Unveiling the Power of Vector Maps: A Deep Dive into California’s Geographic Representation
Related Articles: Unveiling the Power of Vector Maps: A Deep Dive into California’s Geographic Representation
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the Power of Vector Maps: A Deep Dive into California’s Geographic Representation. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unveiling the Power of Vector Maps: A Deep Dive into California’s Geographic Representation
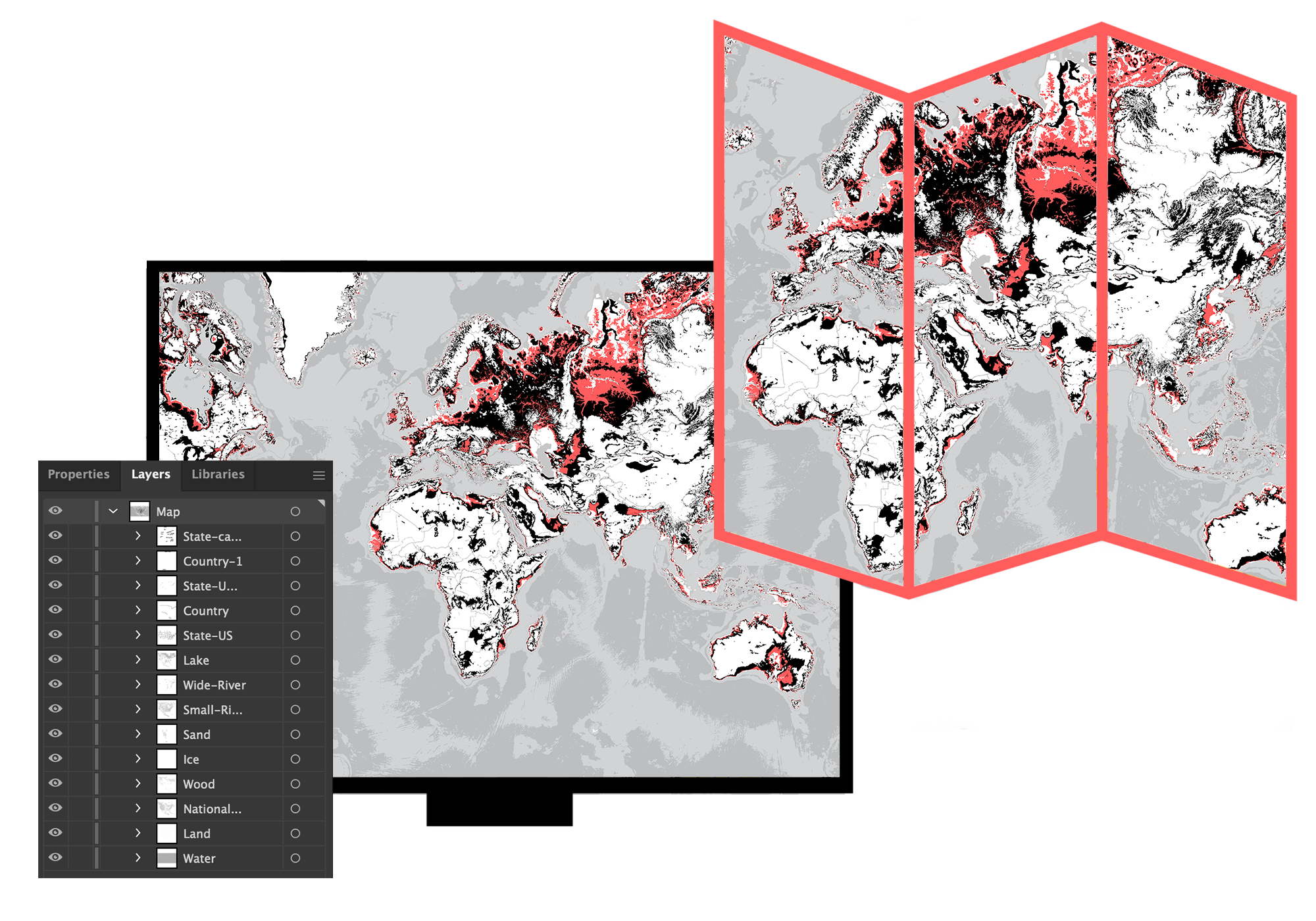
The state of California, with its diverse landscapes, bustling cities, and iconic landmarks, has long been a subject of fascination. Understanding its geography is crucial for a multitude of purposes, from urban planning and environmental management to tourism and historical research. This is where vector maps come into play, offering a powerful tool for visualizing and analyzing California’s intricate spatial data.
