Unveiling the World: A Comprehensive Guide to Color-Coded World Maps
Related Articles: Unveiling the World: A Comprehensive Guide to Color-Coded World Maps
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the World: A Comprehensive Guide to Color-Coded World Maps. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unveiling the World: A Comprehensive Guide to Color-Coded World Maps
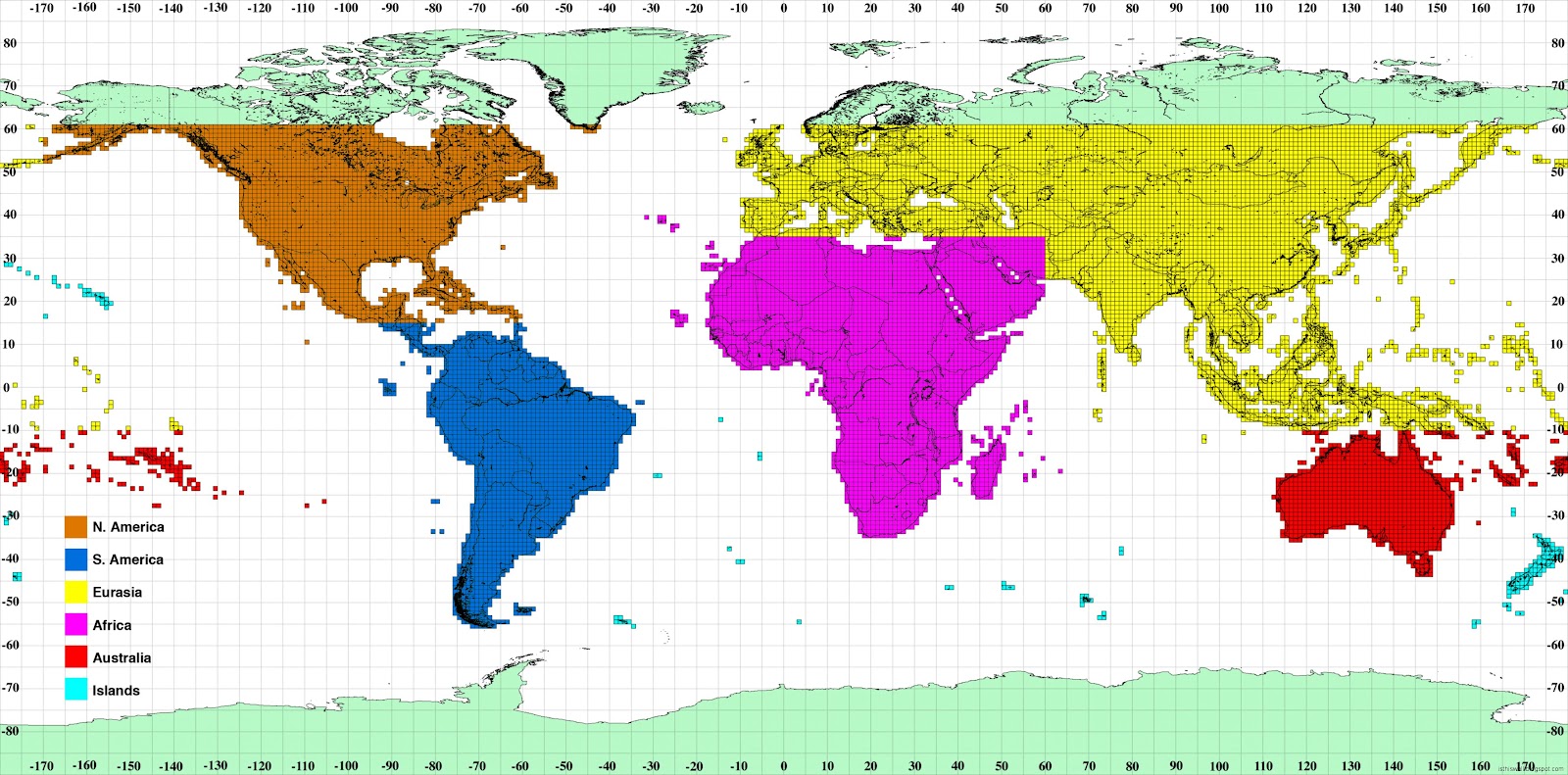
World maps, ubiquitous in classrooms, offices, and homes, are more than just static representations of geographical boundaries. They are powerful tools for visualizing and understanding global data, often employing color to highlight specific information. This color-coding allows for a rapid and intuitive comprehension of complex global patterns, be it population density, economic indicators, or even the distribution of endangered species.
