Unveiling the Diverse Tapestry of Brazil’s Climate: A Comprehensive Guide
Related Articles: Unveiling the Diverse Tapestry of Brazil’s Climate: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the Diverse Tapestry of Brazil’s Climate: A Comprehensive Guide. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unveiling the Diverse Tapestry of Brazil’s Climate: A Comprehensive Guide
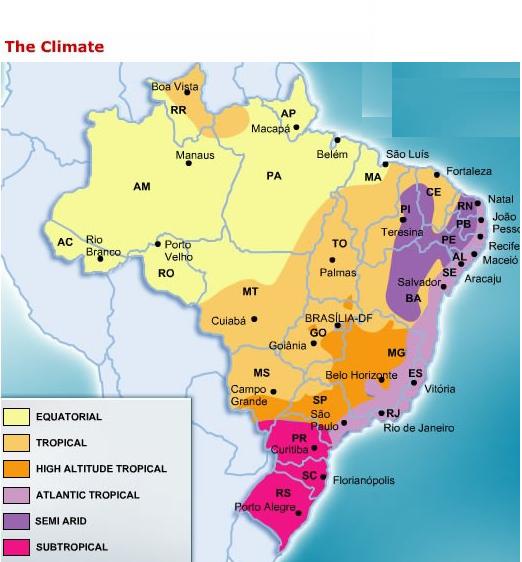
Brazil, a nation of vast geographical expanse and unparalleled biodiversity, boasts a captivating climate landscape as diverse as its natural wonders. Understanding this intricate climatic mosaic is essential for comprehending the nation’s ecological dynamics, agricultural potential, and societal development. This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of Brazil’s climate map, exploring its key characteristics, influencing factors, and implications.
A Symphony of Climates: Unveiling Brazil’s Diverse Climate Zones
Brazil’s climate is a captivating tapestry woven from diverse threads, encompassing a wide range of temperatures, rainfall patterns, and seasonal variations. The nation’s vast geographical expanse, spanning from the equator to the Tropic of Capricorn, and its diverse topography, from the Amazon rainforest to the towering Andes Mountains, contribute to this climatic complexity.
1. Equatorial Climate:
Dominating the Amazon Basin, the equatorial climate reigns supreme, characterized by consistently high temperatures and abundant rainfall throughout the year. This humid, tropical environment is conducive to the growth of lush rainforests, teeming with biodiversity.
2. Tropical Climate:
Stretching across much of Brazil’s eastern and central regions, the tropical climate exhibits distinct wet and dry seasons. The wet season, typically occurring during summer months, is characterized by heavy rainfall, while the dry season, during winter, experiences significantly lower precipitation. This climate supports a wide variety of vegetation, from savannahs to deciduous forests.
3. Semi-Arid Climate:
In northeastern Brazil, the semi-arid climate prevails, characterized by low rainfall and high temperatures, particularly during the dry season. This region experiences a distinct contrast between the dry and wet periods, with the latter marked by short, intense bursts of rain.
4. Temperate Climate:
Nestled in the southernmost part of Brazil, the temperate climate offers cooler temperatures and distinct seasons. This region experiences four distinct seasons, with relatively cold winters and warm summers, making it suitable for a diverse range of agricultural practices.
5. Subtropical Climate:
The southeastern region of Brazil, encompassing the state of São Paulo, exhibits a subtropical climate, characterized by warm temperatures and abundant rainfall. This climate supports a diverse range of ecosystems, including forests, grasslands, and coastal areas.
The Architects of Climate: Unraveling the Factors Shaping Brazil’s Climate
Several factors intertwine to create the intricate climate tapestry of Brazil:
1. Latitude:
Brazil’s location, straddling the equator and extending into the Southern Hemisphere, plays a pivotal role in determining its climate. The equatorial region experiences consistent sunlight and high temperatures throughout the year, leading to the prevalence of tropical and equatorial climates.
2. Altitude:
As elevation increases, temperatures generally decrease. This phenomenon is evident in Brazil’s mountainous regions, such as the Serra do Mar and the Andes Mountains, where cooler temperatures and higher rainfall prevail.
3. Ocean Currents:
The warm currents flowing along Brazil’s eastern coastline, such as the Brazil Current, influence the nation’s climate by moderating temperatures and increasing humidity.
4. Topography:
Brazil’s diverse topography, encompassing vast plains, towering mountains, and extensive river systems, creates distinct microclimates within different regions. The Amazon Basin, for instance, experiences a unique combination of high humidity and abundant rainfall due to its low elevation and dense vegetation.
5. Trade Winds:
The prevailing trade winds, blowing from the east across the Atlantic Ocean, bring moisture to Brazil’s eastern coast, contributing to the abundance of rainfall in this region.
The Impact of Climate: Shaping Brazil’s Landscape and Society
Brazil’s climate, a dynamic force shaping its natural environment and human activities, exerts a profound influence on various aspects of the nation’s life:
1. Biodiversity:
The diverse climate zones of Brazil support an unparalleled abundance of plant and animal life, contributing to the nation’s global reputation as a biodiversity hotspot. The Amazon rainforest, fueled by the equatorial climate, is a testament to this rich biodiversity.
2. Agriculture:
Brazil’s climate plays a crucial role in its agricultural sector, supporting a wide range of crops and livestock. The tropical climate, with its ample rainfall and warm temperatures, is ideal for growing coffee, sugarcane, soybeans, and other important agricultural commodities.