What are Vector Maps?
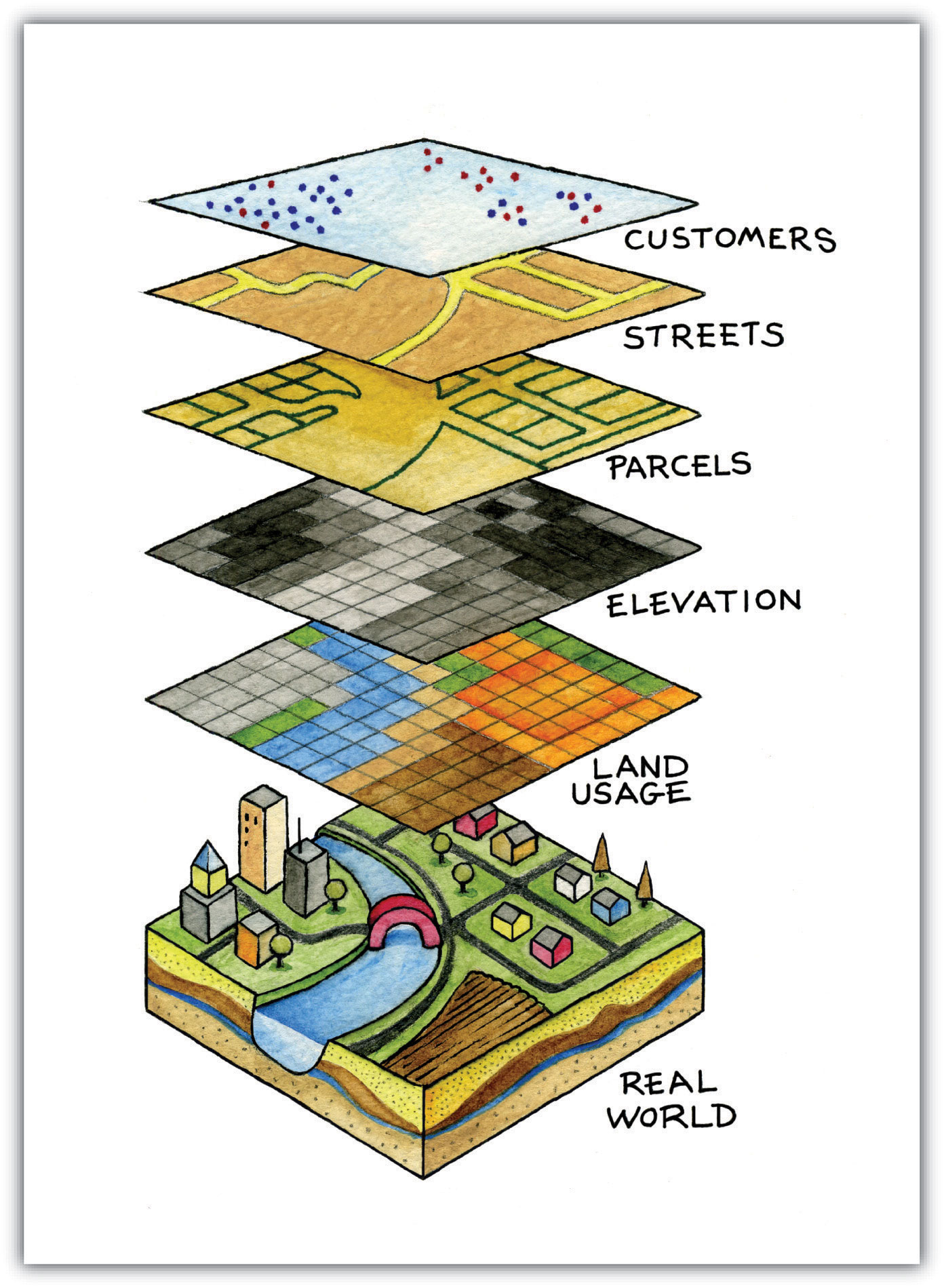
Vector maps are digital representations of geographic features, such as roads, rivers, buildings, and political boundaries. Unlike raster maps, which use pixels to represent images, vector maps utilize points, lines, and polygons to define these features. Each element is defined by mathematical coordinates, allowing for precise representation and scalability without loss of quality.