Understanding the Power of Color
Color, in the context of maps, serves as a visual language, enabling the quick identification and comparison of diverse data points. The human brain is wired to perceive color variations instinctively, making color-coded maps highly effective in communicating information.
Decoding the Colors: A Spectrum of Information
The color scheme employed on a map is crucial for conveying meaning. Here are some common color coding strategies:
-
Categorical Data: Categorical maps use distinct colors to represent different categories or groups. For example, a map showcasing global religions might assign blue to Christianity, green to Islam, and yellow to Hinduism.
-
Continuous Data: Continuous data maps utilize a color gradient to depict a range of values. A map illustrating global population density might use shades of blue, ranging from light blue for sparsely populated areas to dark blue for densely populated regions.
-
Choropleth Maps: These maps use color intensity to represent the magnitude of a particular variable within each geographical unit. For instance, a choropleth map displaying GDP per capita might use darker shades of green for countries with higher GDP and lighter shades for countries with lower GDP.
The Importance of Color-Coded Maps
Color-coded world maps play a vital role in various fields:
-
Education: Maps are instrumental in teaching geography, history, and social studies. Color-coding helps students visualize complex concepts and understand global relationships.
-
Research: Researchers across disciplines rely on color-coded maps for data analysis and visualization. They are essential for identifying trends, patterns, and anomalies in global data.
-
Policymaking: Governments and international organizations use color-coded maps to inform policy decisions. For example, maps depicting climate change impacts can guide environmental policies.
-
Media and Communication: News outlets and publications often employ color-coded maps to present global events and data in a visually appealing and informative way.
Beyond the Basics: Exploring Different Map Types
While color-coding is a common feature of most world maps, there are various map types that utilize color in unique ways:
-
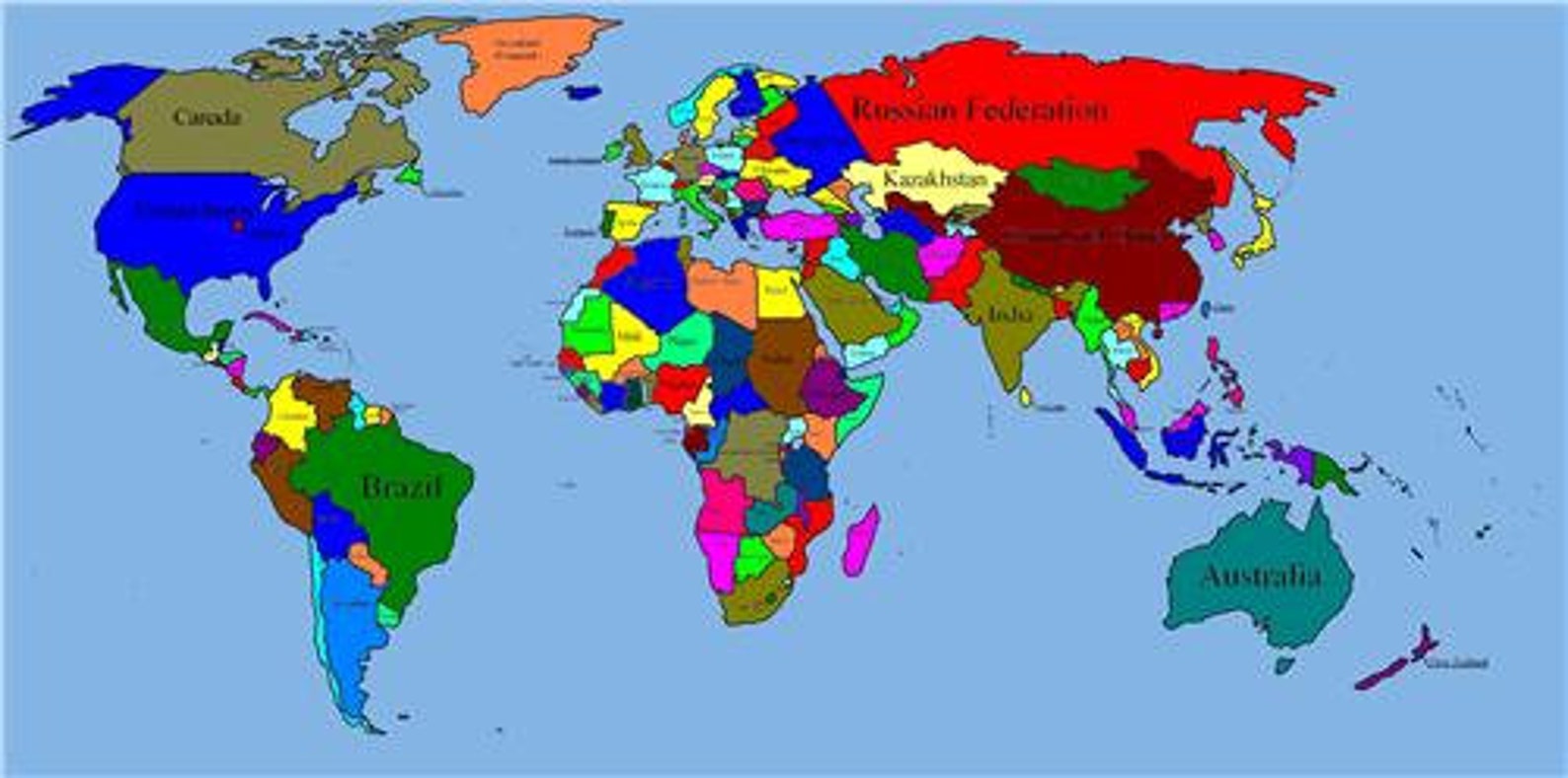
Political Maps: These maps primarily focus on national boundaries, often using different colors to distinguish between countries.
-
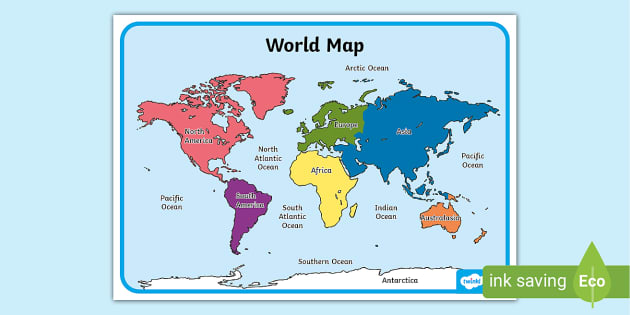
Physical Maps: Physical maps highlight geographical features such as mountains, rivers, and oceans. Color is used to represent elevation, landforms, and water bodies.
