Unveiling Brazil’s Climate Tapestry: A Comprehensive Guide to its Diverse Weather Patterns
Related Articles: Unveiling Brazil’s Climate Tapestry: A Comprehensive Guide to its Diverse Weather Patterns
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Unveiling Brazil’s Climate Tapestry: A Comprehensive Guide to its Diverse Weather Patterns. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Unveiling Brazil’s Climate Tapestry: A Comprehensive Guide to its Diverse Weather Patterns
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Unveiling Brazil’s Climate Tapestry: A Comprehensive Guide to its Diverse Weather Patterns
- 3.1 A Mosaic of Climates: Understanding Brazil’s Diverse Weather Patterns
- 3.2 Beyond the Basics: Delving Deeper into Brazil’s Climate
- 3.3 The Significance of Understanding Brazil’s Climate
- 3.4 FAQs about Brazil’s Climate
- 3.5 Tips for Adapting to Brazil’s Climate
- 3.6 Conclusion: Embracing the Climate Tapestry of Brazil
- 4 Closure
Unveiling Brazil’s Climate Tapestry: A Comprehensive Guide to its Diverse Weather Patterns

Brazil, a nation of vast geographical expanse and diverse ecosystems, experiences a wide range of climatic conditions. Understanding the country’s climate is crucial for various sectors, from agriculture and tourism to infrastructure development and environmental conservation. This comprehensive guide delves into the intricate tapestry of Brazil’s climate, exploring its defining characteristics, regional variations, and the vital role it plays in shaping the country’s landscape and human activities.
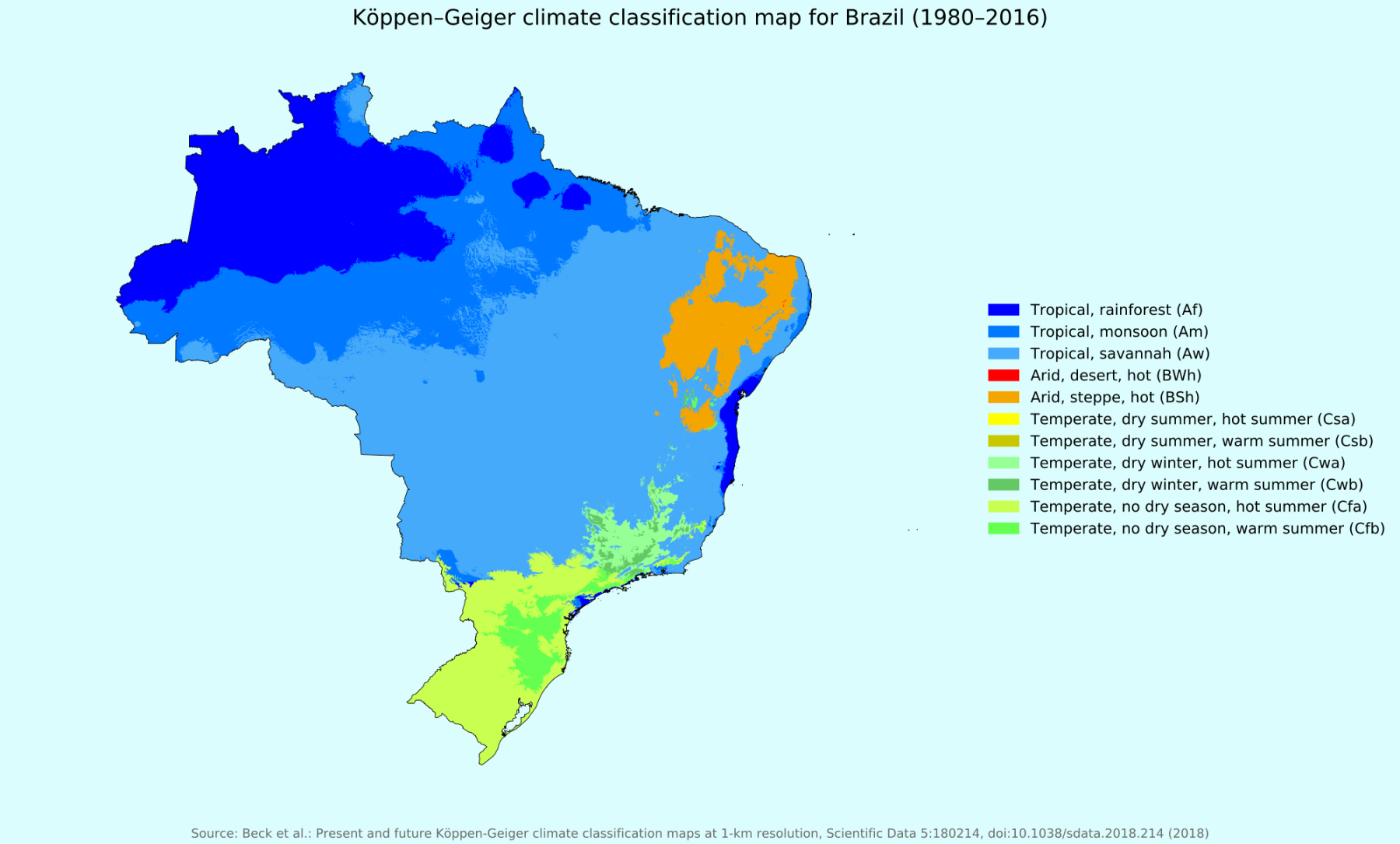
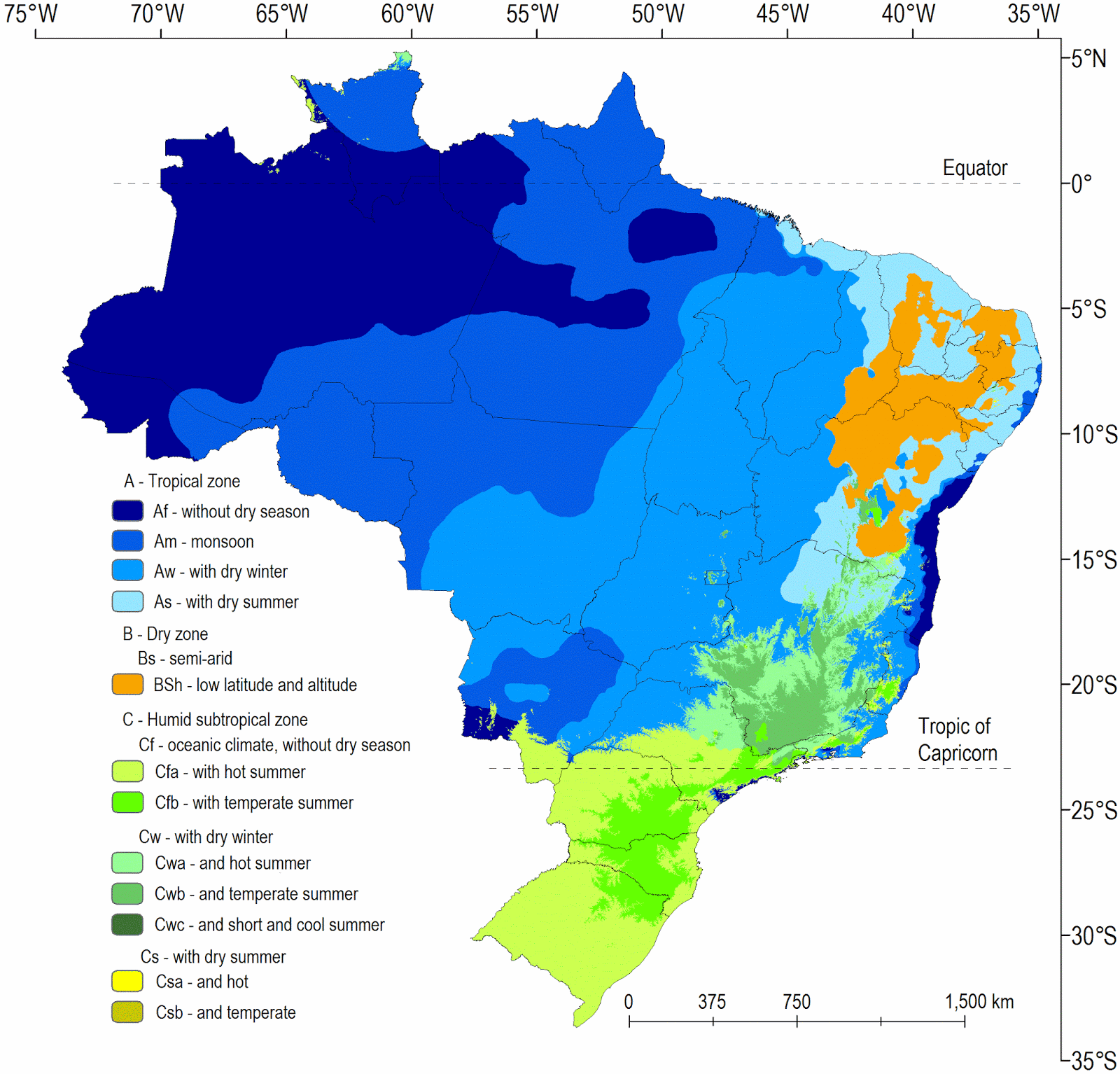
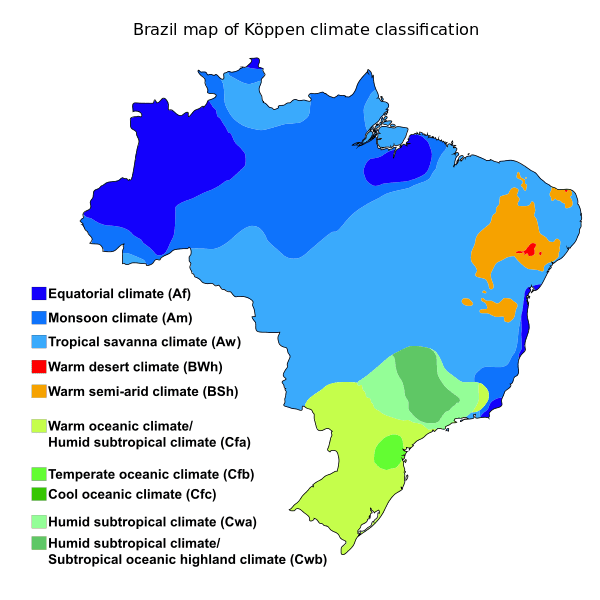
A Mosaic of Climates: Understanding Brazil’s Diverse Weather Patterns
Brazil’s climate is primarily influenced by its geographical location straddling the equator and its extensive coastline along the Atlantic Ocean. These factors contribute to a dynamic interplay of air masses, creating a mosaic of distinct climate zones across the country.
1. Equatorial Climate: Dominating the Amazon Basin, this climate is characterized by consistently high temperatures, abundant rainfall throughout the year, and high humidity. The region experiences minimal temperature fluctuations, with average temperatures hovering around 25°C (77°F).
2. Tropical Climate: This climate prevails along the Brazilian coast, extending from the northeast to the south. It is characterized by warm temperatures year-round, with distinct wet and dry seasons. The wet season, typically from October to May, brings heavy rainfall, while the dry season, from June to September, experiences lower precipitation.
3. Semi-Arid Climate: Found primarily in the northeastern region of the country, this climate is characterized by low rainfall, high temperatures, and a distinct dry season that can extend for several months. This region is susceptible to drought, which can have significant implications for agriculture and water resources.
4. Temperate Climate: This climate occurs in the southernmost regions of Brazil, primarily in the states of Rio Grande do Sul and Santa Catarina. It is characterized by four distinct seasons, with cool winters and warm summers. Rainfall is relatively evenly distributed throughout the year.