The Advantages of Vector Maps for California
Vector maps offer a plethora of advantages when it comes to representing California’s complex geography:
- High Accuracy and Precision: The mathematical basis of vector maps ensures accurate representation of spatial data. This precision is essential for tasks requiring precise measurements, such as urban planning, infrastructure development, and environmental analysis.
- Scalability and Flexibility: Vector maps can be scaled to any size without losing resolution or detail. This makes them ideal for a wide range of applications, from large-scale regional planning to detailed local mapping.
- Data Richness: Vector maps can store and display vast amounts of information about each geographic feature. This includes attributes like road names, population density, elevation, and land use, allowing for deeper analysis and understanding of the state’s landscape.
- Easy Editing and Modification: Vector maps are highly editable, allowing for changes to be made with ease. This facilitates updates to data, such as new road construction or changes in political boundaries.
- Integration with Other Systems: Vector maps can be seamlessly integrated with other geographic information systems (GIS) and software applications, enabling powerful data analysis and visualization.
Applications of Vector Maps in California
The versatility of vector maps makes them indispensable for various sectors in California:
- Urban Planning and Development: Vector maps are used to plan city growth, manage infrastructure projects, and analyze land use patterns. They help in identifying suitable locations for new developments, optimizing transportation networks, and mitigating environmental impacts.
- Environmental Management: Vector maps facilitate mapping of natural resources, monitoring environmental changes, and managing protected areas. They play a crucial role in conservation efforts, pollution control, and disaster preparedness.
- Transportation and Logistics: Vector maps are essential for navigation, route planning, and traffic management. They power GPS systems, optimize delivery routes, and provide valuable insights into transportation infrastructure.
- Tourism and Recreation: Vector maps are used to create interactive maps, guide visitors to attractions, and showcase the state’s diverse landscapes. They enhance the tourism experience and promote exploration of California’s natural wonders.
