Unmasking the Global Threat: A Comprehensive Look at Rabies Maps
Related Articles: Unmasking the Global Threat: A Comprehensive Look at Rabies Maps
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Unmasking the Global Threat: A Comprehensive Look at Rabies Maps. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unmasking the Global Threat: A Comprehensive Look at Rabies Maps

Rabies, a viral disease transmitted through the saliva of infected animals, poses a significant public health threat worldwide. Understanding the geographical distribution of rabies cases is crucial for implementing effective prevention and control strategies. This is where rabies maps come into play, serving as powerful tools to visualize and analyze the global landscape of rabies transmission.
Decoding the Rabies Map: A Visual Guide to Understanding Transmission
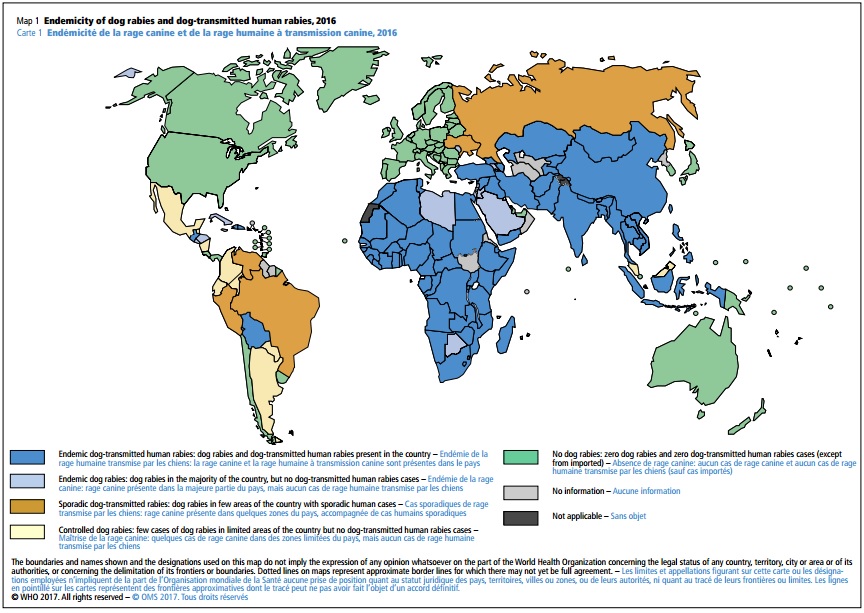
Rabies maps are visual representations of the geographical distribution of rabies cases, typically depicted on a world map or regional maps. These maps provide a clear and concise overview of the areas where rabies is endemic, sporadic, or absent. They utilize color-coding or other visual cues to indicate the prevalence of rabies in different regions, offering a snapshot of the global rabies situation.
Types of Rabies Maps and Their Significance
Several types of rabies maps are used to understand the complex dynamics of rabies transmission:
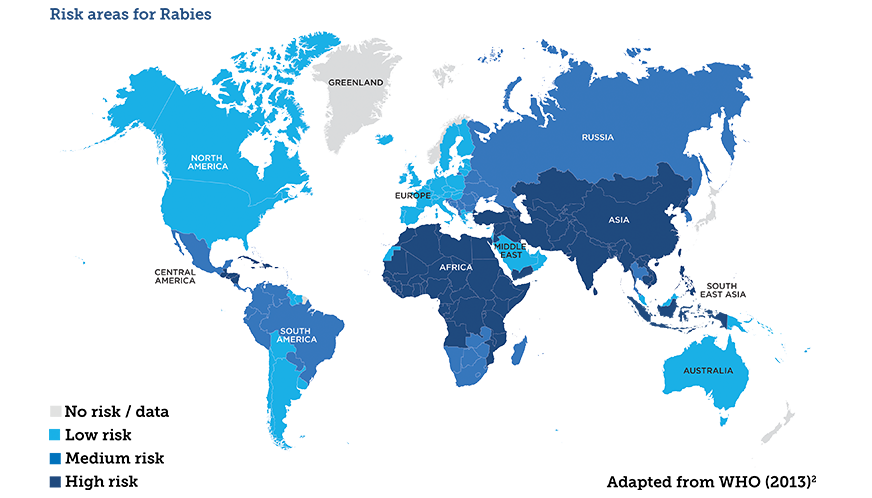
- Global Rabies Maps: These maps provide a broad overview of the global distribution of rabies, highlighting areas with high, medium, and low incidence rates. They are particularly useful for identifying high-risk regions and guiding international collaborations for rabies control.
