Unlocking the Energy Potential: A Comprehensive Guide to the US Oil and Gas Basins Map
Related Articles: Unlocking the Energy Potential: A Comprehensive Guide to the US Oil and Gas Basins Map
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Unlocking the Energy Potential: A Comprehensive Guide to the US Oil and Gas Basins Map. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unlocking the Energy Potential: A Comprehensive Guide to the US Oil and Gas Basins Map
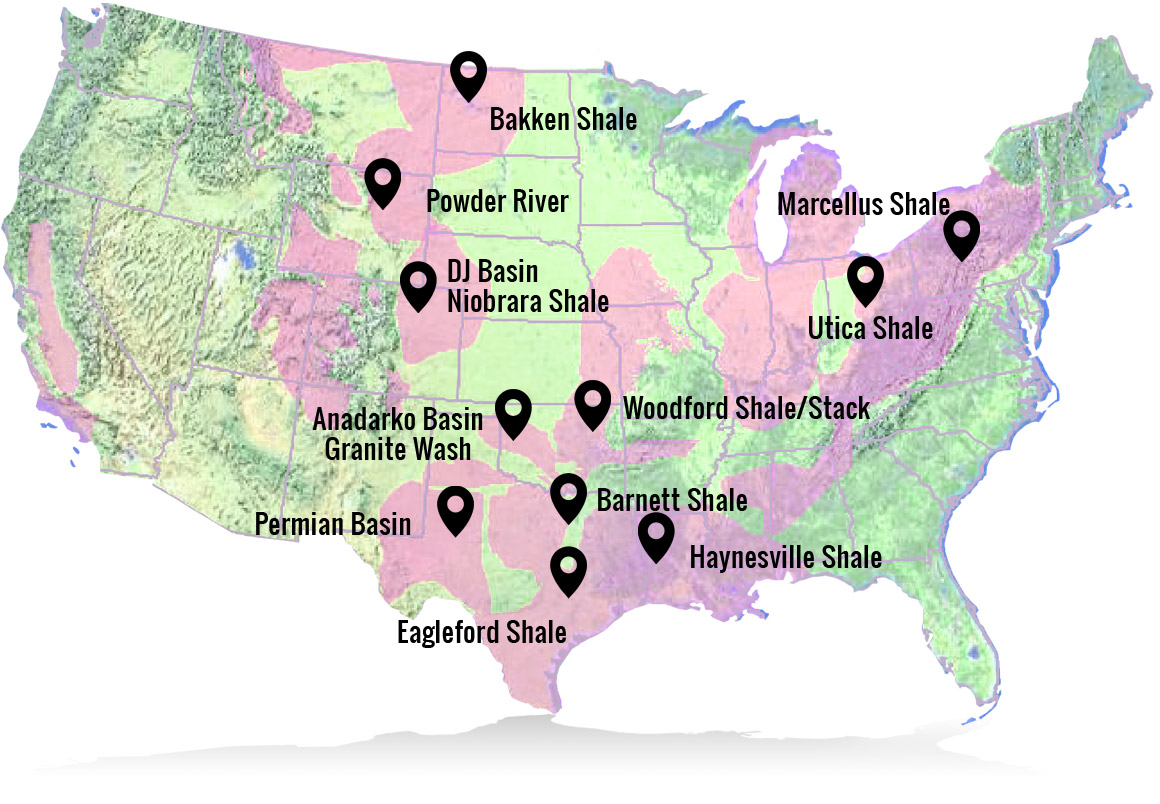
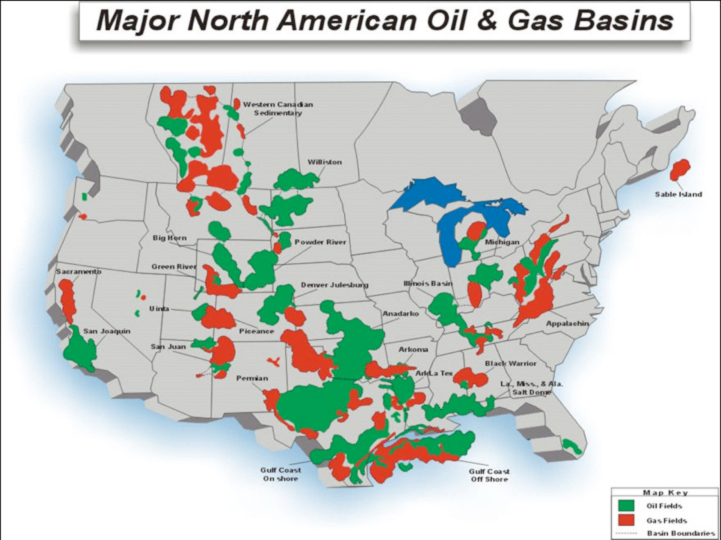
The United States, a global energy powerhouse, boasts a vast and complex geological landscape that has yielded significant oil and natural gas reserves. Understanding the distribution of these resources is crucial for policymakers, investors, and industry professionals alike. The US Oil and Gas Basins Map serves as an indispensable tool, providing a visual representation of the nation’s hydrocarbon potential and its associated geological structures.
