Unveiling the Tapestry of Timor: A Comprehensive Guide to the Island’s Geography and History
Related Articles: Unveiling the Tapestry of Timor: A Comprehensive Guide to the Island’s Geography and History
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the Tapestry of Timor: A Comprehensive Guide to the Island’s Geography and History. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unveiling the Tapestry of Timor: A Comprehensive Guide to the Island’s Geography and History
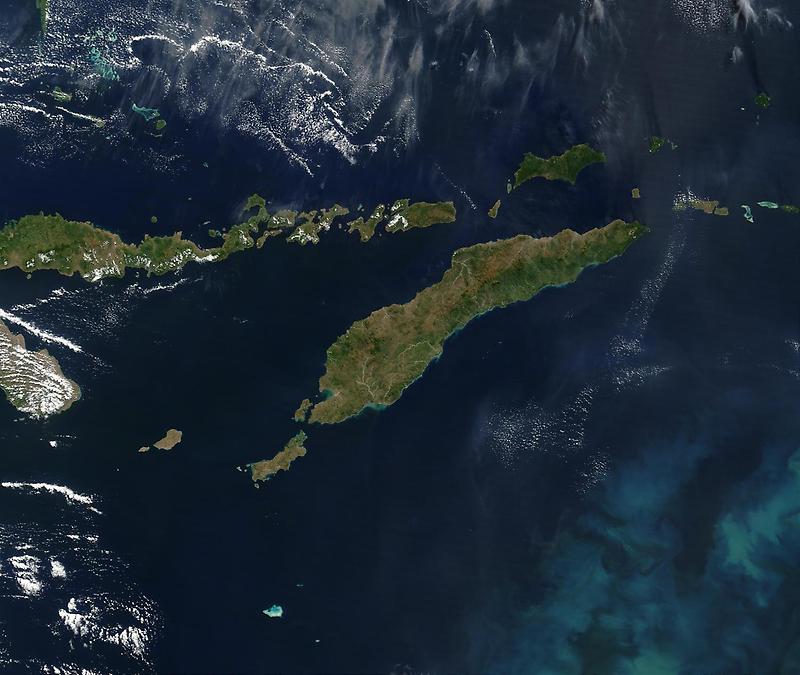
Timor, an island nation nestled in the heart of Southeast Asia, boasts a rich tapestry of history, culture, and natural beauty. Understanding its geography and history is crucial to appreciating its unique character. This comprehensive guide explores the island’s diverse landscapes, its historical evolution, and its current geopolitical significance.
A Land of Contrasts: The Geography of Timor
Timor, the largest island in the Lesser Sunda Islands, is divided into two distinct entities:
- East Timor, officially the Democratic Republic of Timor-Leste, occupies the eastern half of the island.
- West Timor, a province of Indonesia, encompasses the western portion.
Diverse Landscapes:
Timor’s landscape is a captivating blend of contrasting features:
- Mountains and Valleys: The island’s interior is dominated by rugged mountain ranges, including the highest peak, Mount Ramelau, which reaches 2,963 meters. These mountains give way to fertile valleys that support a diverse array of flora and fauna.
- Coastal Plains: The island’s coasts are characterized by narrow coastal plains that provide vital access to the sea. These plains are often dotted with traditional villages and agricultural land.
- Coral Reefs: Timor’s waters are home to vibrant coral reefs, teeming with marine life. These reefs are a vital resource for local communities, providing sustenance and income through fishing and tourism.
A History Woven with Threads of Colonialism and Independence:
Timor’s history is a complex narrative marked by periods of foreign influence and a long struggle for self-determination:
- Portuguese Colonialism: The Portuguese established a presence in Timor in the 16th century, claiming the island as a colony. Their influence shaped the island’s culture, language, and architecture.
- Indonesian Occupation: In 1975, Indonesia invaded and annexed East Timor, triggering a protracted period of conflict and human rights abuses.
- Independence: After years of international pressure and a protracted struggle, East Timor finally gained independence in 2002, becoming the newest nation in Southeast Asia.
The Geopolitical Significance of Timor:
Timor’s strategic location at the crossroads of Southeast Asia and Oceania has made it a focal point of regional geopolitical dynamics:
- Resource Potential: The island possesses significant natural resources, including oil and gas reserves, which have attracted international attention.