- Regional Rabies Maps: Focusing on specific regions or countries, these maps offer a more detailed understanding of rabies transmission patterns within a specific geographic area. They help identify local hotspots, track the spread of rabies outbreaks, and inform targeted intervention strategies.
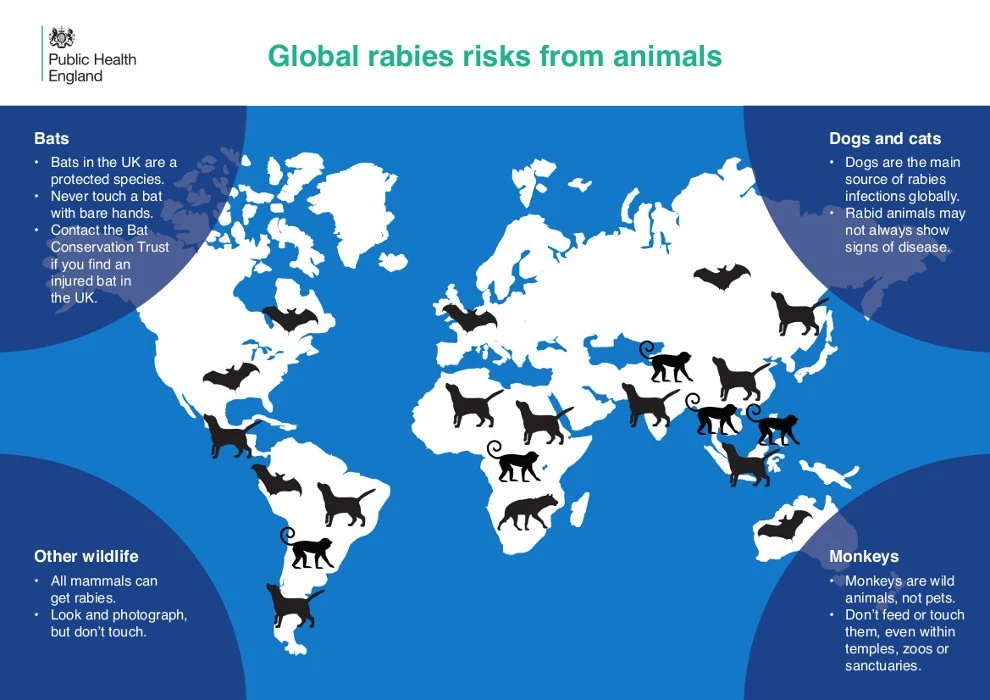
- Species-Specific Rabies Maps: These maps illustrate the distribution of rabies in specific animal species, such as dogs, bats, or foxes. They are essential for understanding the role of different animal reservoirs in rabies transmission and developing effective control programs targeting specific animal populations.