Delving into the Depths: Exploring the US Oil and Gas Basins
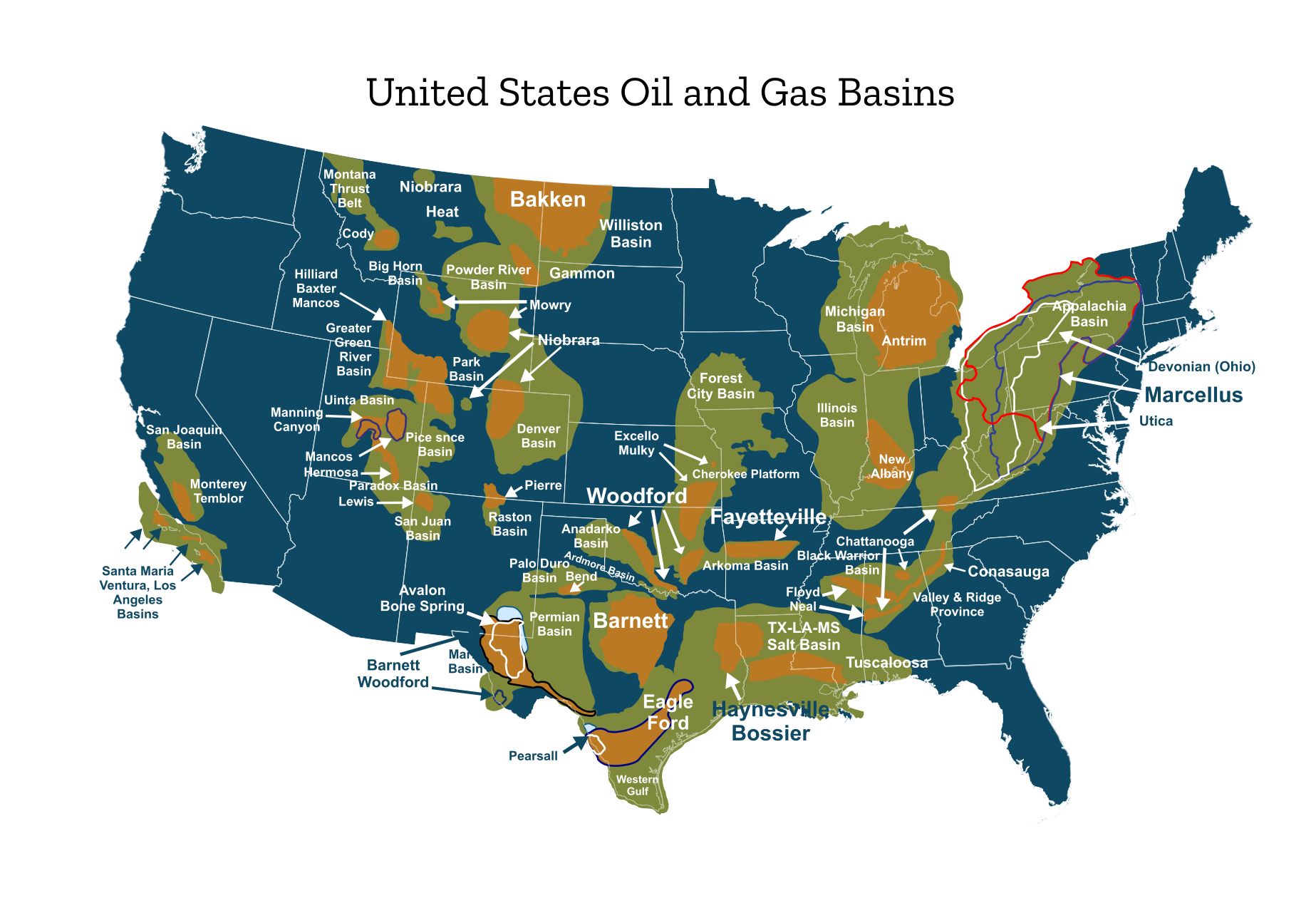
The US Oil and Gas Basins Map is a visual depiction of the various geological formations, known as basins, that hold significant hydrocarbon reserves. These basins are formed over millions of years through tectonic activity and sedimentation, creating environments conducive to the accumulation of organic matter, which eventually transforms into oil and natural gas.