- Historical Research and Archaeology: Vector maps can be used to analyze historical maps, reconstruct past landscapes, and identify archaeological sites. They provide invaluable insights into California’s rich history and cultural heritage.
Types of Vector Maps Used for California
Several types of vector maps are commonly used for representing California’s geography:
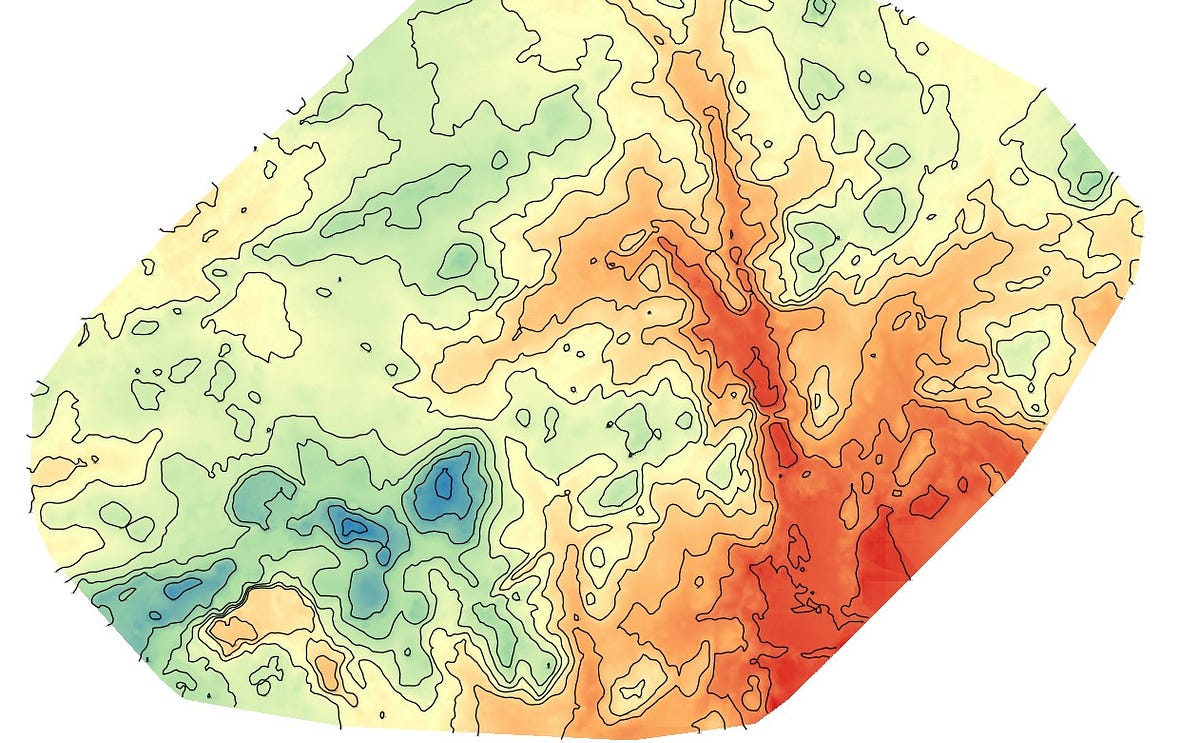
- Topographic Maps: These maps depict elevation, terrain features, and landforms, providing a detailed representation of the state’s topography.
- Road Maps: As the name suggests, these maps focus on road networks, including highways, local roads, and intersections. They are essential for navigation and transportation planning.
- Political Maps: These maps highlight administrative boundaries, such as counties, cities, and state lines. They are useful for understanding political divisions and demographics.
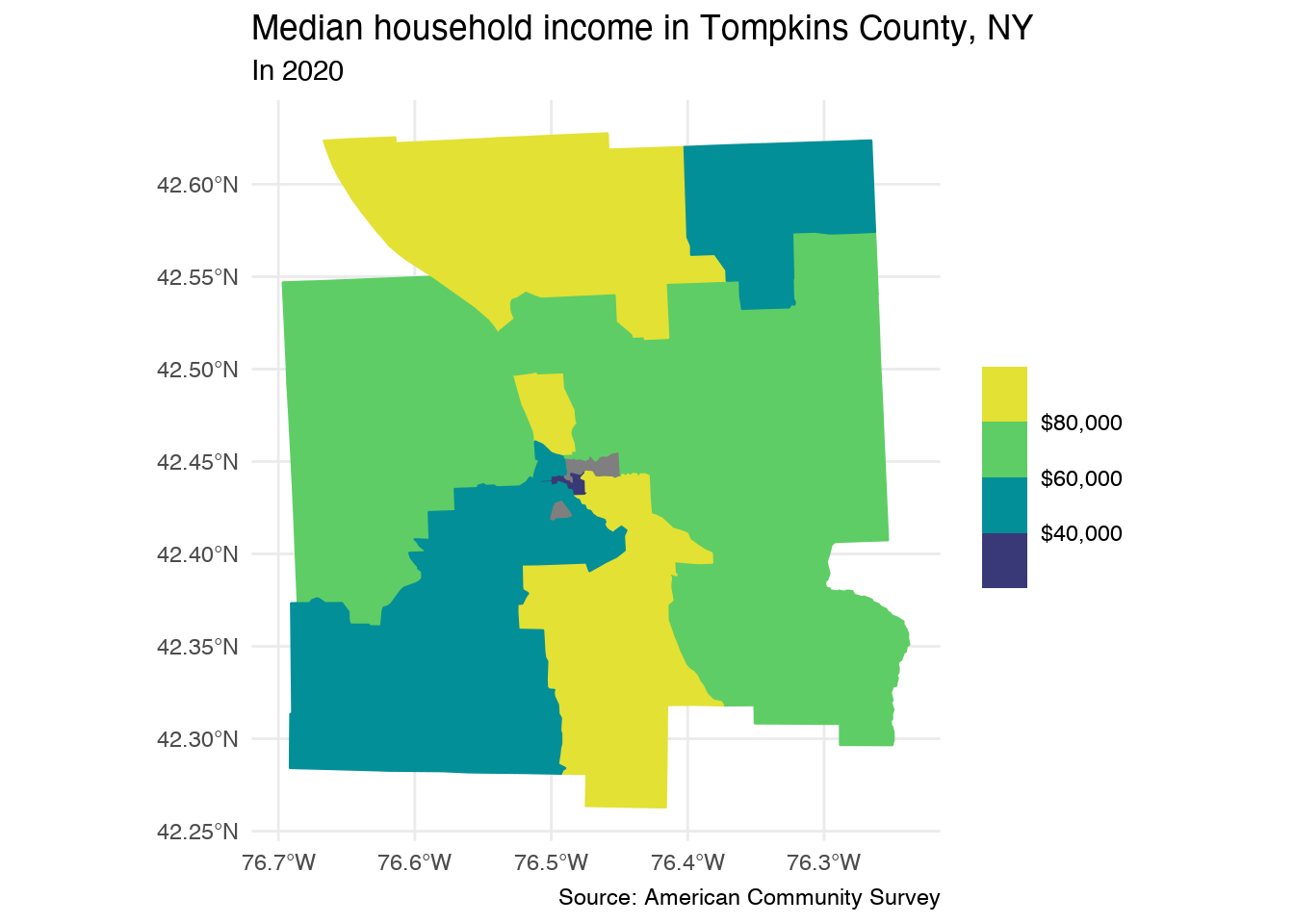
- Thematic Maps: These maps represent specific data themes, such as population density, land use, or environmental hazards. They provide insights into various aspects of California’s geography and society.
Understanding the Importance of Data Accuracy
The accuracy of vector maps is paramount. Inaccurate data can lead to flawed decision-making, inefficient resource allocation, and potentially even environmental damage. It is crucial to use reliable data sources and ensure data quality control to ensure the accuracy and integrity of vector maps.
FAQs on Vector Maps of California
Q: What are the best sources for obtaining vector maps of California?
A: Several sources provide reliable vector maps of California, including:
- Government Agencies: State and local government agencies often provide free or low-cost vector maps, such as the California Department of Transportation (Caltrans) and the U.S. Geological Survey (USGS).
- Commercial Providers: Companies like ESRI, Mapbox, and Google Maps offer commercial vector map data and services, often with advanced features and customization options.
- Open Data Platforms: Open data platforms like OpenStreetMap provide crowdsourced vector map data that is freely available for use.
Q: How are vector maps created and updated?