-
Thematic Maps: Thematic maps focus on specific themes or data sets. These maps utilize color to represent various aspects such as population density, economic indicators, or environmental factors.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) about Color-Coded World Maps
Q: What are the most common color schemes used on world maps?
A: There is no single standard color scheme. However, some common color choices include:
- Blue: Often used to represent water bodies, oceans, and low elevations.
- Green: Frequently used to represent vegetation, forests, and land areas.
- Brown: Often used to represent mountains, deserts, and high elevations.
- Red: Often used to represent areas of conflict, political boundaries, or high population density.
Q: How can I interpret the colors on a world map?
A: Always pay attention to the map’s legend or key. This provides information on the specific data represented by each color.
Q: Are there any guidelines for choosing colors on maps?
A: Yes, certain guidelines help ensure effective communication:
- Color Contrast: Choose colors that have good contrast for clarity and readability.
- Colorblindness: Consider colorblindness when selecting colors. Avoid using red and green together, as they can be difficult to distinguish for some people.
- Cultural Context: Be mindful of cultural connotations associated with certain colors.
Tips for Understanding and Using Color-Coded World Maps
- Focus on the Legend: Always carefully examine the map’s legend to understand the meaning of each color.
- Consider the Scale: Pay attention to the map’s scale, as it can influence the interpretation of color variations.
- Look for Patterns: Observe how colors cluster together or change across the map. These patterns can reveal important insights.
- Compare Maps: Compare different color-coded maps to gain a more comprehensive understanding of the data.
Conclusion: The Power of Visual Communication
Color-coded world maps offer a powerful tool for understanding our world. They enable us to visualize complex data, identify global patterns, and gain insights into a wide range of phenomena. By understanding the principles of color-coding and map types, we can effectively interpret and utilize these visual representations to make informed decisions and enhance our understanding of the world around us.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the World: A Comprehensive Guide to Color-Coded World Maps. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!