A Mosaic of Basins: Key Features and Significance
The map reveals a diverse array of basins across the United States, each possessing unique characteristics that influence their hydrocarbon potential. Key features include:
- Location: Basins are geographically distributed across various regions, from the coastal plains to the Rocky Mountains.
- Geological Age: The age of a basin dictates the type and maturity of its hydrocarbons. Older basins typically contain more mature hydrocarbons, while younger basins may hold lighter, less mature resources.
- Sedimentary Rocks: The type and thickness of sedimentary rocks within a basin influence the potential for hydrocarbon accumulation.
- Source Rocks: These rocks are rich in organic matter that transforms into oil and gas over time.
- Reservoir Rocks: These porous and permeable rocks trap and store hydrocarbons.
- Traps: Geological structures that prevent hydrocarbons from migrating further, allowing them to accumulate in commercially viable quantities.
Navigating the Map: Understanding the Key Basins
The US Oil and Gas Basins Map highlights several major basins that contribute significantly to the nation’s energy production:
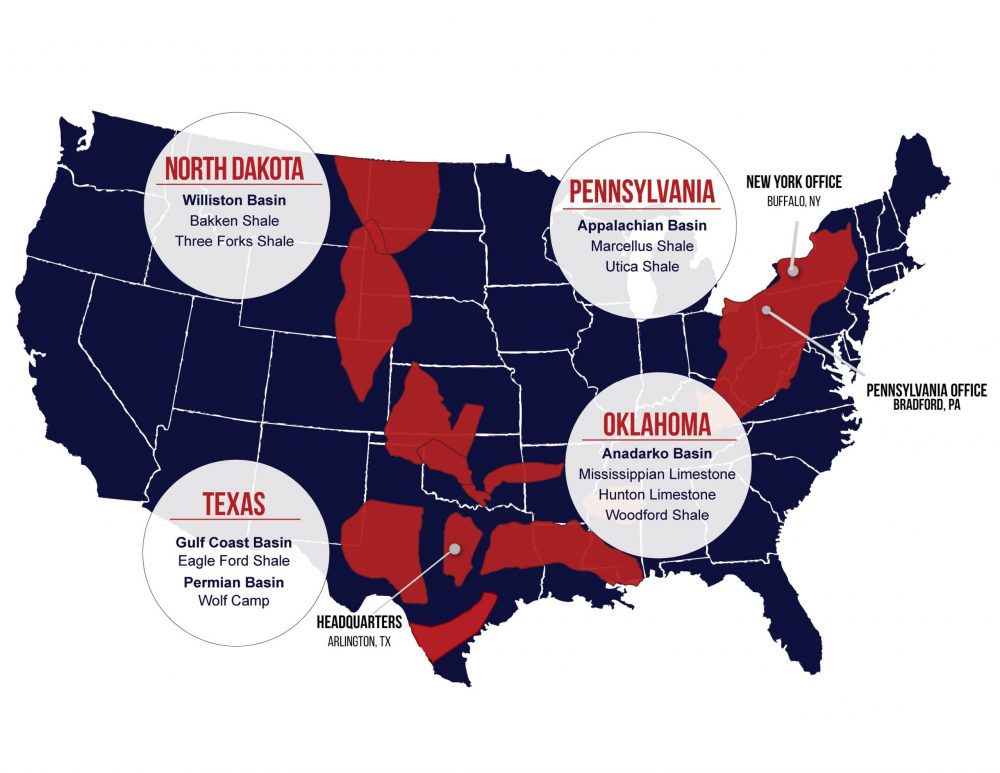
- Permian Basin (Texas and New Mexico): Known for its prolific shale formations, particularly the Permian Basin is a leading source of oil and natural gas in the United States.