A: Vector maps are created through a process called georeferencing, where geographic features are identified and assigned coordinates. This is often done through aerial photography, satellite imagery, and ground surveys. Updates are made through regular data collection and analysis, incorporating changes in land use, infrastructure, and other relevant features.
Q: What are the limitations of vector maps?
A: While powerful, vector maps do have some limitations:
- Data Availability: Not all areas have comprehensive and accurate vector map data available. This can be a challenge for specific regions or applications.
- Complexity of Data Management: Managing large vector datasets can be complex, requiring specialized software and expertise.
- Dynamic Environments: Vector maps are static representations of the environment, and changes can occur rapidly, requiring frequent updates to maintain accuracy.
Tips for Using Vector Maps of California
- Choose the Right Map for Your Needs: Different types of vector maps cater to specific purposes. Carefully select the map that best suits your application and data requirements.
- Verify Data Accuracy: Always check the source and accuracy of vector map data to ensure its reliability.
- Explore Visualization Options: Utilize advanced visualization tools to create compelling maps and communicate complex spatial information effectively.
- Combine Data Sources: Integrate vector maps with other data sources, such as aerial imagery and census data, to gain a comprehensive understanding of the landscape.
- Stay Updated: Regularly update your vector map data to reflect changes in the environment and ensure accurate information.
Conclusion
Vector maps are a fundamental tool for understanding and representing California’s diverse and dynamic geography. Their accuracy, scalability, and data richness make them invaluable for a wide range of applications, from urban planning and environmental management to tourism and historical research. By leveraging the power of vector maps, we can gain a deeper understanding of California’s landscape and make informed decisions about its future.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the Power of Vector Maps: A Deep Dive into California’s Geographic Representation. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!
