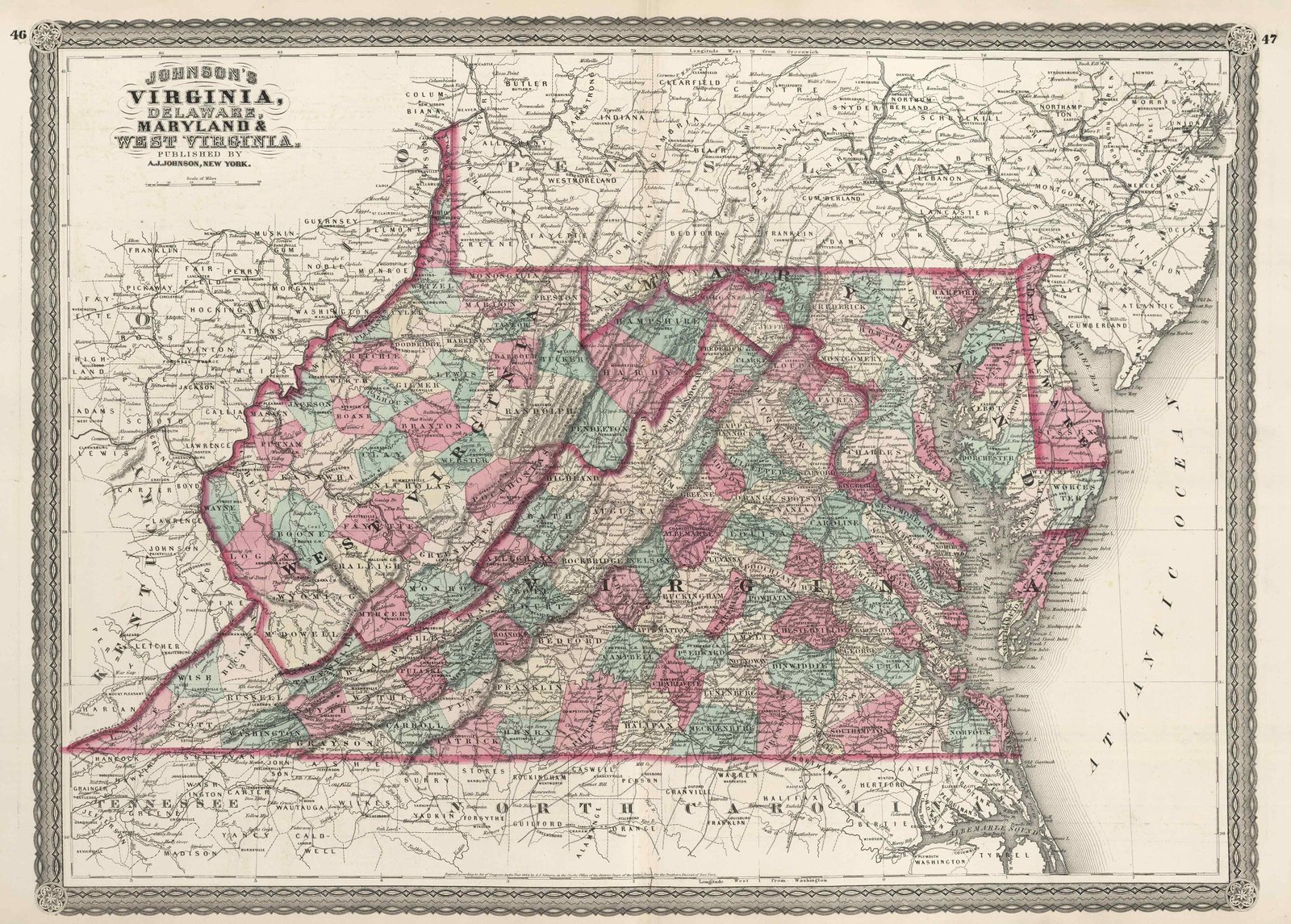
The Mason-Dixon Line: The most significant event in defining the Virginia-Maryland border was the establishment of the Mason-Dixon Line. In 1767, Charles Mason and Jeremiah Dixon, two English surveyors, were commissioned by the proprietors of Pennsylvania and Maryland to resolve a boundary dispute. Their work established a precise line running westward from the Delaware River to the westernmost point of Maryland. This line became the official boundary between Pennsylvania and Maryland, but it also served as the northern boundary of Virginia, effectively resolving the long-standing disputes.