- Maritime Security: Timor’s waters are vital for maritime trade and security in the region, making the island a key player in regional cooperation efforts.
- Cultural and Historical Significance: Timor’s unique cultural heritage and its history of struggle for independence have made it a symbol of resilience and self-determination.
Exploring Timor: A Journey Through Time and Culture
Visiting Timor offers a unique opportunity to experience the island’s rich cultural heritage and stunning natural beauty:
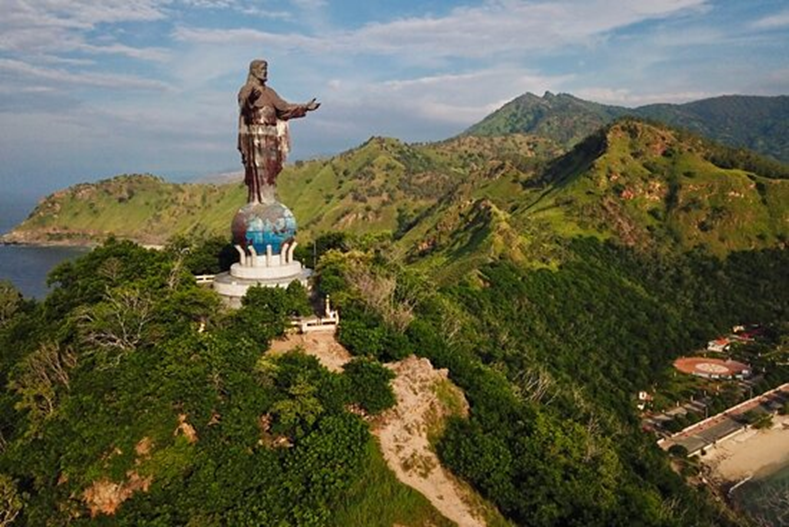
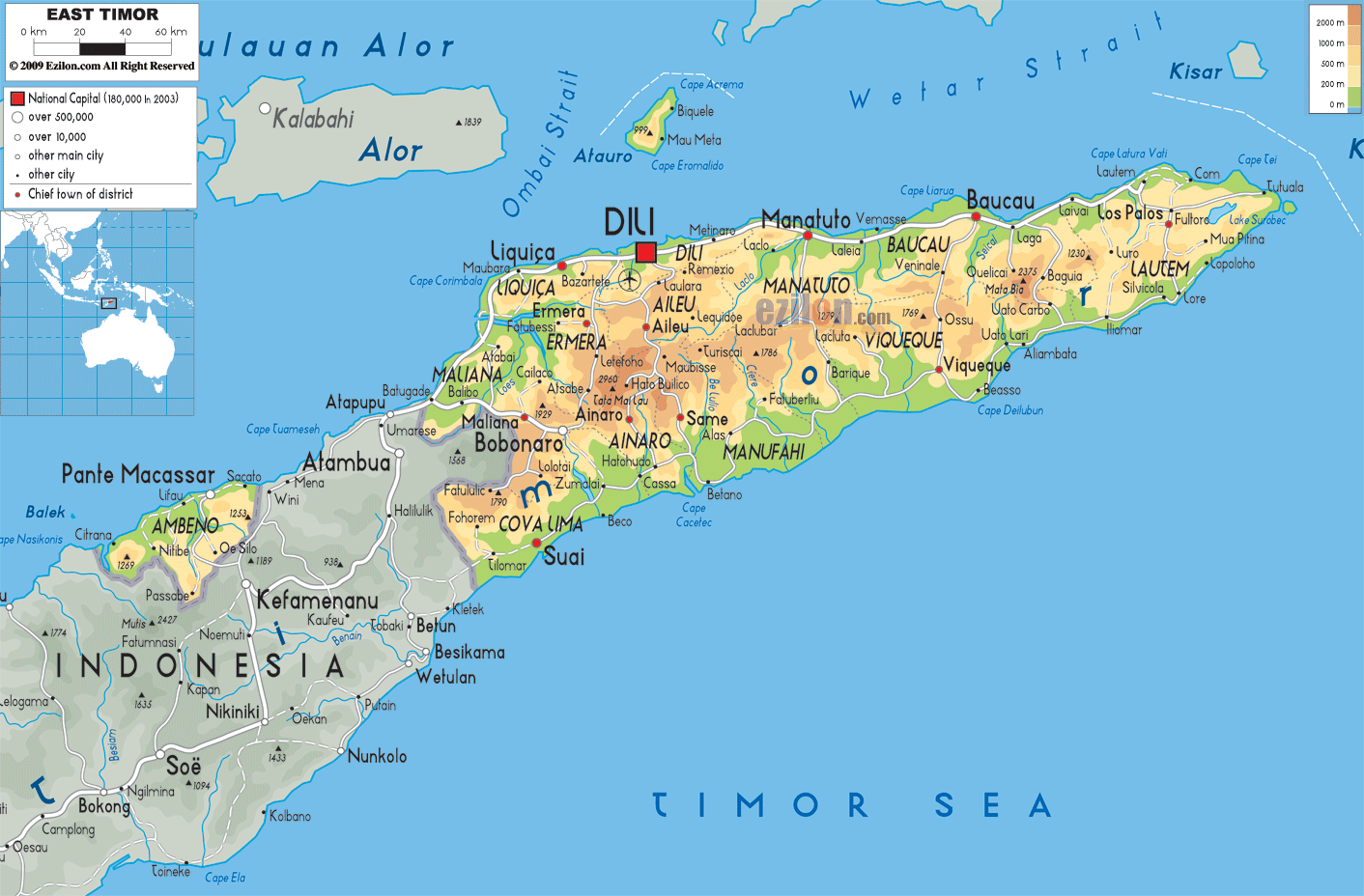
- Dili, the Capital: Dili, the capital of East Timor, offers a glimpse into the country’s history and modern development. Visitors can explore colonial-era architecture, vibrant markets, and the Timor-Leste National Museum.
- The Atauro Island: Just off the coast of Dili, Atauro Island is a pristine paradise with stunning beaches, crystal-clear waters, and abundant marine life.
- The Baucau Region: The Baucau region in the east is known for its lush landscapes, traditional villages, and the historical site of the Battle of Lospalos.
- The Maubisse Region: The Maubisse region in the south is home to the iconic Mount Ramelau, offering breathtaking views and opportunities for hiking and trekking.
FAQs about Timor:
1. What are the main languages spoken in Timor?
The official languages of East Timor are Tetum and Portuguese. In West Timor, the official language is Indonesian.
2. What are the major religions practiced in Timor?
The majority of the population in both East and West Timor are Roman Catholic. However, there are also significant communities of Protestants, Muslims, and traditional animists.
3. What is the currency used in Timor?