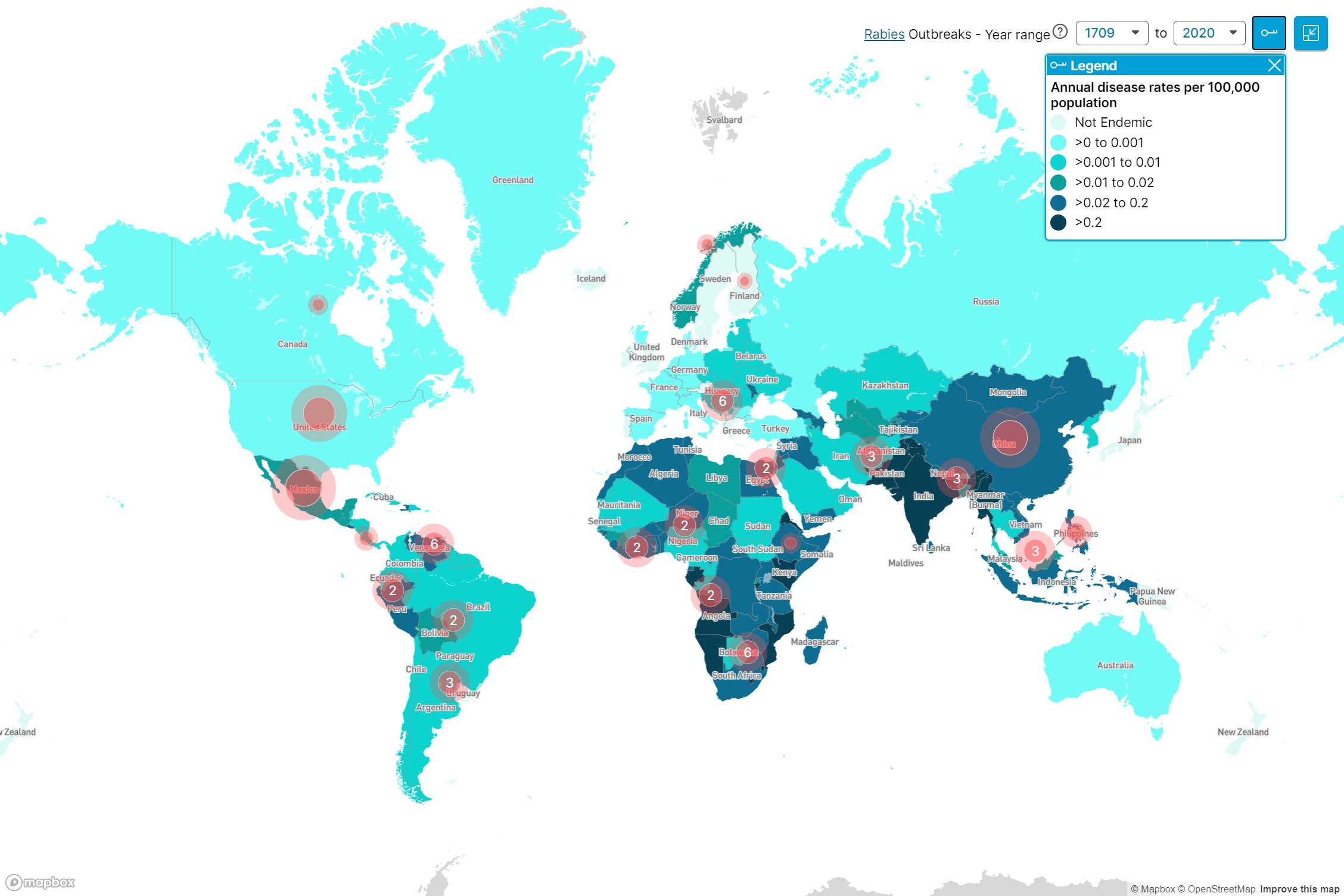
- Temporal Rabies Maps: These maps track the temporal trends in rabies incidence over time, providing insights into the evolution of rabies transmission patterns. They are crucial for identifying potential outbreaks, monitoring the effectiveness of control measures, and predicting future trends.
Beyond Visuals: The Importance of Rabies Maps in Public Health
Rabies maps are not merely visual representations; they serve as vital tools for public health decision-making and intervention strategies. Their significance lies in their ability to:
- Identify High-Risk Areas: Rabies maps pinpoint areas with high rabies incidence, allowing for targeted resource allocation and intervention programs to focus on regions most susceptible to the disease.