The Border’s Evolution: A Dynamic Landscape
The Virginia-Maryland border is not a static entity but a dynamic landscape that has evolved over time. Its shape has been influenced by various factors, including geographical features, political changes, and economic developments.
-
The Potomac River: The Potomac River, a major waterway flowing through the region, plays a crucial role in defining the border. Its course, with its meanders and tributaries, shapes the intricate line that separates the two states.
-
Boundary Adjustments: Throughout history, there have been adjustments to the border based on surveys, legal rulings, and negotiated agreements. For instance, in 1791, a small portion of land near the city of Alexandria was transferred from Virginia to the District of Columbia.
-
Economic and Social Changes: The border has witnessed significant economic and social changes, including the rise of major cities, the development of transportation infrastructure, and the shifting patterns of population movement. These changes have influenced the character of the border region and its inhabitants.
The Border’s Significance: A Tapestry of Interdependence
The Virginia-Maryland border is not merely a geographical boundary; it is a vital link between two states with intertwined histories, cultures, and economies.
-
Economic Interdependence: The two states share a close economic relationship, with businesses and industries operating across the border. The Washington, D.C., metropolitan area, which spans both Virginia and Maryland, is a major economic engine, providing jobs and opportunities for residents of both states.
-
Cultural Exchange: The border fosters cultural exchange, as residents of both states interact and share traditions, customs, and values. The region is home to numerous historical sites, museums, and cultural institutions that celebrate the shared heritage of Virginia and Maryland.
-
Environmental Collaboration: The border region faces shared environmental challenges, such as air and water pollution, which require cooperation between the two states. Environmental agencies in Virginia and Maryland work together to address these issues and protect the natural resources of the region.
FAQs about the Virginia-Maryland Border
Q: What is the longest point of the Virginia-Maryland border?
A: The longest point of the Virginia-Maryland border is along the Potomac River, extending approximately 125 miles.
Q: What is the significance of the Mason-Dixon Line in the context of the Virginia-Maryland border?
A: The Mason-Dixon Line, originally established as the boundary between Pennsylvania and Maryland, also served as the northern boundary of Virginia. It played a crucial role in resolving long-standing boundary disputes and defining the geographical relationship between the three states.
Q: How does the Virginia-Maryland border impact the lives of residents in the region?
A: The border impacts residents in various ways, including their access to employment, healthcare, education, and cultural opportunities. It also influences their daily lives, as they may cross the border for shopping, entertainment, or commuting.
Q: What are some of the challenges facing the Virginia-Maryland border region?
A: The border region faces challenges such as environmental degradation, traffic congestion, and economic disparities. These challenges require collaboration between the two states to find solutions.
Tips for Exploring the Virginia-Maryland Border
-
Visit historical sites: Explore historical sites along the border, such as Mount Vernon, George Washington’s estate in Virginia, or the Annapolis State House in Maryland.
-
Enjoy outdoor recreation: Hike, bike, or kayak along the Potomac River, or visit the numerous parks and forests in the region.
-
Explore local towns and cities: Discover the unique charm of towns and cities along the border, such as Alexandria, Virginia, or Frederick, Maryland.
-
Attend cultural events: Attend festivals, concerts, and other cultural events that celebrate the shared heritage of Virginia and Maryland.
Conclusion
The Virginia-Maryland border is a complex and fascinating entity, a testament to the intertwined history, geography, and culture of two states. It is a dynamic landscape that continues to evolve, shaped by economic forces, environmental challenges, and the ongoing interactions of its residents. Understanding the Virginia-Maryland border provides valuable insights into the history, present, and future of this vital region.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Virginia-Maryland Border: A Historical and Geographical Tapestry. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!