East Timor uses the US dollar as its official currency. West Timor uses the Indonesian Rupiah.
4. What are the best times to visit Timor?
The best time to visit Timor is during the dry season, which runs from May to October.
5. What are some of the challenges facing Timor today?
Timor faces a range of challenges, including poverty, unemployment, and limited infrastructure development. However, the country is making progress in addressing these issues through economic development and social programs.
Tips for Visiting Timor:
- Respect Local Customs: Timor is a culturally rich country with strong traditions. It is essential to show respect for local customs and traditions.
- Plan Ahead: It is advisable to plan your trip in advance, particularly if you are traveling during peak season.
- Learn a Few Basic Phrases: Learning a few basic Tetum or Indonesian phrases can be helpful for interacting with locals.
- Support Local Businesses: When possible, support local businesses and artisans to contribute to the local economy.
- Be Aware of Your Surroundings: As with any travel destination, it is important to be aware of your surroundings and take precautions to ensure your safety.
Conclusion: A Land of Hope and Resilience
Timor, a nation emerging from a tumultuous past, stands as a testament to the human spirit’s resilience. Its diverse landscapes, rich cultural heritage, and determined people offer a glimpse into a land of hope and promise. By understanding its geography, history, and present-day challenges, we can appreciate the unique character of this island nation and its vital role in the Southeast Asian region.







Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the Tapestry of Timor: A Comprehensive Guide to the Island’s Geography and History. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!