- Monitor Disease Spread: By tracking the temporal and spatial distribution of rabies cases, these maps help monitor the spread of the disease, identify potential outbreaks, and guide public health responses.
- Evaluate Control Measures: Rabies maps provide valuable data for evaluating the effectiveness of rabies control programs, such as vaccination campaigns, animal population control, and public awareness initiatives.
- Inform Policy Development: The insights derived from rabies maps can inform policy decisions, including resource allocation for rabies control programs, development of national rabies control strategies, and international collaborations for combating the disease.
The Power of Data: Leveraging Rabies Maps for Informed Action
Rabies maps are powerful tools for visualizing and understanding the global rabies situation. They provide crucial insights into disease distribution, transmission patterns, and the effectiveness of control measures. By leveraging the data presented in these maps, public health officials, researchers, and policymakers can make informed decisions, implement targeted interventions, and ultimately work towards eliminating rabies as a public health threat.
FAQs: Addressing Common Questions about Rabies Maps
Q: How are rabies maps created?
A: Rabies maps are created using data collected from various sources, including:
- Surveillance data: This includes reports of confirmed rabies cases in humans and animals from national and international health organizations.
- Animal population data: Information on the distribution and density of different animal species, particularly those known to carry rabies, is crucial for understanding rabies transmission patterns.
- Environmental data: Factors such as climate, vegetation, and human population density can influence rabies transmission, and this data is incorporated into rabies maps.
Q: What are the limitations of rabies maps?
A: While rabies maps offer valuable insights, they also have limitations:
- Data availability: The accuracy of rabies maps depends on the availability and reliability of data. In some regions, reporting and surveillance systems may be inadequate, leading to incomplete or inaccurate data.
- Reporting biases: Reporting biases can occur, with some areas having higher reporting rates than others, potentially skewing the perceived rabies distribution.
- Spatial resolution: Rabies maps often have limited spatial resolution, meaning they may not accurately reflect the distribution of rabies at the local level.
- Dynamic nature of rabies: Rabies transmission patterns can change rapidly due to factors such as animal movement, environmental changes, and vaccination efforts. Rabies maps may not always capture these dynamic shifts in real-time.
Q: How can I access rabies maps?
A: Rabies maps are available from various sources, including:
- World Health Organization (WHO): The WHO maintains a global rabies map and provides data on rabies incidence worldwide.
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC): The CDC provides rabies maps for the United States and specific regions.
- National and regional health organizations: Many countries and regions have their own rabies maps available on government websites or through public health agencies.
- Research institutions: Universities and research organizations involved in rabies research often publish and share their own rabies maps.
Tips for Using Rabies Maps Effectively
- Consider the source: Always check the source of the rabies map and ensure it is a reliable and up-to-date source.
- Understand the data: Familiarize yourself with the data used to create the map, including the time period covered, data sources, and limitations.
- Use caution with interpretation: Rabies maps provide a general overview, and it’s important to avoid over-interpreting the data or drawing conclusions based on limited information.
- Combine with other information: Rabies maps should be considered alongside other relevant information, such as animal population data, vaccination coverage, and environmental factors, for a comprehensive understanding of rabies transmission.
Conclusion: A Call for Action
Rabies maps are powerful tools for visualizing and understanding the global rabies situation. They provide crucial insights into disease distribution, transmission patterns, and the effectiveness of control measures. By leveraging the data presented in these maps, public health officials, researchers, and policymakers can make informed decisions, implement targeted interventions, and ultimately work towards eliminating rabies as a public health threat. It is crucial to continue investing in research, surveillance, and control programs, and to use the information provided by rabies maps to guide our efforts towards a world free from rabies.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unmasking the Global Threat: A Comprehensive Look at Rabies Maps. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!