3. Water Resources:
Brazil’s climate, particularly its abundant rainfall, contributes to its vast water resources, including its extensive river systems and abundant groundwater reserves. These resources are essential for agriculture, industry, and human consumption.
4. Natural Disasters:
Brazil’s climate can also pose challenges, as it is prone to natural disasters such as droughts, floods, and landslides. These events can have significant impacts on agriculture, infrastructure, and human settlements.
5. Human Health:
Brazil’s climate can affect human health, with factors like humidity, temperature, and rainfall influencing the prevalence of certain diseases. The tropical climate, with its high humidity, can contribute to the spread of mosquito-borne diseases such as malaria and dengue fever.
Navigating the Climate Landscape: A Look at the Importance of Brazil’s Climate Map
Brazil’s climate map, a visual representation of the nation’s climatic zones and their defining characteristics, serves as a vital tool for understanding and managing the nation’s diverse climate landscape. It provides valuable insights into:
1. Agricultural Planning:
The climate map helps farmers identify suitable regions for growing specific crops, optimizing agricultural production and ensuring food security.
2. Infrastructure Development:
Understanding the climatic conditions of a region is essential for designing and constructing infrastructure, such as roads, bridges, and buildings, that can withstand extreme weather events.
3. Resource Management:
The climate map aids in managing water resources, ensuring their sustainable use and mitigating the risks of water scarcity or flooding.
4. Disaster Preparedness:
By identifying areas prone to natural disasters, the climate map enables authorities to develop effective disaster preparedness plans and mitigate the impact of extreme weather events.
5. Environmental Conservation:
The climate map is crucial for understanding the ecological dynamics of different regions, informing conservation efforts and promoting sustainable land management practices.
FAQs: Addressing Common Questions about Brazil’s Climate Map
1. What are the hottest and coldest regions in Brazil?
The hottest regions in Brazil are located in the interior of the Northeast and the Amazon Basin, where temperatures can reach over 40°C (104°F). The coldest regions are found in the southernmost part of the country, with temperatures dipping below freezing during winter.
2. How does Brazil’s climate compare to other countries in South America?
Compared to other South American countries, Brazil’s climate is characterized by its wide range of temperatures and rainfall patterns. The Amazon rainforest, for instance, experiences significantly higher rainfall than other regions in South America.
3. What are the main challenges posed by Brazil’s climate?
Brazil faces challenges such as droughts, floods, and landslides due to its diverse climate. These events can have significant impacts on agriculture, infrastructure, and human settlements.
4. How is climate change impacting Brazil?
Climate change is impacting Brazil in various ways, including increased temperatures, altered rainfall patterns, and rising sea levels. These changes pose significant challenges to agriculture, water resources, and biodiversity.
5. What are the key initiatives being undertaken to address climate change in Brazil?
Brazil is actively addressing climate change through initiatives such as promoting renewable energy sources, reducing deforestation, and implementing sustainable land management practices.
Tips for Understanding and Utilizing Brazil’s Climate Map
1. Explore the Map: Take the time to thoroughly examine the climate map, paying attention to the different climate zones and their defining characteristics.
2. Consult Resources: Utilize online resources, books, and articles to gain a deeper understanding of the factors influencing Brazil’s climate and the implications of different climatic zones.
3. Connect with Experts: Engage with climatologists, meteorologists, and other experts to gain insights into specific aspects of Brazil’s climate and its impact on different regions.
4. Analyze Data: Examine climate data, such as temperature, rainfall, and wind patterns, to gain a comprehensive understanding of the climatic dynamics of different regions.
5. Apply Knowledge: Use your knowledge of Brazil’s climate map to inform decision-making in various sectors, such as agriculture, infrastructure development, and environmental conservation.
Conclusion: Embracing the Diversity of Brazil’s Climate
Brazil’s climate map is a powerful tool for understanding the intricate tapestry of the nation’s climate, revealing its diverse zones, influencing factors, and profound impact on the environment, society, and economy. By recognizing the importance of this climatic mosaic, we can harness its strengths, mitigate its challenges, and foster sustainable development for a brighter future. As we delve deeper into the complexities of Brazil’s climate, we gain a deeper appreciation for the nation’s remarkable biodiversity, its agricultural potential, and its resilience in the face of environmental challenges.
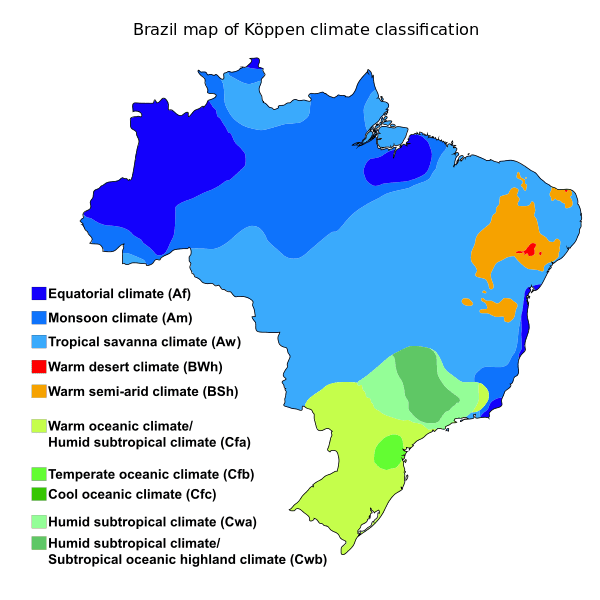




+7x10.jpg)
Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the Diverse Tapestry of Brazil’s Climate: A Comprehensive Guide. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!