- Appalachian Basin (Pennsylvania, West Virginia, and Ohio): This basin is historically significant for its natural gas production, particularly from Marcellus Shale.
- Williston Basin (North Dakota, Montana, and Saskatchewan, Canada): This basin is a major producer of oil, particularly from the Bakken Shale.
- Anadarko Basin (Oklahoma, Texas, and Kansas): This basin is a major source of both oil and natural gas, with significant production from the Woodford Shale.
- San Juan Basin (New Mexico and Colorado): This basin is known for its natural gas production, primarily from the San Juan Basin Coalbed Methane play.
- Gulf of Mexico: This offshore basin is a significant producer of oil and natural gas, with numerous discoveries and ongoing exploration activities.
Beyond the Map: Exploring the Benefits and Importance
The US Oil and Gas Basins Map serves as a valuable resource for a variety of purposes:
- Resource Assessment: The map provides a clear visualization of the nation’s hydrocarbon potential, assisting in identifying areas with the most promising reserves.
- Exploration and Development: The map guides exploration efforts by highlighting areas with favorable geological conditions for hydrocarbon accumulation.
- Production Planning: Understanding the characteristics of different basins helps optimize production strategies and maximize resource recovery.
- Policymaking: The map provides critical data for policymakers to develop energy strategies, address environmental concerns, and ensure energy security.
- Investment Decisions: The map assists investors in making informed decisions about allocating capital to promising oil and gas projects.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: What is the difference between an oil basin and a gas basin?
A: While some basins may produce both oil and gas, there are distinctions. Oil basins typically contain source rocks that generate oil, while gas basins contain source rocks that generate natural gas. The specific geological conditions and the maturity of the hydrocarbons determine the dominant type of resource.
Q: How are new oil and gas basins discovered?
A: New basins are discovered through a combination of geological studies, seismic surveys, and exploratory drilling. Scientists analyze geological data, including rock samples, seismic images, and well logs, to identify potential hydrocarbon-bearing structures. Exploratory drilling is then used to confirm the presence of hydrocarbons and assess their commercial viability.