5. Highland Climate: Brazil’s mountainous regions, particularly in the Serra do Mar and Serra da Mantiqueira, experience a highland climate. This climate is characterized by lower temperatures than surrounding lowlands, with cooler nights and cooler summers. Rainfall is abundant in these regions, contributing to the formation of lush forests and unique ecosystems.
Beyond the Basics: Delving Deeper into Brazil’s Climate
Understanding Brazil’s climate requires examining factors beyond its broad climate zones. Key factors influencing regional variations include:
- Altitude: As elevation increases, temperatures decrease, leading to cooler climates in mountainous regions compared to lowlands.
- Ocean Currents: The Brazilian Current, a warm current flowing along the country’s east coast, influences the climate of coastal regions, bringing warmer temperatures and higher humidity.
- Latitude: Brazil’s vast geographical expanse across different latitudes contributes to variations in solar radiation, leading to differences in temperature and precipitation patterns.
- Relief: The country’s diverse topography, including mountains, valleys, and plateaus, influences airflow patterns and precipitation distribution.
- Vegetation: Forests, grasslands, and other vegetation types play a role in regulating local climate by influencing evapotranspiration rates and reflecting solar radiation.
The Significance of Understanding Brazil’s Climate
Understanding Brazil’s climate is crucial for various reasons:
1. Agriculture: Knowledge of climate patterns is essential for farmers to select appropriate crops, plan irrigation schedules, and mitigate the impacts of extreme weather events.
2. Tourism: Climate information helps tourists choose the best time to visit different regions, ensuring optimal weather conditions for their activities.
3. Infrastructure Development: Climate data is vital for planning infrastructure projects, such as dams, roads, and airports, to ensure their resilience against extreme weather events.
4. Environmental Conservation: Understanding climate patterns is crucial for monitoring and managing ecosystems, protecting biodiversity, and mitigating the effects of climate change.
5. Public Health: Climate information helps health authorities prepare for and respond to heat waves, droughts, and other climate-related health risks.
FAQs about Brazil’s Climate
1. What are the average temperatures in Brazil?
Average temperatures vary significantly across Brazil, ranging from the high 20s to low 30s Celsius (80s to 90s Fahrenheit) in equatorial and tropical regions to the low 20s Celsius (70s Fahrenheit) in temperate regions.
2. What is the wettest region in Brazil?
The Amazon Basin, with its equatorial climate, receives the highest rainfall, averaging over 2,000 mm (79 inches) annually.
3. What is the driest region in Brazil?
The northeastern region, with its semi-arid climate, experiences the lowest rainfall, averaging less than 500 mm (20 inches) annually.
4. What are the most common natural disasters in Brazil?
Brazil is susceptible to various natural disasters, including floods, droughts, landslides, and wildfires.
5. How is climate change affecting Brazil?
Climate change is intensifying extreme weather events in Brazil, leading to more frequent and severe droughts, floods, and heat waves. These changes are impacting agriculture, water resources, and public health.
Tips for Adapting to Brazil’s Climate
1. Stay Hydrated: Drink plenty of water, especially during hot and humid weather.
2. Protect Yourself from the Sun: Wear sunscreen, hats, and sunglasses to prevent sunburn.
3. Dress Appropriately: Choose lightweight, breathable clothing during hot weather and layered clothing during cooler periods.
4. Be Aware of Extreme Weather Events: Stay informed about weather forecasts and take necessary precautions during storms, floods, or droughts.
5. Support Sustainable Practices: Choose eco-friendly products and support organizations working to mitigate climate change.
Conclusion: Embracing the Climate Tapestry of Brazil
Brazil’s climate is a defining feature of its landscape, shaping its biodiversity, influencing human activities, and presenting both challenges and opportunities. By understanding the complex interplay of factors that drive Brazil’s climate, we can better appreciate its unique characteristics and develop strategies for sustainable development, environmental conservation, and resilience in the face of climate change. This knowledge empowers us to navigate the diverse weather patterns of this extraordinary country, leveraging its climate assets for the benefit of its people and its environment.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling Brazil’s Climate Tapestry: A Comprehensive Guide to its Diverse Weather Patterns. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!