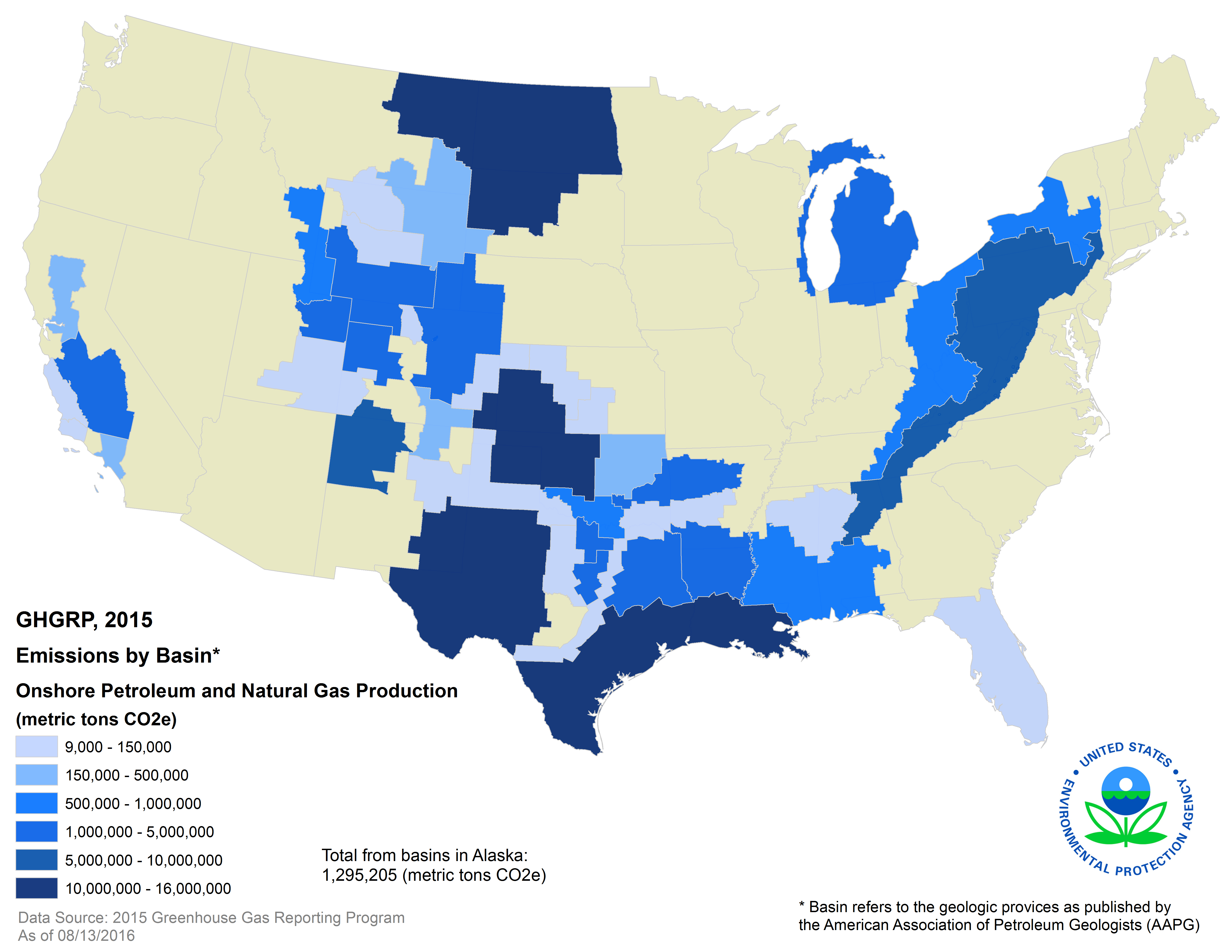
Q: What are the environmental concerns associated with oil and gas production?
A: Oil and gas production can have environmental impacts, including air and water pollution, habitat destruction, and greenhouse gas emissions. Responsible exploration and production practices, such as minimizing waste, using advanced technologies, and adhering to environmental regulations, are crucial to mitigate these impacts.
Q: What are the future prospects for oil and gas exploration in the United States?
A: The future of oil and gas exploration in the United States is dependent on a variety of factors, including technological advancements, regulatory policies, and global energy demand. While the United States remains a major producer of oil and natural gas, the industry is facing challenges related to declining production from mature fields, environmental concerns, and the transition to renewable energy sources.
Tips for Utilizing the US Oil and Gas Basins Map
- Focus on Specific Regions: The map provides a broad overview, but it’s essential to focus on specific regions of interest for detailed analysis.
- Consider Geological Data: Combine the map with geological data, such as seismic surveys and well logs, to gain a deeper understanding of the basin’s characteristics.
- Evaluate Environmental Impacts: Assess potential environmental impacts associated with oil and gas development in specific basins.
- Stay Informed about Industry Trends: Monitor industry trends, technological advancements, and regulatory changes that may influence oil and gas exploration and production.
Conclusion
The US Oil and Gas Basins Map is a vital tool for understanding the nation’s hydrocarbon resources and guiding responsible exploration and development. By providing a visual representation of geological formations and their potential, the map empowers policymakers, investors, and industry professionals to make informed decisions that balance energy needs with environmental sustainability. As the United States continues to navigate the evolving energy landscape, the US Oil and Gas Basins Map will remain a critical resource for unlocking the nation’s energy potential while ensuring a responsible and sustainable future.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unlocking the Energy Potential: A Comprehensive Guide to the US Oil and Gas Basins Map. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!
